But Ma, how do all the body systems fit together?
... of nerves called neurons which conduct electrochemical signals throughout the body. ...
... of nerves called neurons which conduct electrochemical signals throughout the body. ...
The Nervous System
... – Small samples of brain tissue from a person and a monkey are basically indistinguishable ...
... – Small samples of brain tissue from a person and a monkey are basically indistinguishable ...
Key - Cornell
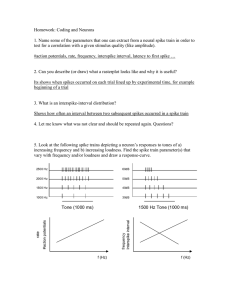
... channels, what is a good alternative? How is a refractory period modeled in that case? How can noise be introduced in these simulations? You reset the voltage to 0 after a spike, which creates a refractory period. Or you can even reset it to a negative valule. Noise can be added by making the thresh ...
... channels, what is a good alternative? How is a refractory period modeled in that case? How can noise be introduced in these simulations? You reset the voltage to 0 after a spike, which creates a refractory period. Or you can even reset it to a negative valule. Noise can be added by making the thresh ...
Visceral Nervous System
... RADICULAR NEURONS: they form the anterior roots. In the spinal cord the cell body is in the anterior horn of the grey metter; in the brain stem in motor nuclei. FASCICULAR NEURONS: they represent the second neuron of a sensory pathway. In the spinal cord the cell body is in the posterior horn of the ...
... RADICULAR NEURONS: they form the anterior roots. In the spinal cord the cell body is in the anterior horn of the grey metter; in the brain stem in motor nuclei. FASCICULAR NEURONS: they represent the second neuron of a sensory pathway. In the spinal cord the cell body is in the posterior horn of the ...
Nervous Regulation
... These 2 systems are antagonistic. The autonomic nervous system is made entirely of ________________. Impulses in this system start in motor neurons in the ______________ __________. The axons of these nerves ________________________ _________________________________________________________. ...
... These 2 systems are antagonistic. The autonomic nervous system is made entirely of ________________. Impulses in this system start in motor neurons in the ______________ __________. The axons of these nerves ________________________ _________________________________________________________. ...
6. LIMBIC SYSTEM AND THE HYPOTHALAMUS
... body within a range of homeostatic conditions. The hypothalamus connects with most structures of the limbic system, thus, it receives and processes sensory information and generates information that can be distributed into three main categories (Fig. 63). To the autonomic nervous system. This inform ...
... body within a range of homeostatic conditions. The hypothalamus connects with most structures of the limbic system, thus, it receives and processes sensory information and generates information that can be distributed into three main categories (Fig. 63). To the autonomic nervous system. This inform ...
Module 3 - DHS Home
... • The mixing of + and – ions (Union of Opposites) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Sodium-Na) while closing the original portal. • Positive Potassium (K) is pumped out AS THE PROCESS OCCURS DOWN THE AXON and now the neuron is in a state of ...
... • The mixing of + and – ions (Union of Opposites) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Sodium-Na) while closing the original portal. • Positive Potassium (K) is pumped out AS THE PROCESS OCCURS DOWN THE AXON and now the neuron is in a state of ...
SChapter 12
... that is usually caused by neurotransmitters. 5) Response of postsynaptic cell can vary depending on the response of the receptor that was stimulated *see fig. 12-7 for an overview of these important processes* ▪Transmembrane Potential- three important concepts regarding the transmembrane potential: ...
... that is usually caused by neurotransmitters. 5) Response of postsynaptic cell can vary depending on the response of the receptor that was stimulated *see fig. 12-7 for an overview of these important processes* ▪Transmembrane Potential- three important concepts regarding the transmembrane potential: ...
nervous system physiology 1
... Neurons classified on the basis of their axonal projection, dendritic geometry, and the number of processes emanating from the cell body CNS nerve cells - great structural diversity, correlated with their functions. -axonal projection long axons: Axonal Projection Neurons = principal neurons or Gol ...
... Neurons classified on the basis of their axonal projection, dendritic geometry, and the number of processes emanating from the cell body CNS nerve cells - great structural diversity, correlated with their functions. -axonal projection long axons: Axonal Projection Neurons = principal neurons or Gol ...
Pituitary Gland - PROFESSOR AC BROWN
... PITUTARY GLAND page 1 PITUITARY(also called the "Hypophysis") A. Structure 1. Small gland at the base of the brain 2. Divided into the anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis) and posterior pituitary (also called the neurohypophysis); there also is an intermediate region (intermediate lo ...
... PITUTARY GLAND page 1 PITUITARY(also called the "Hypophysis") A. Structure 1. Small gland at the base of the brain 2. Divided into the anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis) and posterior pituitary (also called the neurohypophysis); there also is an intermediate region (intermediate lo ...
Connectionism
... different letters are pronounced under different circumstances. (It has been argued that ''ghiti'' could be pronounced ''fish'' - ''gh'' from ''enough'' and ''ti'' from ''nation.'') • But once the system has evolved, it acts as though it knows the rules. They become implicitly coded in the network o ...
... different letters are pronounced under different circumstances. (It has been argued that ''ghiti'' could be pronounced ''fish'' - ''gh'' from ''enough'' and ''ti'' from ''nation.'') • But once the system has evolved, it acts as though it knows the rules. They become implicitly coded in the network o ...
Objective 1 | Explain why psychologists are concerned with human
... functions of the brainstem, thalamus, and cerebellum. The brainstem is the oldest part of the brain and is responsible for automatic survival functions. Its components are the medulla (which controls heartbeat and breathing), the pons (which helps coordinate movements), and the reticular formation ( ...
... functions of the brainstem, thalamus, and cerebellum. The brainstem is the oldest part of the brain and is responsible for automatic survival functions. Its components are the medulla (which controls heartbeat and breathing), the pons (which helps coordinate movements), and the reticular formation ( ...
Nervous System 2
... 2. What type of muscle is controlled by the autonomic nervous system? What type of muscle is controlled by the somatic nervous system? 3. Compare the parasympathetic and sympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system: a. Where do they branch off the spinal cord? b. Where do the pre-ganglionic ...
... 2. What type of muscle is controlled by the autonomic nervous system? What type of muscle is controlled by the somatic nervous system? 3. Compare the parasympathetic and sympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system: a. Where do they branch off the spinal cord? b. Where do the pre-ganglionic ...
The Nervous System
... Nervous System Functions • 1. Sensory-receptors gather information and pass it on toward the CNS • 2. Integrative-in the spinal cord or brain, we put information together and make sense of it • 3. Motor-carry impulses to effectors such as muscles and glands ...
... Nervous System Functions • 1. Sensory-receptors gather information and pass it on toward the CNS • 2. Integrative-in the spinal cord or brain, we put information together and make sense of it • 3. Motor-carry impulses to effectors such as muscles and glands ...
How is the Nervous System Organized? Class Objectives:
... Understand the function and purpose of the nervous system Identify and define the structures of the neuron Identify and discuss the role of neurotransmitters on behavior ...
... Understand the function and purpose of the nervous system Identify and define the structures of the neuron Identify and discuss the role of neurotransmitters on behavior ...
BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR
... 1. Neurons are surrounded by a membrane. 2. Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. 3. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other "organelles". However, neurons differ from other cells in the body in some ways such as: 1. Neurons have specialized projections called dendrites and axons. De ...
... 1. Neurons are surrounded by a membrane. 2. Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. 3. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other "organelles". However, neurons differ from other cells in the body in some ways such as: 1. Neurons have specialized projections called dendrites and axons. De ...
Nerve Impulses - manorlakesscience
... change in the charge across the axon membrane. A nerve impulse is a wave of electrical change (an action potential) that passes rapidly along an axon. After the nerve impulse has been transmitted – the distribution of ions across the cell membrane is restored. ...
... change in the charge across the axon membrane. A nerve impulse is a wave of electrical change (an action potential) that passes rapidly along an axon. After the nerve impulse has been transmitted – the distribution of ions across the cell membrane is restored. ...
Ch6 - Unit3Biology
... • last for a very short time only (enzymes produced by muscles tissue inactive the substances for example) Example: acetycholine ...
... • last for a very short time only (enzymes produced by muscles tissue inactive the substances for example) Example: acetycholine ...
Document
... a) cytoplasmb) axon hillockc) initial segmentd) nucleus of schwann celle) node of Ranvierf) synaptic end bulbg) dendrites- ...
... a) cytoplasmb) axon hillockc) initial segmentd) nucleus of schwann celle) node of Ranvierf) synaptic end bulbg) dendrites- ...
Sheep Brain Dissection
... 2. The darker tissue is the grey matter, which contains the cell bodies of the neurons. Histological sections reveal several distinct layers of tissue with different predominant cell types and very specific interconnections to other brain regions. The grey matter is also called the cortex, or outer ...
... 2. The darker tissue is the grey matter, which contains the cell bodies of the neurons. Histological sections reveal several distinct layers of tissue with different predominant cell types and very specific interconnections to other brain regions. The grey matter is also called the cortex, or outer ...