The Costs of Production
... • I am willing to hire as many workers as I need at a wage that is set by the market. • I am willing to pay between $5 and $25. • Write down how much you are willing to work for on your paper. • I will hire the workers that are willing to work for the lowest wage. ...
... • I am willing to hire as many workers as I need at a wage that is set by the market. • I am willing to pay between $5 and $25. • Write down how much you are willing to work for on your paper. • I will hire the workers that are willing to work for the lowest wage. ...
Theory of Production
... (capital) constant, leads to a decreasing amount of additional output. ∂ MPl / ∂L <0 In other words, total output Q increases at a decreasing rate with the addition of more labor. Eventually Q could actually decrease with more labor, but the rational firm would not produce at that level. The margina ...
... (capital) constant, leads to a decreasing amount of additional output. ∂ MPl / ∂L <0 In other words, total output Q increases at a decreasing rate with the addition of more labor. Eventually Q could actually decrease with more labor, but the rational firm would not produce at that level. The margina ...
Document
... The Other Factors of Production With land and capital, must distinguish between: purchase price – the price a person pays to own that factor indefinitely rental price – the price a person pays to use that factor for a limited period of time ...
... The Other Factors of Production With land and capital, must distinguish between: purchase price – the price a person pays to own that factor indefinitely rental price – the price a person pays to use that factor for a limited period of time ...
Slide 1
... The Other Factors of Production With land and capital, must distinguish between: purchase price – the price a person pays to own that factor indefinitely rental price – the price a person pays to use that factor for a limited period of time ...
... The Other Factors of Production With land and capital, must distinguish between: purchase price – the price a person pays to own that factor indefinitely rental price – the price a person pays to use that factor for a limited period of time ...
Eco201, Fall 2005, Prof. Bill Even Quiz 1 Name Assigned
... d. None of the above will create an incentive to increase the amount of an activity. 7) Which of the following is a positive statement? a. Because they decrease productivity, labor unions should be eliminated. b. The United States should fight inflation even if it raises unemployment. c. A 5 percent ...
... d. None of the above will create an incentive to increase the amount of an activity. 7) Which of the following is a positive statement? a. Because they decrease productivity, labor unions should be eliminated. b. The United States should fight inflation even if it raises unemployment. c. A 5 percent ...
Class 1 - Workbook - The Bored of Studies Community
... Wages, social welfare, interest and commission (B) Wages, rent, interest and profit (C) Land, labour, capital and enterprise (D) Wages, rent, interest and commission ...
... Wages, social welfare, interest and commission (B) Wages, rent, interest and profit (C) Land, labour, capital and enterprise (D) Wages, rent, interest and commission ...
Bourbon County High School
... Disequilibrium Shortage Surplus Price ceiling Price floor Rent control Minimum wage ...
... Disequilibrium Shortage Surplus Price ceiling Price floor Rent control Minimum wage ...
Absolute Advantage vs. Comparative Advantage
... Clothes and Accessories. He specializes in creating women's clothing and accessories. He has found that he is able to produce his shirts at a lower production cost than his competitors can. However, he has also found that he has a greater opportunity cost when producing handbags. His opportunity cos ...
... Clothes and Accessories. He specializes in creating women's clothing and accessories. He has found that he is able to produce his shirts at a lower production cost than his competitors can. However, he has also found that he has a greater opportunity cost when producing handbags. His opportunity cos ...
Dominant Firm Model and Factor Market Outline 1 Dominant Firm
... w = M RPL (L), so the marginal revenue and marginal cost at hiring one more unit of labor are the same. • If output market is competitive, MR = P; if it is not competitive, MR < P (see Figure 2 and 3). • Given w, we derive the firm’s demand for labor from w = M RPL (L). M RPL decreases in L; therefor ...
... w = M RPL (L), so the marginal revenue and marginal cost at hiring one more unit of labor are the same. • If output market is competitive, MR = P; if it is not competitive, MR < P (see Figure 2 and 3). • Given w, we derive the firm’s demand for labor from w = M RPL (L). M RPL decreases in L; therefor ...
Chapter 3 The Demand for Labor
... • Long run effect of an increase in price of capital on labor. – substitution effect: for every given level of output, use more labor and less capital. – scale effect: an increase in price of capital reduces product supply, reduces equilibrium quantity produced, and reduces amount of labor employed. ...
... • Long run effect of an increase in price of capital on labor. – substitution effect: for every given level of output, use more labor and less capital. – scale effect: an increase in price of capital reduces product supply, reduces equilibrium quantity produced, and reduces amount of labor employed. ...
Document
... – It makes sense for a firm to hire to the point where MVP = w, w = MPL*P and therefore w/MPL = P ...
... – It makes sense for a firm to hire to the point where MVP = w, w = MPL*P and therefore w/MPL = P ...
Principles of Economics, Case and Fair,9e
... Price changes affect households in two ways. First, if we assume that households confine their choices to products that improve their well-being, then a decline in the price of any product, ceteris paribus, will make the household unequivocally better off. ...
... Price changes affect households in two ways. First, if we assume that households confine their choices to products that improve their well-being, then a decline in the price of any product, ceteris paribus, will make the household unequivocally better off. ...
The Labor Market
... • 30-01. Know what factors shape labor supply and demand. • 30-02. Know how market wage rates are established. • 30-03. Know how wage floors alter labor market outcomes. ...
... • 30-01. Know what factors shape labor supply and demand. • 30-02. Know how market wage rates are established. • 30-03. Know how wage floors alter labor market outcomes. ...
Marginal Product of Labor - Effingham County Schools
... • An upward-sloping labor supply curve means that an increase in the wage induces workers to increase the Q of labor they supply. • For now, assume that the labor supply curve is ...
... • An upward-sloping labor supply curve means that an increase in the wage induces workers to increase the Q of labor they supply. • For now, assume that the labor supply curve is ...
File
... 1. Economists say that the demand for labor is a derived demand, they mean that it is: _________________________________________________________ 2. If the demand for airline pilots increases, what can be said about the product market demand? ______________________________________________________ 3. ...
... 1. Economists say that the demand for labor is a derived demand, they mean that it is: _________________________________________________________ 2. If the demand for airline pilots increases, what can be said about the product market demand? ______________________________________________________ 3. ...
Principles of Economics, Case and Fair,8e
... Production Is Not Limited to Firms firm An organization that comes into being when a person or a group of people decides to produce a good or service to meet a perceived demand. Most firms exist to make a profit. ...
... Production Is Not Limited to Firms firm An organization that comes into being when a person or a group of people decides to produce a good or service to meet a perceived demand. Most firms exist to make a profit. ...
Word
... marginal product has increased by 10% due to the improved technology, so labor’s wage in units of X has gone up by that amount. However, the price of X has fallen, and we don’t know by how much. If the price falls by less than 10%, then this is necessarily an improvement in its real wage. But if it ...
... marginal product has increased by 10% due to the improved technology, so labor’s wage in units of X has gone up by that amount. However, the price of X has fallen, and we don’t know by how much. If the price falls by less than 10%, then this is necessarily an improvement in its real wage. But if it ...
My notes
... Unemployment insurance is very generous. Benefits and severance pay provisions are much higher than US. ...
... Unemployment insurance is very generous. Benefits and severance pay provisions are much higher than US. ...
File
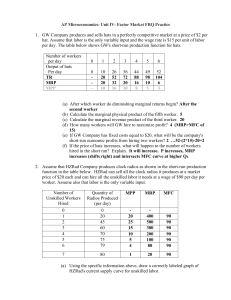
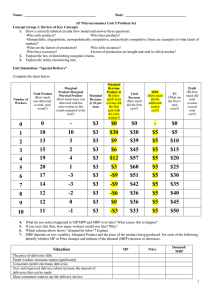
... The table above gives the short-run marginal revenue product of labor per day for a perfectly competitive firm. The firm is currently selling its product at the market price of $5. (a) Calculate the marginal (physical) product of the third worker. 90; 450 = 90 * 5 (RP = MPP * P) (b) Define the law o ...
... The table above gives the short-run marginal revenue product of labor per day for a perfectly competitive firm. The firm is currently selling its product at the market price of $5. (a) Calculate the marginal (physical) product of the third worker. 90; 450 = 90 * 5 (RP = MPP * P) (b) Define the law o ...
Profit-Maximization by a Monopsonist
... A monopsony is defined as the only buyer in a given input market. A monopsony, the sole buyer in an input market, is the mirror image of a monopoly, the sole seller in an output market. A monopsony exercise some control over the price paid for an input and faces an upward sloping supply curve. Like ...
... A monopsony is defined as the only buyer in a given input market. A monopsony, the sole buyer in an input market, is the mirror image of a monopoly, the sole seller in an output market. A monopsony exercise some control over the price paid for an input and faces an upward sloping supply curve. Like ...
unit5problemset
... 39. Why does MRP shift to the right if demand for a product increases? 40. List and explain the three shifters of resource demand? 41. How is the demand for a resource (e.g. labor) affected when demand for that good increases? 42. How is the demand for a resource (e.g. labor) affected when workers b ...
... 39. Why does MRP shift to the right if demand for a product increases? 40. List and explain the three shifters of resource demand? 41. How is the demand for a resource (e.g. labor) affected when demand for that good increases? 42. How is the demand for a resource (e.g. labor) affected when workers b ...
Chapter 5: Household Behavior and Consumer Choice
... • A key assumption in the study of household and firm behavior is that all input and output markets are perfectly competitive. ...
... • A key assumption in the study of household and firm behavior is that all input and output markets are perfectly competitive. ...
Derived Demand and MRP
... Perfectly Competitive Labor Market Characteristics: •Many small firms are hiring workers ...
... Perfectly Competitive Labor Market Characteristics: •Many small firms are hiring workers ...
AP Economics December 8, 2014
... • Marginal Resource Cost (MRC): change in Total Cost that results from employment of an ...
... • Marginal Resource Cost (MRC): change in Total Cost that results from employment of an ...