module 6 - sandrablake
... the ___________________________ period, when a neuron after firing, cannot generate another action potential. Think of a camera flash that has to recharge before it can be used again. After the refractory period, the neuron is capable of another action potential when it is stimulated. When the neur ...
... the ___________________________ period, when a neuron after firing, cannot generate another action potential. Think of a camera flash that has to recharge before it can be used again. After the refractory period, the neuron is capable of another action potential when it is stimulated. When the neur ...
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord PNS consists of nerves 1
... Contain neuron cell bodies associated with nerves in PNS Ganglia associated with afferent nerve fibers contain cell bodies of sensory ...
... Contain neuron cell bodies associated with nerves in PNS Ganglia associated with afferent nerve fibers contain cell bodies of sensory ...
CNS
... Pathways (non-conscious) – Spinocerebellar tracts • Relay information from golgi organs and muscle spindles • Posterior (dorsal) tract is ipsilateral to cerebellum via cerebellar peduncles • Anterior (ventral) tract contains crossed and ipsilateral fibers for lower limbs • Some proprioceptive signal ...
... Pathways (non-conscious) – Spinocerebellar tracts • Relay information from golgi organs and muscle spindles • Posterior (dorsal) tract is ipsilateral to cerebellum via cerebellar peduncles • Anterior (ventral) tract contains crossed and ipsilateral fibers for lower limbs • Some proprioceptive signal ...
dual-center hypothesis
... Systems That Control Hunger • Ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) lesions cause animals to eat to excess (hyperphagia) and become obese, suggesting the VMH is a satiety center. • Lateral hypothalamus (LH) lesions cause aphagia—refusal to eat—suggesting LH is a hunger center. • However, the dual-center h ...
... Systems That Control Hunger • Ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) lesions cause animals to eat to excess (hyperphagia) and become obese, suggesting the VMH is a satiety center. • Lateral hypothalamus (LH) lesions cause aphagia—refusal to eat—suggesting LH is a hunger center. • However, the dual-center h ...
Bolt IRM Mod 03
... Lecture/Discussion Topic: Multiple Sclerosis and Guillain-Barré Syndrome As mentioned in the text, myelin is a fatty sheath that helps speed impulses down some neurons’ axons. Its importance for the normal transfer of information in the human nervous system is evident in the demyelinating diseases o ...
... Lecture/Discussion Topic: Multiple Sclerosis and Guillain-Barré Syndrome As mentioned in the text, myelin is a fatty sheath that helps speed impulses down some neurons’ axons. Its importance for the normal transfer of information in the human nervous system is evident in the demyelinating diseases o ...
atterning the nervous system through development and evolution: a
... Two talks dealt with the fish Astyanax fasciatus, also named mexicanus for this is where it lives. Bill Jeffery (University of Maryland) examined the developmental basis of blindness and depigmentation in cave forms of Astyanax, compared to the surface form it was presumably derived from (Figure 3). ...
... Two talks dealt with the fish Astyanax fasciatus, also named mexicanus for this is where it lives. Bill Jeffery (University of Maryland) examined the developmental basis of blindness and depigmentation in cave forms of Astyanax, compared to the surface form it was presumably derived from (Figure 3). ...
Chapter 17.2 Review
... 16. Communicating Concepts Sensory organs, such as your eyes and ears, have special structures. Write a brief essay describing the relationship between the structures and functions of your eyes or ears. ______________________________________________________________ __________________________________ ...
... 16. Communicating Concepts Sensory organs, such as your eyes and ears, have special structures. Write a brief essay describing the relationship between the structures and functions of your eyes or ears. ______________________________________________________________ __________________________________ ...
Module_3vs9_Final - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • Central nervous system – Made up of neurons located in the ______________________________ ...
... • Central nervous system – Made up of neurons located in the ______________________________ ...
chapt10answers
... Do they adapt easily? no _visceral____ pain receptors are the only receptors in the organs that produce sensations. __referred____ pain occurs because of the common nerve pathways leading from skin and internal organs. An example would be a heart attack being felt as pain in the arm or as heartburn. ...
... Do they adapt easily? no _visceral____ pain receptors are the only receptors in the organs that produce sensations. __referred____ pain occurs because of the common nerve pathways leading from skin and internal organs. An example would be a heart attack being felt as pain in the arm or as heartburn. ...
Chapter Two
... A. Except for differences that are directly related to reproductive function, there are very few differences that are of real consequence between male and female brains. Nonetheless, some research suggests that there is more activity in the limbic system (associated with emotional reactions, rewards ...
... A. Except for differences that are directly related to reproductive function, there are very few differences that are of real consequence between male and female brains. Nonetheless, some research suggests that there is more activity in the limbic system (associated with emotional reactions, rewards ...
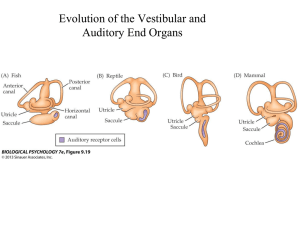
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 25.1 Drawing of the auditory periphery
... FIGURE 25.1 Drawing of the auditory periphery within the human head. The external ear (pinna and external auditory canal) and the middle ear (tympanic membrane or eardrum, and the three middle ear ossicles: malleus, incus, and stapes) are indicated. Also shown is the inner ear, which includes the co ...
... FIGURE 25.1 Drawing of the auditory periphery within the human head. The external ear (pinna and external auditory canal) and the middle ear (tympanic membrane or eardrum, and the three middle ear ossicles: malleus, incus, and stapes) are indicated. Also shown is the inner ear, which includes the co ...
Box 9.1 The Basics of Sound (Part 1)
... • Auditory object is the fundamental perceptual unit in hearing • Similar to visual objects although made up of spectrotemporal regularities • Auditory scene contains numerous acoustic stimuli ...
... • Auditory object is the fundamental perceptual unit in hearing • Similar to visual objects although made up of spectrotemporal regularities • Auditory scene contains numerous acoustic stimuli ...
SBI4U Homeostasis Name:
... Multiple Choice. Choose the most correct answer for each, answer in the space provided. [17] _____ 1. When a person sweats and does not drink enough fluid: a) less reabsorption of water occurs c) the pituitary gland releases ADH b) urine will become less concentrated d) all of the above ______2. The ...
... Multiple Choice. Choose the most correct answer for each, answer in the space provided. [17] _____ 1. When a person sweats and does not drink enough fluid: a) less reabsorption of water occurs c) the pituitary gland releases ADH b) urine will become less concentrated d) all of the above ______2. The ...
File
... system and commands unconscious body procedures, such as keeping the heart rate constant and controlling food ...
... system and commands unconscious body procedures, such as keeping the heart rate constant and controlling food ...
Investigating Nervous and Sensory Systems
... functions of these two systems often complement one another, biologists often speak of the neuroendocrine system. The nervous system has three functions: 1. to receive signals from the environment and from within the body through the sense organs 2. to process the information received, which can inv ...
... functions of these two systems often complement one another, biologists often speak of the neuroendocrine system. The nervous system has three functions: 1. to receive signals from the environment and from within the body through the sense organs 2. to process the information received, which can inv ...
The mind`s mirror
... Since then, most studies on the human mirror-neuron system have used some sort of neuroimaging, generally functional magnetic-resonance imaging (fMRI). For example, University of California, Los Angeles, neuroscientist Marco Iacoboni, MD, PhD, used fMRI to image the brain activity of college-student ...
... Since then, most studies on the human mirror-neuron system have used some sort of neuroimaging, generally functional magnetic-resonance imaging (fMRI). For example, University of California, Los Angeles, neuroscientist Marco Iacoboni, MD, PhD, used fMRI to image the brain activity of college-student ...
lecture CNS
... •epithalamus – consists of the pineal gland and habenular nuclei -pineal gland – part of the endocrine system -secretes the hormone melatonin -increased secretion in dark -promote sleepiness and helps set the circadian rhythms of the body (awake/sleep period) ...
... •epithalamus – consists of the pineal gland and habenular nuclei -pineal gland – part of the endocrine system -secretes the hormone melatonin -increased secretion in dark -promote sleepiness and helps set the circadian rhythms of the body (awake/sleep period) ...
The Nervous System
... axon - the long extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the body of the cell to other neurons. axon terminals - the hair-like ends of the axon cell body - the cell body of the neuron; it contains the nucleus (also called the soma) dendrites - the branching structure of a neuron t ...
... axon - the long extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the body of the cell to other neurons. axon terminals - the hair-like ends of the axon cell body - the cell body of the neuron; it contains the nucleus (also called the soma) dendrites - the branching structure of a neuron t ...
Nervous System Reading from SparkNotes
... transmission are highly specialized cells known as neurons, which are the functional unit of the nervous system. The neuron is an elongated cell that usually consists of three main parts: the dendrites, the cell body, and the axon. The typical neuron contains many dendrites, which have the appearanc ...
... transmission are highly specialized cells known as neurons, which are the functional unit of the nervous system. The neuron is an elongated cell that usually consists of three main parts: the dendrites, the cell body, and the axon. The typical neuron contains many dendrites, which have the appearanc ...
embryo ch 18 and 19 [10-26
... o Marginal layer of each basal plate enlarges and forms crus cerebri – these crura serve as pathways for nerve fibers descending from cerebral cortex to lower centers in pons and spinal cord o Initially alar plates appear as 2 longitudinal elevations separated by shallow midline depression – with fu ...
... o Marginal layer of each basal plate enlarges and forms crus cerebri – these crura serve as pathways for nerve fibers descending from cerebral cortex to lower centers in pons and spinal cord o Initially alar plates appear as 2 longitudinal elevations separated by shallow midline depression – with fu ...
NEUROSCIENCE 2. THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM 2.1
... stand for the cognitive capabilities of the brain. Connecting each of the hemispheres is the corpus callosum as well as several additional commissures. One of the most important parts of the cerebral hemispheres is the cortex, which is made up of gray matter covering the surface of the brain. Functi ...
... stand for the cognitive capabilities of the brain. Connecting each of the hemispheres is the corpus callosum as well as several additional commissures. One of the most important parts of the cerebral hemispheres is the cortex, which is made up of gray matter covering the surface of the brain. Functi ...
the physiological approach
... Na+ channels inactivate (absolute refractory period) – completely unresponsive to a second stimulus Potassium flows out of the axon ...
... Na+ channels inactivate (absolute refractory period) – completely unresponsive to a second stimulus Potassium flows out of the axon ...