Abstract Browser - The Journal of Neuroscience
... six patients with focal vmPFC lesions, in comparison with forty neurologically intact controls and six brain-damaged controls. There were three computational signals of interest as participants played a fairness game (ultimatum game): sensitivity to the fairness of offers, sensitivity to deviations ...
... six patients with focal vmPFC lesions, in comparison with forty neurologically intact controls and six brain-damaged controls. There were three computational signals of interest as participants played a fairness game (ultimatum game): sensitivity to the fairness of offers, sensitivity to deviations ...
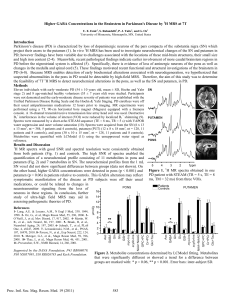
Figure 2. Metabolite concentrations determined by LCModel
... Parkinson’s disease (PD) is characterized by loss of dopaminergic neurons of the pars compacta of the substantia nigra (SN) which project their axons to the putamen (1). In vivo 1H MRS has been used to investigate neurochemical changes of the SN and putamen in PD; however findings have been variable ...
... Parkinson’s disease (PD) is characterized by loss of dopaminergic neurons of the pars compacta of the substantia nigra (SN) which project their axons to the putamen (1). In vivo 1H MRS has been used to investigate neurochemical changes of the SN and putamen in PD; however findings have been variable ...
Physiology - Soran University
... The right hemisphere is associated with 'unconscious' awareness (in the sense it is not linguistically based), perception of faces and patterns, comprehension of body language and social cues, creativity and insight, intuitive reasoning, visual-spatial processing, and holistic comprehension. ...
... The right hemisphere is associated with 'unconscious' awareness (in the sense it is not linguistically based), perception of faces and patterns, comprehension of body language and social cues, creativity and insight, intuitive reasoning, visual-spatial processing, and holistic comprehension. ...
Objectives 38 - U
... - visceral nuclei in brainstem and spinal cord keep hypothalamus updated on internal condition of body - limbic structures like hippocampus, amygdala, and septal nuclei; limbic inputs arrive by way of the fornix (from the hippocampus), the medial forebrain bundle (from septal nuclei); collectively ...
... - visceral nuclei in brainstem and spinal cord keep hypothalamus updated on internal condition of body - limbic structures like hippocampus, amygdala, and septal nuclei; limbic inputs arrive by way of the fornix (from the hippocampus), the medial forebrain bundle (from septal nuclei); collectively ...
The Central Nervous System
... temporal lobe from the fontal/parietal lobes. Regions of the cerebral cortex are associated with particular bodily functions. The frontal lobe tends to be involved with motor and executive function. The temporal lobe is principally involved in audition and olfaction. The parietal lobe is involved in ...
... temporal lobe from the fontal/parietal lobes. Regions of the cerebral cortex are associated with particular bodily functions. The frontal lobe tends to be involved with motor and executive function. The temporal lobe is principally involved in audition and olfaction. The parietal lobe is involved in ...
The Brain and The Nervous System
... Dexterity= Fine motor skill is the coordination of small muscle movements which occur in body parts such as the fingers. ...
... Dexterity= Fine motor skill is the coordination of small muscle movements which occur in body parts such as the fingers. ...
Introduction to ANNs
... and Cajal who received a Nobel Prize in 1906. You can see roundish neurons with their output axons. Some leave the area (those at the bottom which form the ‘optic nerve’) and other axons input into other neurons via their input connections called dendrites. Neuron e receives its input from four othe ...
... and Cajal who received a Nobel Prize in 1906. You can see roundish neurons with their output axons. Some leave the area (those at the bottom which form the ‘optic nerve’) and other axons input into other neurons via their input connections called dendrites. Neuron e receives its input from four othe ...
Project Self-Discovery
... • Second most neuron rich place is your gut (which is called the second brain by some!) • 1 sand grain-sized piece of brain can have 100,000 neurons and 1 MILLION synapses (small space between neurons across which messages are sent) • Types Different kinds for different messages and functions • moto ...
... • Second most neuron rich place is your gut (which is called the second brain by some!) • 1 sand grain-sized piece of brain can have 100,000 neurons and 1 MILLION synapses (small space between neurons across which messages are sent) • Types Different kinds for different messages and functions • moto ...
PDF
... Stay tuned for more information and the launch announcement. Announcing the CereStage 96 channel Headstage This is exciting news for all Plexon OmniPlex® or MAP Data Acquisition System customers using the Utah Array in their research. We have just launched the CereStage 96 channel unity, gain headst ...
... Stay tuned for more information and the launch announcement. Announcing the CereStage 96 channel Headstage This is exciting news for all Plexon OmniPlex® or MAP Data Acquisition System customers using the Utah Array in their research. We have just launched the CereStage 96 channel unity, gain headst ...
Chapter 10: Nervous System I
... W. The nervous system can detect changes in the body, make decisions, and stimulate muscles or glands to respond. X. The three parts all neurons have are cell body, axon, and dendrites. Y. A neuron’s cell body contains granular cytoplasm, mitochondria, lysosomes, a Golgi apparatus, and many microtub ...
... W. The nervous system can detect changes in the body, make decisions, and stimulate muscles or glands to respond. X. The three parts all neurons have are cell body, axon, and dendrites. Y. A neuron’s cell body contains granular cytoplasm, mitochondria, lysosomes, a Golgi apparatus, and many microtub ...
Sensory signals during active versus passive movement
... test passive rather than active sensation. Recent results from several laboratories have, however, yielded major insights into our understanding of how sensory signals are processed during movement. In this review, I consider recent advances in this field, focusing on experiments in the vestibular s ...
... test passive rather than active sensation. Recent results from several laboratories have, however, yielded major insights into our understanding of how sensory signals are processed during movement. In this review, I consider recent advances in this field, focusing on experiments in the vestibular s ...
Abstract Browser - The Journal of Neuroscience
... different sleep stages. The functions of these activity patterns are not fully understood, but they might contribute to memory consolidation. Indeed, different types of memory appear to be consolidated during different sleep stages. Evidence suggests, for example, that slow-wave sleep (SWS) is parti ...
... different sleep stages. The functions of these activity patterns are not fully understood, but they might contribute to memory consolidation. Indeed, different types of memory appear to be consolidated during different sleep stages. Evidence suggests, for example, that slow-wave sleep (SWS) is parti ...
Lecture Cranial Nerves 1
... Gross Anatomy: Cranial Nerve Introduction (Grays, pages 807; 848-854) ...
... Gross Anatomy: Cranial Nerve Introduction (Grays, pages 807; 848-854) ...
Term - k20 learn
... One of the organs of the nervous system, the body’s central “computer” that receives, integrates, and sends messages. ...
... One of the organs of the nervous system, the body’s central “computer” that receives, integrates, and sends messages. ...
the human brain
... these changes help to fine-tune brain activity in response to immediate events, while others rewire the brain in the long term, which is thought to explain how memories are stored. Many neuromodulators act on just a few neurons, but some can penetrate through large swathes of brain tissue creating s ...
... these changes help to fine-tune brain activity in response to immediate events, while others rewire the brain in the long term, which is thought to explain how memories are stored. Many neuromodulators act on just a few neurons, but some can penetrate through large swathes of brain tissue creating s ...
Nervous System:
... Ion pumps in the cell membranes of neurons release three positively charged sodium ions, while taking in only two positively charged potassium ions which creates a negative charge inside the cell. The space inside the neuron now has a resting potential, which is a kind of membrane potential, because ...
... Ion pumps in the cell membranes of neurons release three positively charged sodium ions, while taking in only two positively charged potassium ions which creates a negative charge inside the cell. The space inside the neuron now has a resting potential, which is a kind of membrane potential, because ...
Nervous system Lab - Sonoma Valley High School
... Name the system that responds quickly and the system that responds slowly to the body’s needs. Name the three basic functions of the nervous system. Name the two types of cells found in the nervous system. Contrast neurons and neuroglial cells as to size, numbers, and types. Identify and give a func ...
... Name the system that responds quickly and the system that responds slowly to the body’s needs. Name the three basic functions of the nervous system. Name the two types of cells found in the nervous system. Contrast neurons and neuroglial cells as to size, numbers, and types. Identify and give a func ...
Towards an Empirically Grounded Predictive Coding Account of
... studies should consider such experimental designs to directly ground the theoretical constructs of the predictive coding account. One question that remains unanswered is where the prior information is generated in the predictive coding account of action understanding. Maranesi et al. (2014) suggest ...
... studies should consider such experimental designs to directly ground the theoretical constructs of the predictive coding account. One question that remains unanswered is where the prior information is generated in the predictive coding account of action understanding. Maranesi et al. (2014) suggest ...
Dissecting appetite
... the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Janelia Farm campus in Ashburn, Virginia, has been studying the AgRP and POMC neurons, which promote and suppress eating, respectively. Using optogenetics, he showed that activating only 800 AgRP neurons gave the mice a voracious appetite. “What fascinates me,” ...
... the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Janelia Farm campus in Ashburn, Virginia, has been studying the AgRP and POMC neurons, which promote and suppress eating, respectively. Using optogenetics, he showed that activating only 800 AgRP neurons gave the mice a voracious appetite. “What fascinates me,” ...
Character Recognition using Spiking Neural Networks
... It is well known that biological neurons use pulses or spikes to encode information. Neurological research also shows that the biological neurons store information in the timing of spikes. Spiking neural networks belong to the third generation of neural networks and like their biological counterpart ...
... It is well known that biological neurons use pulses or spikes to encode information. Neurological research also shows that the biological neurons store information in the timing of spikes. Spiking neural networks belong to the third generation of neural networks and like their biological counterpart ...
Vestibular Signals of Posterior Parietal Cortex Neurons during
... presence of activity only during active movement. Furthermore, in approximately one-third of the neurons, a change of vestibular on-direction depending on active versus passive movement mode was observed, that is, type I neurons became type II neurons, etc. We suggest that the role of parietal vesti ...
... presence of activity only during active movement. Furthermore, in approximately one-third of the neurons, a change of vestibular on-direction depending on active versus passive movement mode was observed, that is, type I neurons became type II neurons, etc. We suggest that the role of parietal vesti ...
spinal cord - (canvas.brown.edu).
... Origin: Dorsal root ganglia Ultimate target: somatosensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) Primary afferents ascend in DORSAL COLUMNS SYNAPSE: DORSAL COLUMN NUCLEI of caudal medulla Decussation of secondary fibers Ascent of secondary fibers as MEDIAL LEMNISCUS Synapse in VPL nucleus of thalamus Projectio ...
... Origin: Dorsal root ganglia Ultimate target: somatosensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) Primary afferents ascend in DORSAL COLUMNS SYNAPSE: DORSAL COLUMN NUCLEI of caudal medulla Decussation of secondary fibers Ascent of secondary fibers as MEDIAL LEMNISCUS Synapse in VPL nucleus of thalamus Projectio ...
The Neuron
... Action Potential = electrical charge that travels down the axon when a message is sent Group of axons bundled together like electrical cable is called a nerve Myelin sheath Fatty covering that surrounds axon Not all axons are covered Provides insulation Improves efficiency Continues to ...
... Action Potential = electrical charge that travels down the axon when a message is sent Group of axons bundled together like electrical cable is called a nerve Myelin sheath Fatty covering that surrounds axon Not all axons are covered Provides insulation Improves efficiency Continues to ...
Dispatch Vision: How to Train Visual Cortex to Predict Reward Time
... that may even contribute to visual awareness [7,10]. A simple, yet dramatic example for how behavioral state impacts V1 is the observation that when mice run, the stimulus-evoked firing of V1 neurons can double while retaining stimulus selectivity [11,12,13]. In fact, primary sensory cortices have d ...
... that may even contribute to visual awareness [7,10]. A simple, yet dramatic example for how behavioral state impacts V1 is the observation that when mice run, the stimulus-evoked firing of V1 neurons can double while retaining stimulus selectivity [11,12,13]. In fact, primary sensory cortices have d ...