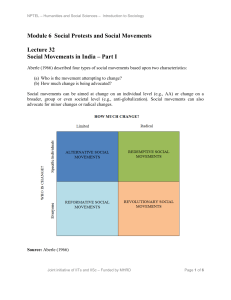
Module 6 Social Protests and Social Movements Lecture 32 Social
... agricultural labourers for higher wages and better working condition. The second type of movements is of the more prosperous peasants, those who produce a considerable surplus within the rural economy. These movements are often in social science literature referred to as „Farmers‟ Movement‟ or „New ...
... agricultural labourers for higher wages and better working condition. The second type of movements is of the more prosperous peasants, those who produce a considerable surplus within the rural economy. These movements are often in social science literature referred to as „Farmers‟ Movement‟ or „New ...
Slide 1
... • Wernicke’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. • Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resultin ...
... • Wernicke’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Wernicke’s area (usually in left temporal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable to understand or produce meaningful language. • Spatial neglect - condition produced by damage to the association areas of the right hemisphere resultin ...
Chapter 5 Gases - LCMR School District
... ADP + Pi cytoplasm A Sodium–potassium cotransporters actively transport three Na+ out of a neuron for every two K+ they pump in. ...
... ADP + Pi cytoplasm A Sodium–potassium cotransporters actively transport three Na+ out of a neuron for every two K+ they pump in. ...
Chapter 5 Gases - Bethel Local Schools
... ADP + Pi cytoplasm A Sodium–potassium cotransporters actively transport three Na+ out of a neuron for every two K+ they pump in. ...
... ADP + Pi cytoplasm A Sodium–potassium cotransporters actively transport three Na+ out of a neuron for every two K+ they pump in. ...
SDL 2- CNS Malformations Neural Tube Defects Failure of a portion
... Radially arranged configuration of medullary veins (caput medusae) separated by normal brain parenchyma Usually supratentorial with a frontal lobe predominance Commonly present with seizures, progressive neurologic deficits and hemorrhage Most common autopsy series (2%); Benign Headache is most comm ...
... Radially arranged configuration of medullary veins (caput medusae) separated by normal brain parenchyma Usually supratentorial with a frontal lobe predominance Commonly present with seizures, progressive neurologic deficits and hemorrhage Most common autopsy series (2%); Benign Headache is most comm ...
Neurons
... potential. During an action potential there is a transitory change in the polarity of the electrical charge across the cell membrane. The membrane then alters its permeability to the charged ions, and the charge across the cell membrane becomes briefly less positive or negative. Action potentials re ...
... potential. During an action potential there is a transitory change in the polarity of the electrical charge across the cell membrane. The membrane then alters its permeability to the charged ions, and the charge across the cell membrane becomes briefly less positive or negative. Action potentials re ...
chapt09answers
... SKIP THIS SECTION!!! Impulse processing: How impulses are processed is dependent upon how neurons are organized in the brain and spinal cord. pools: Neurons within the CNS are organized into neuronal pools with varying numbers of cells. Each pool receives input from afferent nerves and processes the ...
... SKIP THIS SECTION!!! Impulse processing: How impulses are processed is dependent upon how neurons are organized in the brain and spinal cord. pools: Neurons within the CNS are organized into neuronal pools with varying numbers of cells. Each pool receives input from afferent nerves and processes the ...
Skeletal System
... The nervous system is the master controlling and communicating system of the body It is responsible for all behavior Along with the endocrine system it is responsible for regulating and ...
... The nervous system is the master controlling and communicating system of the body It is responsible for all behavior Along with the endocrine system it is responsible for regulating and ...
Slide ()
... Organization of the anterior and posterior pituitary gland. Hypothalamic neurons in the supraoptic (SON) and paraventricular (PVN) nuclei synthesize arginine vasopressin (AVP) or oxytocin (OXY). Most of their axons project directly to the posterior pituitary, from which AVP and OXY are secreted into ...
... Organization of the anterior and posterior pituitary gland. Hypothalamic neurons in the supraoptic (SON) and paraventricular (PVN) nuclei synthesize arginine vasopressin (AVP) or oxytocin (OXY). Most of their axons project directly to the posterior pituitary, from which AVP and OXY are secreted into ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_8_lecture_part_1
... Primary motor cortex involved with the control of voluntary muscles ...
... Primary motor cortex involved with the control of voluntary muscles ...
What are Computational Neuroscience and Neuroinformatics
... system. Central pattern generators are groups of neurons found in vertebrate and invertebrate nervous systems responsible for the generation of specific rhythmic behaviors such as walking, ...
... system. Central pattern generators are groups of neurons found in vertebrate and invertebrate nervous systems responsible for the generation of specific rhythmic behaviors such as walking, ...
Eye research part of a bigger picture (PDF File 1.7 MB)
... accounts for almost half of all legal blindness in Australia. So if we aim to replicate retinal function to treat retinal disorders such as retinitis pigmentosa and macular degeneration, we should have a more complete understanding of how retina functions.’ Bright sunlight is about 10 billion times ...
... accounts for almost half of all legal blindness in Australia. So if we aim to replicate retinal function to treat retinal disorders such as retinitis pigmentosa and macular degeneration, we should have a more complete understanding of how retina functions.’ Bright sunlight is about 10 billion times ...
6-Autonomic nervous system
... in head, thorax & abdomen. 2. Cells located in 2nd, 3rd & 4th sacral segments of spinal cord. Preganglionic axons leave the spinal cord, join corresponding sacral spinal nerves to reach peripheral ganglia in pelvis where they synapse. Postganglionic neurons are cells of peripheral ganglia. Postgangl ...
... in head, thorax & abdomen. 2. Cells located in 2nd, 3rd & 4th sacral segments of spinal cord. Preganglionic axons leave the spinal cord, join corresponding sacral spinal nerves to reach peripheral ganglia in pelvis where they synapse. Postganglionic neurons are cells of peripheral ganglia. Postgangl ...
5-Autonomic nervous system
... in head, thorax & abdomen. 2. Cells located in 2nd, 3rd & 4th sacral segments of spinal cord. Preganglionic axons leave the spinal cord, join corresponding sacral spinal nerves to reach peripheral ganglia in pelvis where they synapse. Postganglionic neurons are cells of peripheral ganglia. Postgangl ...
... in head, thorax & abdomen. 2. Cells located in 2nd, 3rd & 4th sacral segments of spinal cord. Preganglionic axons leave the spinal cord, join corresponding sacral spinal nerves to reach peripheral ganglia in pelvis where they synapse. Postganglionic neurons are cells of peripheral ganglia. Postgangl ...
Neural computations that underlie decisions about sensory stimuli
... light, with some values being more likely than others when light is present (see Box 1). How do you use the value from the detector to decide if the light was present? This problem consists of deciding which hypothesis – light is present (h1) or light is absent (h2) – is most likely to be true given ...
... light, with some values being more likely than others when light is present (see Box 1). How do you use the value from the detector to decide if the light was present? This problem consists of deciding which hypothesis – light is present (h1) or light is absent (h2) – is most likely to be true given ...
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS
... Schematic diagram of the ventrobasal complex in the monkey, indicating the cutaneous somatotopic representation of the body surface on the left. Neurons responsive to stimulation of deep receptors lie in a dorsal shell. Areas representing the head, face and tongue lie in the ventral posteromedial (V ...
... Schematic diagram of the ventrobasal complex in the monkey, indicating the cutaneous somatotopic representation of the body surface on the left. Neurons responsive to stimulation of deep receptors lie in a dorsal shell. Areas representing the head, face and tongue lie in the ventral posteromedial (V ...
UNC-55, an Orphan Nuclear Hormone Receptor, Orchestrates
... modifying the common genetic programs of neurons to create different synaptic specificities. The precisely defined sets of nerve and muscle cells responsible for locomotion in C. elegans allow genetic and cellular manipulations that provide a unique opportunity for investigating the generation of sp ...
... modifying the common genetic programs of neurons to create different synaptic specificities. The precisely defined sets of nerve and muscle cells responsible for locomotion in C. elegans allow genetic and cellular manipulations that provide a unique opportunity for investigating the generation of sp ...
Slide 1
... In response to the sensory pathway, the CNS issues motor commands distributed by the somatic and ...
... In response to the sensory pathway, the CNS issues motor commands distributed by the somatic and ...
Nerves Powerpoint
... – Physical protection – Myelination (more on that later) – Chemical protection – Antimicrobial protection ...
... – Physical protection – Myelination (more on that later) – Chemical protection – Antimicrobial protection ...
Distributed Modular Architectures Linking Basal Ganglia
... Cerebral Cortex: Their Role in Planning and Controlling Action ...
... Cerebral Cortex: Their Role in Planning and Controlling Action ...
11th International Conference Advances in Pneumology Cologne
... microinjection represented fiber populations providing excitatory drive into expiratory neurons at 2 levels (DLH1 - more synaptic connections with lower synaptic strength and DLH2 - less synaptic connections with higher synaptic strength). Our simulations manifested high level of analogy with cough ...
... microinjection represented fiber populations providing excitatory drive into expiratory neurons at 2 levels (DLH1 - more synaptic connections with lower synaptic strength and DLH2 - less synaptic connections with higher synaptic strength). Our simulations manifested high level of analogy with cough ...
Sparse Neural Systems: The Ersatz Brain gets Thin
... See if we can integrate relatively dense local connections with relatively sparse projections to and from other layers to form module assemblies. ...
... See if we can integrate relatively dense local connections with relatively sparse projections to and from other layers to form module assemblies. ...
Neural Development - inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... But there is no vision in the womb. Recent research shows that systematic moving patterns of activity are spontaneously generated prenatally in the retina. A predictable pattern, changing over time, provides excellent training data for tuning the connections between visual maps. ...
... But there is no vision in the womb. Recent research shows that systematic moving patterns of activity are spontaneously generated prenatally in the retina. A predictable pattern, changing over time, provides excellent training data for tuning the connections between visual maps. ...
The role of Pitx3 in survival of midbrain dopaminergic neurons
... The heterogeneity of midbrain dopaminergic (mDA) neurons The mDA system (A8–A10 cell groups) is involved in many brain functions including motor control, reward, emotional and motivated behavior, and is of clinical importance because of its implication in neurological and psychiatric disorders. The ...
... The heterogeneity of midbrain dopaminergic (mDA) neurons The mDA system (A8–A10 cell groups) is involved in many brain functions including motor control, reward, emotional and motivated behavior, and is of clinical importance because of its implication in neurological and psychiatric disorders. The ...