Class 3 slides Sprin..
... capital used to produce output Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution Slope of the Production function Shows relative productivities of 2 inputs: Technological relationship MRTS = MPL/MPK ...
... capital used to produce output Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution Slope of the Production function Shows relative productivities of 2 inputs: Technological relationship MRTS = MPL/MPK ...
Labor
... from 1 to 5 results in a decreasing MRTS from 1 to 1/2. Diminishing MRTS occurs because of diminishing returns and implies isoquants are convex. ...
... from 1 to 5 results in a decreasing MRTS from 1 to 1/2. Diminishing MRTS occurs because of diminishing returns and implies isoquants are convex. ...
Study Guide
... VII. Public Goods, externalities and the role of government Public goods and externalities Private v. public goods Private goods – rival and excludable (ex. Snickers bar, Hummer) Public goods – non-rival and nonexcludable (ex. National defense, environmental protection) Private goods are priced acco ...
... VII. Public Goods, externalities and the role of government Public goods and externalities Private v. public goods Private goods – rival and excludable (ex. Snickers bar, Hummer) Public goods – non-rival and nonexcludable (ex. National defense, environmental protection) Private goods are priced acco ...
Name ______ last 4 PSU ID
... from $10 to $9. What could cause such a change (name at least 2 reasons)? The price dropping from $10 to $9 could be caused by a variety of things, including things on both the supply and demand side. For example, on the supply side, if more people are producing this product, it will cause the price ...
... from $10 to $9. What could cause such a change (name at least 2 reasons)? The price dropping from $10 to $9 could be caused by a variety of things, including things on both the supply and demand side. For example, on the supply side, if more people are producing this product, it will cause the price ...
t7. scarcity, opportunity cost, marginal analysis, and
... In 1932 Lionel Robbins (who taught me when I was at the LSE) formulated the most famous definition of economics: “Economics is the science which studies human behaviour as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses”. This was one of the definitions of economics that we ...
... In 1932 Lionel Robbins (who taught me when I was at the LSE) formulated the most famous definition of economics: “Economics is the science which studies human behaviour as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses”. This was one of the definitions of economics that we ...
18.2 labor markets - Pearson Higher Education
... Can Unions Restrict the Supply of Labor The union’s ability to restrict the supply of labor is limited by how well it can prevent nonunion workers from offering their labor in the same market as union workers. It is difficult for unions to operate in markets where there is an abundant supply of will ...
... Can Unions Restrict the Supply of Labor The union’s ability to restrict the supply of labor is limited by how well it can prevent nonunion workers from offering their labor in the same market as union workers. It is difficult for unions to operate in markets where there is an abundant supply of will ...
18.2 labor markets
... Can Unions Restrict the Supply of Labor The union’s ability to restrict the supply of labor is limited by how well it can prevent nonunion workers from offering their labor in the same market as union workers. It is difficult for unions to operate in markets where there is an abundant supply of will ...
... Can Unions Restrict the Supply of Labor The union’s ability to restrict the supply of labor is limited by how well it can prevent nonunion workers from offering their labor in the same market as union workers. It is difficult for unions to operate in markets where there is an abundant supply of will ...
Markets for Factors of Production C H A P T E R C H E C K L I S T
... Can Unions Restrict the Supply of Labor The union’s ability to restrict the supply of labor is limited by how well it can prevent nonunion workers from offering their labor in the same market as union workers. It is difficult for unions to operate in markets where there is an abundant supply of will ...
... Can Unions Restrict the Supply of Labor The union’s ability to restrict the supply of labor is limited by how well it can prevent nonunion workers from offering their labor in the same market as union workers. It is difficult for unions to operate in markets where there is an abundant supply of will ...
ECON 3070-002 Intermediate Microeconomic Theory
... Microeconomics, Eighth Edition, by Edwin Mansfield, published by W.W. Norton & Company, 1994. ...
... Microeconomics, Eighth Edition, by Edwin Mansfield, published by W.W. Norton & Company, 1994. ...
Second Midterm
... the market, they would face the exact same costs as this firm. However, due to barriers to entry, no other firms can enter this market. 14. By how much will the price change if the barriers to entry in this market are eliminated and this market becomes perfectly competitive? a. b. c. d. ...
... the market, they would face the exact same costs as this firm. However, due to barriers to entry, no other firms can enter this market. 14. By how much will the price change if the barriers to entry in this market are eliminated and this market becomes perfectly competitive? a. b. c. d. ...
Econ 3070 Prof. Barham 1 Problem Set 5 Answers 1. Ch 7, Problem
... Mr. Moore always has the option of closing down his shop and renting out the land for $100,000. Also, Mr. Moore himself has job offers at a local supermarket at a salary of $95,000 and at a nearby restaurant at $65,000. He can only work one job, though. What are the shop’s accounting costs? What are ...
... Mr. Moore always has the option of closing down his shop and renting out the land for $100,000. Also, Mr. Moore himself has job offers at a local supermarket at a salary of $95,000 and at a nearby restaurant at $65,000. He can only work one job, though. What are the shop’s accounting costs? What are ...
Ch 2 Economizing Problem
... “Real Capital” [machinery, physical plants & tools] [capital is a factor of production] v. “Financial Capital” [stocks, bonds, & $] [not factors of production] A product can be both a consumer good & a capital good –depends on its use. Ex: Jet aircraft used by a movie star to visit friends (consumer ...
... “Real Capital” [machinery, physical plants & tools] [capital is a factor of production] v. “Financial Capital” [stocks, bonds, & $] [not factors of production] A product can be both a consumer good & a capital good –depends on its use. Ex: Jet aircraft used by a movie star to visit friends (consumer ...
Topic 1: Basic Economics
... beer, or he can bake 6 pizzas If Sally specializes, every week she can brew 6 gallons of beer, or she can bake 12 pizzas Pizza and beer go together, so people must consume 1 gallon of beer for every 1 pizza they eat. Assume constant opportunity costs Draw Aidan’s PPF Draw Sally’s PPF ...
... beer, or he can bake 6 pizzas If Sally specializes, every week she can brew 6 gallons of beer, or she can bake 12 pizzas Pizza and beer go together, so people must consume 1 gallon of beer for every 1 pizza they eat. Assume constant opportunity costs Draw Aidan’s PPF Draw Sally’s PPF ...
Chapter 4: Demand for Labor in Short Run
... Effects of Subsidy Program • Good effects: – 1) employment of target group; – 2) gives largest subsidy to hardest to employ (since their wages are lowest); – 3) as hard-to-employ take jobs and gain experience, their wages rise so subsidy cost falls. ...
... Effects of Subsidy Program • Good effects: – 1) employment of target group; – 2) gives largest subsidy to hardest to employ (since their wages are lowest); – 3) as hard-to-employ take jobs and gain experience, their wages rise so subsidy cost falls. ...
Chapter 29 - The Citadel
... – But as the volume of global commerce rises, there may be more of a demand by foreign firms to hire U.S. workers as well. ...
... – But as the volume of global commerce rises, there may be more of a demand by foreign firms to hire U.S. workers as well. ...
Exam #1 - Jacob Hochard
... (1) When a society cannot produce all the goods and services people wish to have, it is said that the economy is experiencing a. scarcity. b. surpluses. c. inefficiencies. d. inequalities. (2) In most societies, resources are allocated by a. a single central planner. b. a small number of central pl ...
... (1) When a society cannot produce all the goods and services people wish to have, it is said that the economy is experiencing a. scarcity. b. surpluses. c. inefficiencies. d. inequalities. (2) In most societies, resources are allocated by a. a single central planner. b. a small number of central pl ...
The Market as a Principle of Exchange
... • Regions within poor nations – do not trade, compete or cooperate with each other – – only with the capitol city – where goods leave for other countries ...
... • Regions within poor nations – do not trade, compete or cooperate with each other – – only with the capitol city – where goods leave for other countries ...
Week - apgreenecon
... Please arrange to have access to a daily newspaper. The Wall Street Journal is the preferred option, but the New York Times and Boston Globe will be fine. We will be constantly connecting what we are learning in class to what is actually happening in our economy. If you have a subscription to Busine ...
... Please arrange to have access to a daily newspaper. The Wall Street Journal is the preferred option, but the New York Times and Boston Globe will be fine. We will be constantly connecting what we are learning in class to what is actually happening in our economy. If you have a subscription to Busine ...
ch11, lecture
... Derived demand means that a firm demands labor because labor is productive. Changes in consumer demand for a product cause changes in demand for labor and for other resources used to make the product. ...
... Derived demand means that a firm demands labor because labor is productive. Changes in consumer demand for a product cause changes in demand for labor and for other resources used to make the product. ...
Assigment 1 Microeconomics
... one person can perform every task with the lowest opportunity cost, nor can any one country. Because the world and the USA in particular participate in a global economy, everyone person is effected by comparative advantage and specialization. All one need to do is look at issues such as trade defici ...
... one person can perform every task with the lowest opportunity cost, nor can any one country. Because the world and the USA in particular participate in a global economy, everyone person is effected by comparative advantage and specialization. All one need to do is look at issues such as trade defici ...
hw2sol
... firm has an incentive to reduce its production in order to again equate MR and MC. When production decreases, the firm has a need for smaller quantities of all inputs. Therefore, it will reduce its demand for both capital and labor. In order to isolate the scale and substitution effects, the cost an ...
... firm has an incentive to reduce its production in order to again equate MR and MC. When production decreases, the firm has a need for smaller quantities of all inputs. Therefore, it will reduce its demand for both capital and labor. In order to isolate the scale and substitution effects, the cost an ...
Week 11 - Lancaster University
... A famous research paper by David Card and Alan Krueger from Princeton University (in New Jersey) looked at the impact of a rise in the minimum wage in New Jersey that occurred in 1992 (from $4.25 per hour to $5.05 per hour) on employment - by comparing what happened to employment in fast food restau ...
... A famous research paper by David Card and Alan Krueger from Princeton University (in New Jersey) looked at the impact of a rise in the minimum wage in New Jersey that occurred in 1992 (from $4.25 per hour to $5.05 per hour) on employment - by comparing what happened to employment in fast food restau ...
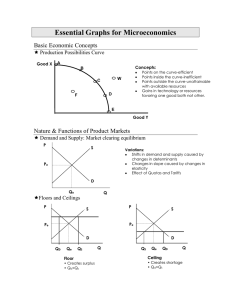
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics
... production or consumption costs conferred on a third party or community at large without their compensating the producer education, vaccinations are examples Market Demand, reflecting only private benefits moves to left producing a smaller output that society would like— under allocation of resource ...
... production or consumption costs conferred on a third party or community at large without their compensating the producer education, vaccinations are examples Market Demand, reflecting only private benefits moves to left producing a smaller output that society would like— under allocation of resource ...
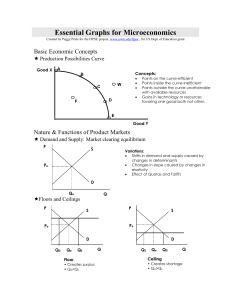
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics
... production or consumption costs conferred on a third party or community at large without their compensating the producer education, vaccinations are examples Market Demand, reflecting only private benefits moves to left producing a smaller output that society would like— under allocation of resource ...
... production or consumption costs conferred on a third party or community at large without their compensating the producer education, vaccinations are examples Market Demand, reflecting only private benefits moves to left producing a smaller output that society would like— under allocation of resource ...