Chapter 3 The Nervous System and the Brain
... fibers. These fibers supply the cardiac muscles, smooth muscles, and the glands. The glands, smooth muscles and the cardiac muscles make up the Autonomic Nervous System. The Autonomic Nervous System is then made up of two divisions. The first is the Parasympathetic Division, which is important for t ...
... fibers. These fibers supply the cardiac muscles, smooth muscles, and the glands. The glands, smooth muscles and the cardiac muscles make up the Autonomic Nervous System. The Autonomic Nervous System is then made up of two divisions. The first is the Parasympathetic Division, which is important for t ...
Modeling and Imagery
... • The γ activation of the intrafusal fibers serves as a reflexive check on the α activated extrafusal fibers • If there’s a match, all is well • If there’s a mismatch, the α–motor neuron fires some ...
... • The γ activation of the intrafusal fibers serves as a reflexive check on the α activated extrafusal fibers • If there’s a match, all is well • If there’s a mismatch, the α–motor neuron fires some ...
an appraisal of the mechanism of action of
... related issues9. Shirodhara bring a calming effect because after completion of procedure patient feel relax and sleepy. So it may say that one of the mechanisms of action of Shirodhara is by raising the level of Serotonin. Probable Mode of Action of Shirodhara: 1. Tranquilizing effect : Continuous p ...
... related issues9. Shirodhara bring a calming effect because after completion of procedure patient feel relax and sleepy. So it may say that one of the mechanisms of action of Shirodhara is by raising the level of Serotonin. Probable Mode of Action of Shirodhara: 1. Tranquilizing effect : Continuous p ...
Topic 1: Cell biology (15 hours)
... 8. Synapses are junctions between neurons and between neurons and acetylcholine receptors. receptor or effector cells. Guidance: Only chemical synapses are 13. Skill: Analysis of required, not electrical, and they can simply be referred to as synapses. oscilloscope traces 9. When presynaptic neurons ...
... 8. Synapses are junctions between neurons and between neurons and acetylcholine receptors. receptor or effector cells. Guidance: Only chemical synapses are 13. Skill: Analysis of required, not electrical, and they can simply be referred to as synapses. oscilloscope traces 9. When presynaptic neurons ...
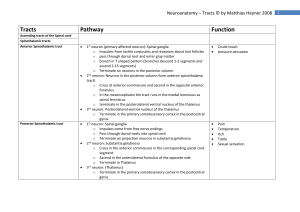
Tracts
... Most important pathway for voluntary motor function Some axons (corticonuclear fibers) terminate at the cranial nerve nuclei Other axons (corticospinal fibers) terminate on the motor anterior horn cells Third group of the axons (corticoreticular fibers) terminate at the nuclei of the reticular forma ...
... Most important pathway for voluntary motor function Some axons (corticonuclear fibers) terminate at the cranial nerve nuclei Other axons (corticospinal fibers) terminate on the motor anterior horn cells Third group of the axons (corticoreticular fibers) terminate at the nuclei of the reticular forma ...
Optical Fractionator
... nucleus must have a size equal to or greater than the diameter of the average TH+ nucleus, (c) it has a macronucleolus and more than one small nucleoli, (d) the shape of the nucleus is round to oval, (e) the nuclear membrane typically smooth, (f) the nucleus was partially or entirely inside the coun ...
... nucleus must have a size equal to or greater than the diameter of the average TH+ nucleus, (c) it has a macronucleolus and more than one small nucleoli, (d) the shape of the nucleus is round to oval, (e) the nuclear membrane typically smooth, (f) the nucleus was partially or entirely inside the coun ...
PG1006 Lecture 2 Nervous Tissue 1
... by nerves, nerve cells and neurones 2. Outline the key structural features of nerve cells or neurons 3. Introduce the methods by which neurones physically interact and func4onally couple. ...
... by nerves, nerve cells and neurones 2. Outline the key structural features of nerve cells or neurons 3. Introduce the methods by which neurones physically interact and func4onally couple. ...
Notes to Resp. 4
... and a motor effector with possible intermediate neuronal processing. Thus, respiratory cycles have an autonomic characteristic that can be modified by a voluntary contribution. Control of breathing involves control of the diaphragm, the most important muscle of inspiration. Remember that when our di ...
... and a motor effector with possible intermediate neuronal processing. Thus, respiratory cycles have an autonomic characteristic that can be modified by a voluntary contribution. Control of breathing involves control of the diaphragm, the most important muscle of inspiration. Remember that when our di ...
Self Assessment Chapter 11 - CM
... and determine an appropriate response • 99% of integrated sensory information is subconsciously disregarded as unimportant • Remaining sensory stimuli that CNS does respond to generally leads to a motor response ...
... and determine an appropriate response • 99% of integrated sensory information is subconsciously disregarded as unimportant • Remaining sensory stimuli that CNS does respond to generally leads to a motor response ...
PowerPoint 11: Nemertea
... Most important in which habitats? Absent in deep-sea, pelagic forms Role in excretion? ...
... Most important in which habitats? Absent in deep-sea, pelagic forms Role in excretion? ...
Neurophysiology
... Afferent neurons interconnected in a certain sequence First-order sensory neuron “Afferent neuron with its peripheral receptor that FIRST detects the stimulus Second-order sensory neuron ...
... Afferent neurons interconnected in a certain sequence First-order sensory neuron “Afferent neuron with its peripheral receptor that FIRST detects the stimulus Second-order sensory neuron ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... protects the spinal cord. • The spinal cord is the link between your brain and the peripheral nervous system. • All of these parts of the brain and spinal cord are surrounded by a liquid to protect them (spinal fluid!). ...
... protects the spinal cord. • The spinal cord is the link between your brain and the peripheral nervous system. • All of these parts of the brain and spinal cord are surrounded by a liquid to protect them (spinal fluid!). ...
Introduction to the Nervous System
... Twelve pairs of cranial nerves emerge from the inferior surface of the brain. All of these nerves, except the vagus nerve, pass through foramina of the skull to innervate structures in the head, neck, and facial region. The cranial nerves are designated both by name and by Roman numerals, according ...
... Twelve pairs of cranial nerves emerge from the inferior surface of the brain. All of these nerves, except the vagus nerve, pass through foramina of the skull to innervate structures in the head, neck, and facial region. The cranial nerves are designated both by name and by Roman numerals, according ...
Chapter 12
... 32. Define the anatomic, chemical, enzymatic, and receptor components of a chemical synapse. 33. Go through the sequence of events that allow an action potential on an axon to be transmitted into a graded potential on a postsynaptic membrane. Excitatory and Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials 34. Ind ...
... 32. Define the anatomic, chemical, enzymatic, and receptor components of a chemical synapse. 33. Go through the sequence of events that allow an action potential on an axon to be transmitted into a graded potential on a postsynaptic membrane. Excitatory and Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials 34. Ind ...
supporting cells - Daniela Sartori
... • Allows only certain compounds to enter brain • Formed by capillary specializations in brain – That appear to be induced by astrocytes – Capillaries are not as leaky as those in body • Gaps between adjacent cells are closed by tight junctions ...
... • Allows only certain compounds to enter brain • Formed by capillary specializations in brain – That appear to be induced by astrocytes – Capillaries are not as leaky as those in body • Gaps between adjacent cells are closed by tight junctions ...
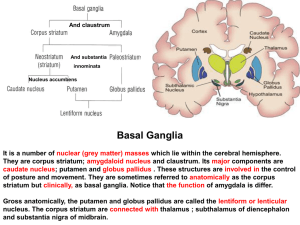
17-Basal ganglion
... temporal lobe where it lies in the roof of the inferior horn of lateral ventricle. ...
... temporal lobe where it lies in the roof of the inferior horn of lateral ventricle. ...
Neurons - Honors Biology 10 - 2222-03
... The messages carried by the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses. Nervous system impulses are transmitted by cells called neurons. ...
... The messages carried by the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses. Nervous system impulses are transmitted by cells called neurons. ...
Nervous System WS (handed out after section exam)
... 6. Neurons are organized into circuits: receptor cells sensory neurons interneuron (CNS) Brain interneuron motor neuron effector cells (muscle or gland) ...
... 6. Neurons are organized into circuits: receptor cells sensory neurons interneuron (CNS) Brain interneuron motor neuron effector cells (muscle or gland) ...
Anatomy of the Spinal Cord
... myelinated nerve fibers The white matter of the spinal cord is arranged in columns/funiculi; anterior, posterior and lateral. The nerve fibers are arranged as bundles, running vertically through the cord. A group of nerve fibers (axons) that share a common origin, termination and function form ...
... myelinated nerve fibers The white matter of the spinal cord is arranged in columns/funiculi; anterior, posterior and lateral. The nerve fibers are arranged as bundles, running vertically through the cord. A group of nerve fibers (axons) that share a common origin, termination and function form ...
The Nervous System
... 2. Can neuroglia undergo action potentials? 3. The type of cell that carries nerve impulses in the nervous system is the ________________________. 4. The type of cell that nourishes, supports, and influences the activity of the neurons is the ________________. 5. The part of the neuron that brings i ...
... 2. Can neuroglia undergo action potentials? 3. The type of cell that carries nerve impulses in the nervous system is the ________________________. 4. The type of cell that nourishes, supports, and influences the activity of the neurons is the ________________. 5. The part of the neuron that brings i ...
Chapter 11-自律神經及體運動神經系統檔案
... Figure 11.7 Neurotransmitters and receptors in the autonomic nervous system. (a) Neurotransmitters and receptors for the three distinct anatomical pathways of the sympathetic nervous system. In all cases, the preganglionic neuron releases acetylcholine (Ach), which then binds to nicotinic cholinergi ...
... Figure 11.7 Neurotransmitters and receptors in the autonomic nervous system. (a) Neurotransmitters and receptors for the three distinct anatomical pathways of the sympathetic nervous system. In all cases, the preganglionic neuron releases acetylcholine (Ach), which then binds to nicotinic cholinergi ...
Chapter 11-自律神經及體運動神經系統檔案
... Because the muscles most frequently affected are those of the head, difficulties in speaking (dysarthria) 發音困難 and in swallowing (dysphagia) 吞嚥困難 are common symptoms; dropping of the eyelids (ptosis) 眼瞼下垂 is also a common sign We now know that myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease 自體免疫疾病— a ...
... Because the muscles most frequently affected are those of the head, difficulties in speaking (dysarthria) 發音困難 and in swallowing (dysphagia) 吞嚥困難 are common symptoms; dropping of the eyelids (ptosis) 眼瞼下垂 is also a common sign We now know that myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease 自體免疫疾病— a ...
Afferent (Sensory) Division Part 1
... perception • Sensation is the awareness of changes in the internal and external environment • Perception is the conscious interpretation of those stimuli ...
... perception • Sensation is the awareness of changes in the internal and external environment • Perception is the conscious interpretation of those stimuli ...
MCB 163: Mammalian Neuroanatomy
... reduced relatively since many descending fibers have already terminated; the relative ratio of gray to white matter favors the gray, suggesting that many tracts are small. 2. GRACILE FASCICULUS: This tract contains ganglion cell axons representing cutaneous Merkel and Meissner and Pacinian corpuscle ...
... reduced relatively since many descending fibers have already terminated; the relative ratio of gray to white matter favors the gray, suggesting that many tracts are small. 2. GRACILE FASCICULUS: This tract contains ganglion cell axons representing cutaneous Merkel and Meissner and Pacinian corpuscle ...