The Spheres of Our Earth
... • 3. UNIQUE in that water is the only substance on Earth that can exist naturally in all 3 states: solid (ice), liquid (water) and gas (water vapor)/ ...
... • 3. UNIQUE in that water is the only substance on Earth that can exist naturally in all 3 states: solid (ice), liquid (water) and gas (water vapor)/ ...
Oceans in motion vocab - Raleigh Charter High School
... is the continental slope, which is still considered part of the continent, together with the continental shelf. continental rise as currents flow along the continental shelf and down the continental slope, they pick up and carry sediments along and deposit them just below the continental slope. Thes ...
... is the continental slope, which is still considered part of the continent, together with the continental shelf. continental rise as currents flow along the continental shelf and down the continental slope, they pick up and carry sediments along and deposit them just below the continental slope. Thes ...
Oceans 11 Bathymetry and the Use of Technology Name Date Our
... Bathymetry and the Use of Technology Our knowledge of the diverse topography of the ocean floor is relatively recent. Up to the 1920’s depths to the ocean floor were determined by lowering a weighted rope until it touched bottom and then measuring the length of the rope. Ocean floor composition was ...
... Bathymetry and the Use of Technology Our knowledge of the diverse topography of the ocean floor is relatively recent. Up to the 1920’s depths to the ocean floor were determined by lowering a weighted rope until it touched bottom and then measuring the length of the rope. Ocean floor composition was ...
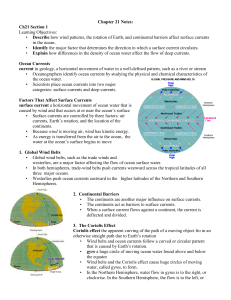
Chapter 21 Notes:
... • Explain how differences in the density of ocean water affect the flow of deep currents. Ocean Currents current in geology, a horizontal movement of water in a well-defined pattern, such as a river or stream • Oceanographers identify ocean currents by studying the physical and chemical characterist ...
... • Explain how differences in the density of ocean water affect the flow of deep currents. Ocean Currents current in geology, a horizontal movement of water in a well-defined pattern, such as a river or stream • Oceanographers identify ocean currents by studying the physical and chemical characterist ...
Ocean Ch 15 Animals-Ben
... Approx. 95% of marine organisms live on the sea floor, which varies from rocky to sandy to muddy. 15 -1. Distribution of Benthic Organisms Most biomass depends on the productivity of the surface waters. Sunlight penetrates to the bottom where the water is shallow. 15 -2. Communities along Rocky Shor ...
... Approx. 95% of marine organisms live on the sea floor, which varies from rocky to sandy to muddy. 15 -1. Distribution of Benthic Organisms Most biomass depends on the productivity of the surface waters. Sunlight penetrates to the bottom where the water is shallow. 15 -2. Communities along Rocky Shor ...
Investigation B, Ocean Bottom Topography
... Driving Question: How does ocean depth vary with distance from the shore? ...
... Driving Question: How does ocean depth vary with distance from the shore? ...
HERE
... Vertical structure of the atmosphere • In meteorology we discuss air pressure in units of hectopascals (hPa) (previously called millibars mb) • The average atmospheric pressure at the Earth surface is 1013.25 hPa • We can sense sudden changes in pressure when our ears ‘pop’ such as that experienced ...
... Vertical structure of the atmosphere • In meteorology we discuss air pressure in units of hectopascals (hPa) (previously called millibars mb) • The average atmospheric pressure at the Earth surface is 1013.25 hPa • We can sense sudden changes in pressure when our ears ‘pop’ such as that experienced ...
Part 1: The Factors of Life!
... surface of the water, much is reflected back. The more movement made by the water, the more light is reflected off of the surface and back into the atmosphere. Most visible light waves are absorbed within 33 ft. (10 meters). Blue and violet waves of light travel deepest, giving most water its color. ...
... surface of the water, much is reflected back. The more movement made by the water, the more light is reflected off of the surface and back into the atmosphere. Most visible light waves are absorbed within 33 ft. (10 meters). Blue and violet waves of light travel deepest, giving most water its color. ...
White Cliffs
... Calcium carbonate is also the building block of limestone. Millions of years ago, the White Cliffs of Dover were located at the bottom of the ocean, and has since reached the surface thanks to the uplifting forces of plate tectonics. When alive, these coccoliths floated near the surface of the ocean ...
... Calcium carbonate is also the building block of limestone. Millions of years ago, the White Cliffs of Dover were located at the bottom of the ocean, and has since reached the surface thanks to the uplifting forces of plate tectonics. When alive, these coccoliths floated near the surface of the ocean ...
Ch. 11 Coastal Ocean - Seattle Central College
... Distinguish deep-water waves from (transitional) intermediate and shallow-water waves. Include these formulas: D>Length/2 and D
... Distinguish deep-water waves from (transitional) intermediate and shallow-water waves. Include these formulas: D>Length/2 and D
Erosion
... The reasons the continents are labeled the way they are is because of continental drift. Each of the continents is on a different continental plate, therefore as the tectonic plates move, the continents move with them. ...
... The reasons the continents are labeled the way they are is because of continental drift. Each of the continents is on a different continental plate, therefore as the tectonic plates move, the continents move with them. ...
Write about this….
... • An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun. Depth contours, shoreline c ...
... • An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun. Depth contours, shoreline c ...
Plate Tectonics
... Developed by Alfred Wegner (1900’s) Believed continents were once all combined into one landmass he called Pangaea meaning “All Earth” Continents seemed to fit together like a jigsaw puzzle Explained why fossils of the same plants and animals are found on the coast of Africa and South Americ ...
... Developed by Alfred Wegner (1900’s) Believed continents were once all combined into one landmass he called Pangaea meaning “All Earth” Continents seemed to fit together like a jigsaw puzzle Explained why fossils of the same plants and animals are found on the coast of Africa and South Americ ...
Chapter 6 Ocean Circulation
... are largely set for an extended period of time. • Based upon depth, surface water masses can be broadly classified as Central waters (from 0 to 1 km), Intermediate waters (from 1 to 2 km), and Deep and bottom waters (greater than 2 km). ...
... are largely set for an extended period of time. • Based upon depth, surface water masses can be broadly classified as Central waters (from 0 to 1 km), Intermediate waters (from 1 to 2 km), and Deep and bottom waters (greater than 2 km). ...
Print flyer - Loch Ness Productions
... journeys of discovery, on the most famous submersibles in history, to come face-to-face with the fascinating creatures that survive where no life was ever expected — Into The Deep! ...
... journeys of discovery, on the most famous submersibles in history, to come face-to-face with the fascinating creatures that survive where no life was ever expected — Into The Deep! ...
INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARING AN ABSTRACT FOR THE 1ST
... fossil fuel CO2 emissions are currently contained in the world's ocean. The Atlantic, especially in its northern part, shows higher column inventories of anthropogenic carbon than the Indian and Pacific Ocean, illustrating the role of North Atlantic Deep Water for the storage of CO2 emissions from t ...
... fossil fuel CO2 emissions are currently contained in the world's ocean. The Atlantic, especially in its northern part, shows higher column inventories of anthropogenic carbon than the Indian and Pacific Ocean, illustrating the role of North Atlantic Deep Water for the storage of CO2 emissions from t ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... wind blowing across its surface. The surface water is dragged along with the wind. However, due to the Coriolis force, it is deflected somewhat to the right (in the NH). The surface water drags along the water immediately beneath it but at a somewhat slower speed, and this layer is also deflected to ...
... wind blowing across its surface. The surface water is dragged along with the wind. However, due to the Coriolis force, it is deflected somewhat to the right (in the NH). The surface water drags along the water immediately beneath it but at a somewhat slower speed, and this layer is also deflected to ...
PRESENTATION NAME
... where cold water rushes up from the bottom of the ocean carrying nutrients to sunlit waters. In this case, the bloom may be related to recent flooding along the Mississippi River and its tributaries. Heavy rains early in December triggered floods across the southeastern United States. The draining f ...
... where cold water rushes up from the bottom of the ocean carrying nutrients to sunlit waters. In this case, the bloom may be related to recent flooding along the Mississippi River and its tributaries. Heavy rains early in December triggered floods across the southeastern United States. The draining f ...
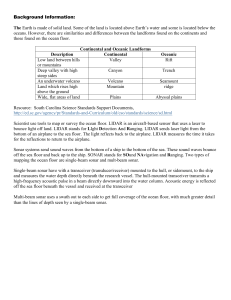
Background Information
... Background Information: The Earth is made of solid land. Some of the land is located above Earth’s water and some is located below the oceans. However, there are similarities and differences between the landforms found on the continents and those found on the ocean floor. ...
... Background Information: The Earth is made of solid land. Some of the land is located above Earth’s water and some is located below the oceans. However, there are similarities and differences between the landforms found on the continents and those found on the ocean floor. ...
Constructive and Destructive Landforms
... Constructive forces: forces that build up an existing landform or create a new one. Caused by: water, gravity, wind and glaciers. Ex: deposition, landslides, volcanic eruptions, floods ...
... Constructive forces: forces that build up an existing landform or create a new one. Caused by: water, gravity, wind and glaciers. Ex: deposition, landslides, volcanic eruptions, floods ...
Ocean

An ocean (from Ancient Greek Ὠκεανός, transc. Okeanós, the sea of classical antiquity) is a body of saline water that composes much of a planet's hydrosphere. On Earth, an ocean is one of the major conventional divisions of the World Ocean, which covers almost 71% of its surface. These are, in descending order by area, the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans. The word sea is often used interchangeably with ""ocean"" in American English but, strictly speaking, a sea is a body of saline water (generally a division of the world ocean) partly or fully enclosed by land.Saline water covers approximately 72% of the planet's surface (~3.6×108 km2) and is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas, with the ocean covering approximately 71% of Earth's surface. The ocean contains 97% of Earth's water, and oceanographers have stated that only 5% of the World Ocean has been explored. The total volume is approximately 1.35 billion cubic kilometers (320 million cu mi) with an average depth of nearly 3,700 meters (12,100 ft).As it is the principal component of Earth's hydrosphere, the world ocean is integral to all known life, forms part of the carbon cycle, and influences climate and weather patterns. It is the habitat of 230,000 known species, although much of the oceans depths remain unexplored, and over two million marine species are estimated to exist. The origin of Earth's oceans remains unknown; oceans are thought to have formed in the Hadean period and may have been the impetus for the emergence of life.Extraterrestrial oceans may be composed of water or other elements and compounds. The only confirmed large stable bodies of extraterrestrial surface liquids are the lakes of Titan, although there is evidence for the existence of oceans elsewhere in the Solar System. Early in their geologic histories, Mars and Venus are theorized to have had large water oceans. The Mars ocean hypothesis suggests that nearly a third of the surface of Mars was once covered by water, and a runaway greenhouse effect may have boiled away the global ocean of Venus. Compounds such as salts and ammonia dissolved in water lower its freezing point, so that water might exist in large quantities in extraterrestrial environments as brine or convecting ice. Unconfirmed oceans are speculated beneath the surface of many dwarf planets and natural satellites; notably, the ocean of Europa is estimated to have over twice the water volume of Earth. The Solar System's giant planets are also thought to have liquid atmospheric layers of yet to be confirmed compositions. Oceans may also exist on exoplanets and exomoons, including surface oceans of liquid water within a circumstellar habitable zone. Ocean planets are a hypothetical type of planet with a surface completely covered with liquid.