AChE inhibitor
... symptoms and improvement of men t al function after remova l of cause (reversible dementi a). Depression : a speci f ic psychiatric entity t hat can preced e or be associated with dementia, and t hat can be dif ferenti ally diagnosed and trea t ed. Benign Senescent Forgetfulness : not pr ogressive a ...
... symptoms and improvement of men t al function after remova l of cause (reversible dementi a). Depression : a speci f ic psychiatric entity t hat can preced e or be associated with dementia, and t hat can be dif ferenti ally diagnosed and trea t ed. Benign Senescent Forgetfulness : not pr ogressive a ...
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems - Biology at Mott
... medulla The medulla oblongata contains centers that control several functions including breathing, cardiovascular activity, swallowing, vomiting, and digestion ...
... medulla The medulla oblongata contains centers that control several functions including breathing, cardiovascular activity, swallowing, vomiting, and digestion ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... The Amygdala [ah-MIGdah-la] consists of two lima bean-sized neural clusters linked to the emotions of fear and anger. ...
... The Amygdala [ah-MIGdah-la] consists of two lima bean-sized neural clusters linked to the emotions of fear and anger. ...
Psychology Chapter 3
... soft tissue, (e.g. ligament and tendon injury, spinal cord injury, brain tumors etc.) while a CT scan is better suited for bone injuries, lung and chest imaging, and detecting cancers. CT scans are widely used in emergency rooms because the procedure takes less than 5 minutes. An MRI, on the other h ...
... soft tissue, (e.g. ligament and tendon injury, spinal cord injury, brain tumors etc.) while a CT scan is better suited for bone injuries, lung and chest imaging, and detecting cancers. CT scans are widely used in emergency rooms because the procedure takes less than 5 minutes. An MRI, on the other h ...
How To Make a Neuron Model
... 2. Take another pipe cleaner and attach it to the new "cell body" by pushing it through the ball so there are two halves sticking out. Take the two halves and twist them together into a single extension. This will be the axon. ...
... 2. Take another pipe cleaner and attach it to the new "cell body" by pushing it through the ball so there are two halves sticking out. Take the two halves and twist them together into a single extension. This will be the axon. ...
Nervous System Crossword Puzzle
... of smooth muscle, and increase heart rate 42. cortex responsible for memory, brooch's area, recognition 43. nerves mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body; there's 31 pairs 46. barrier a layer of tightly packed cells that make up the wall ...
... of smooth muscle, and increase heart rate 42. cortex responsible for memory, brooch's area, recognition 43. nerves mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body; there's 31 pairs 46. barrier a layer of tightly packed cells that make up the wall ...
Nervous System Crossword Puzzle
... increase heart rate 42. cortex responsible for memory, brooch's area, recognition 43. nerves mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body; there's 31 pairs 46. barrier a layer of tightly packed cells that make up the walls of the brain capilla ...
... increase heart rate 42. cortex responsible for memory, brooch's area, recognition 43. nerves mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body; there's 31 pairs 46. barrier a layer of tightly packed cells that make up the walls of the brain capilla ...
Nervous System - science
... What is the main function of the peripheral nervous system? To connect the central nervous system, or brain and spinal cord, with all parts of the body ...
... What is the main function of the peripheral nervous system? To connect the central nervous system, or brain and spinal cord, with all parts of the body ...
The Nervous System - Volunteer State Community College
... brain & spinal cord; responsible for integration of sensory input & associating stimuli with appropriate motor output 2) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) = consists of a network of nerves extending into different parts of the body that carry sensory input to the CNS & motor output away form the CNS ...
... brain & spinal cord; responsible for integration of sensory input & associating stimuli with appropriate motor output 2) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) = consists of a network of nerves extending into different parts of the body that carry sensory input to the CNS & motor output away form the CNS ...
The Nervous System
... unilateral facial paralysis due to disorder of facial nerve partial paralysis & lack of muscular coordination due to damage to cerebrum during birth ...
... unilateral facial paralysis due to disorder of facial nerve partial paralysis & lack of muscular coordination due to damage to cerebrum during birth ...
Glossary
... Left-right imbalances between the cerebral hemispheres in the speed of visual or auditory processing. ...
... Left-right imbalances between the cerebral hemispheres in the speed of visual or auditory processing. ...
Nerve activates contraction
... The lowest part of the brain stem Merges into the spinal cord Includes important fiber tracts Contains important control centers ...
... The lowest part of the brain stem Merges into the spinal cord Includes important fiber tracts Contains important control centers ...
The Endocrine System
... Located in a bony cavity just below the base of the brain Body’s master gland Secretes several hormones that regulate the function of other endocrine glands Regulates the body’s growth Stimulates milk production in women who are breast feeding Also secretes endorphins which are chemicals that act on ...
... Located in a bony cavity just below the base of the brain Body’s master gland Secretes several hormones that regulate the function of other endocrine glands Regulates the body’s growth Stimulates milk production in women who are breast feeding Also secretes endorphins which are chemicals that act on ...
Symptoms: visual disturbances, ______, loss of
... conscience, development depends on feedback from social environment 2. Posterior association area- Plays a role in recognizing patterns and faces and localizing us in space, involved in understanding written and spoken language (Wernicke’s area) 3. Limbic association area- Provides emotional impact ...
... conscience, development depends on feedback from social environment 2. Posterior association area- Plays a role in recognizing patterns and faces and localizing us in space, involved in understanding written and spoken language (Wernicke’s area) 3. Limbic association area- Provides emotional impact ...
I. Introduction to class
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its environment. ...
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its environment. ...
Chapter 28: Nervous System
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its environment. ...
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its environment. ...
Slide ()
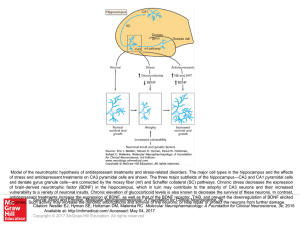
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
107B exam 1 test yourself
... maps 1, 2, 3 project from layer 4 to layer 2-3 where mixed with ___________ input (converged, no longer segregated), then back to layer 5 and out to thalamus (feedback to sensory systems) and other cortical areas Somatosensory inputs segregated to _____________ and ____________ (called pathways), mi ...
... maps 1, 2, 3 project from layer 4 to layer 2-3 where mixed with ___________ input (converged, no longer segregated), then back to layer 5 and out to thalamus (feedback to sensory systems) and other cortical areas Somatosensory inputs segregated to _____________ and ____________ (called pathways), mi ...
Nervous System - science
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
The Nervous System - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... • 3. Midbrain – controls pupil size • 4. Thalamus – relays incoming information from the eyes, ears, and pressure receptors in skin • 5. Hypothalamus – regulates body temp, appetite, sleep ...
... • 3. Midbrain – controls pupil size • 4. Thalamus – relays incoming information from the eyes, ears, and pressure receptors in skin • 5. Hypothalamus – regulates body temp, appetite, sleep ...
Lecture 2: Basics and definitions - Homepages | The University of
... total number of these waves. … But this limitation is really a small matter, for in the body the nervous units do not act in isolation as they do in our experiments. A sensory stimulus will usually affect a number of receptor organs, and its result will depend on the composite message in many nerve ...
... total number of these waves. … But this limitation is really a small matter, for in the body the nervous units do not act in isolation as they do in our experiments. A sensory stimulus will usually affect a number of receptor organs, and its result will depend on the composite message in many nerve ...
The Nervous System - Appoquinimink High School
... opening and allowing positive sodium into the cell. This makes it positive. And is called DEPOLARIZATION 2. Soon after potassium channels open and allow potassium in ions in again bringing the charge back to negative. This is called REPOLARIZATION ...
... opening and allowing positive sodium into the cell. This makes it positive. And is called DEPOLARIZATION 2. Soon after potassium channels open and allow potassium in ions in again bringing the charge back to negative. This is called REPOLARIZATION ...