Fly MARCM and mouse MADM: Genetic methods of labeling and
... projection neurons. (A) Schematic of MARCM. After FLP/FRT site-specific mitotic recombination (cross between triangles), a heterozygous mother cell may give rise to two daughter cells, in which the chromosome arms distal to the FRT recombination site (triangle) become homozygous. GAL80 is ubiquitous ...
... projection neurons. (A) Schematic of MARCM. After FLP/FRT site-specific mitotic recombination (cross between triangles), a heterozygous mother cell may give rise to two daughter cells, in which the chromosome arms distal to the FRT recombination site (triangle) become homozygous. GAL80 is ubiquitous ...
Article Link - Cortical Systems and Behavior Laboratory
... units exhibited significant changes in firing rate during presentation of the light stimulus compared with the 100 ms preceding photostimulation (signed-rank test, P ⬍ 0.05), whereas 16 were not affected by the same stimulus (Fig. 3). A total of 24 neurons from this population exhibited significant ...
... units exhibited significant changes in firing rate during presentation of the light stimulus compared with the 100 ms preceding photostimulation (signed-rank test, P ⬍ 0.05), whereas 16 were not affected by the same stimulus (Fig. 3). A total of 24 neurons from this population exhibited significant ...
12 The Central Nervous System Part A Central Nervous System
... Commissures – connect corresponding gray areas of the two hemispheres Association fibers – connect different parts of the same hemisphere Projection fibers – enter the hemispheres from lower brain or cord centers Fiber Tracts in White Matter Fiber Tracts in White Matter Basal Nuclei Masses of gray m ...
... Commissures – connect corresponding gray areas of the two hemispheres Association fibers – connect different parts of the same hemisphere Projection fibers – enter the hemispheres from lower brain or cord centers Fiber Tracts in White Matter Fiber Tracts in White Matter Basal Nuclei Masses of gray m ...
Test.
... • First attempt in 1956. • Excitement and hype. Stevie Wonder. • Currently – cautious long term optimism. • “To impart a coarse level of vision that would expand a blind person’s autonomy is an ambitious but plausible goal”. John Wyatt (MIT). ...
... • First attempt in 1956. • Excitement and hype. Stevie Wonder. • Currently – cautious long term optimism. • “To impart a coarse level of vision that would expand a blind person’s autonomy is an ambitious but plausible goal”. John Wyatt (MIT). ...
November 2000 Volume 3 Number Supp pp 1184
... and physiologically in vitro35-37, and the excitatory interactions between cortical neurons during the delay phases of working memory tasks have been probed by simultaneous recordings from multiple neurons38. These data do not conclusively show, however, whether recurrent excitation is sufficient to ...
... and physiologically in vitro35-37, and the excitatory interactions between cortical neurons during the delay phases of working memory tasks have been probed by simultaneous recordings from multiple neurons38. These data do not conclusively show, however, whether recurrent excitation is sufficient to ...
Central Nervous System
... - has four lobes that receive and store information and are responsible for giving signals for voluntary movement. ...
... - has four lobes that receive and store information and are responsible for giving signals for voluntary movement. ...
Motor Control - Reza Shadmehr
... inal system to CPGs and spinal motor pools adjust posture and movement based primarily on vestibular and proprioceptive inputs. However, cortical and other higher order inputs supply the information needed for dynamic motor adjustments that allow people to step over and around visible obstacles. b. ...
... inal system to CPGs and spinal motor pools adjust posture and movement based primarily on vestibular and proprioceptive inputs. However, cortical and other higher order inputs supply the information needed for dynamic motor adjustments that allow people to step over and around visible obstacles. b. ...
Slide 1
... • Spinal cord: may involve different sensory tracts, loss of sensation usually begins one or two segments below the level of the lesion because of branching of the afferent fibers in the spinal cord • Brainstem: may have mixed ipsilateral/contralateral sensory loss of the body and the face • Cortica ...
... • Spinal cord: may involve different sensory tracts, loss of sensation usually begins one or two segments below the level of the lesion because of branching of the afferent fibers in the spinal cord • Brainstem: may have mixed ipsilateral/contralateral sensory loss of the body and the face • Cortica ...
Quiz Answers
... sensory nerves, the ability of the neurons to transmit sensory information will be inhibited. This loss of sensory information would be experienced as a “numbness” in areas exposed to the toxin. 15. Paralysis is a term used to describe the loss of function of muscle. If tetrodotoxin ’s effect is on ...
... sensory nerves, the ability of the neurons to transmit sensory information will be inhibited. This loss of sensory information would be experienced as a “numbness” in areas exposed to the toxin. 15. Paralysis is a term used to describe the loss of function of muscle. If tetrodotoxin ’s effect is on ...
Contraction Properties of VLSI Cooperative Competitive Neural
... responses qualitatively similar to standard linear I&F neurons [20]. A steady state solution is easily computable for a network of linear threshold units [5, 21]: it is a fixed point in state space, i.e. a set of activities for the neurons. In a VLSI network of I&F neurons the steady state will be m ...
... responses qualitatively similar to standard linear I&F neurons [20]. A steady state solution is easily computable for a network of linear threshold units [5, 21]: it is a fixed point in state space, i.e. a set of activities for the neurons. In a VLSI network of I&F neurons the steady state will be m ...
Modeling and interpretation of extracellular potentials
... High-frequency band (>~ 500 Hz): Multi-unit activity (MUA), measures spikes in neurons surrounding electron tip ...
... High-frequency band (>~ 500 Hz): Multi-unit activity (MUA), measures spikes in neurons surrounding electron tip ...
Structure and Function of Neurons - Assets
... located in the striatum in large numbers and have a highly ramified dendritic arborization that radiates in all directions and, of course, is densely covered with spines, which receive input from cortex, thalamus, and substantia nigra. Spiny neurons have long axons that either leave the striatum or c ...
... located in the striatum in large numbers and have a highly ramified dendritic arborization that radiates in all directions and, of course, is densely covered with spines, which receive input from cortex, thalamus, and substantia nigra. Spiny neurons have long axons that either leave the striatum or c ...
Practice Quiz - Kingsborough Community College
... 22. The binding of NE to alpha adrenergic receptors in peripheral blood vessels causes _______ and to beta adrenergic receptors in the heart's coronary blood vessels causes _______. a. vasodilation; vasoconstriction b. vasoconstriction; vasodilation c. no effect; vasoconstriction d. no effect; vaso ...
... 22. The binding of NE to alpha adrenergic receptors in peripheral blood vessels causes _______ and to beta adrenergic receptors in the heart's coronary blood vessels causes _______. a. vasodilation; vasoconstriction b. vasoconstriction; vasodilation c. no effect; vasoconstriction d. no effect; vaso ...
m5zn_aeb235b83927ffb
... sheaths, the signals would be over 10 times slower. The debilitating autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis (MS) demonstrates the importance of myelin. MS leads to a gradual destruction of myelin sheaths by the individual’s own immune system. The result is a progressive loss of signal conduction, m ...
... sheaths, the signals would be over 10 times slower. The debilitating autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis (MS) demonstrates the importance of myelin. MS leads to a gradual destruction of myelin sheaths by the individual’s own immune system. The result is a progressive loss of signal conduction, m ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... axon, by which process they travel faster than they would otherwise. This process is outlined as the charge will passively spread to the next node of Ranvier to depolarize it to threshold which will then trigger an action potential at the next node. ...
... axon, by which process they travel faster than they would otherwise. This process is outlined as the charge will passively spread to the next node of Ranvier to depolarize it to threshold which will then trigger an action potential at the next node. ...
Dissociation of Mnemonic Coding and Other Functional Neuronal
... its hands and legs and to put pieces of food into its mouth, after which also chewing and licking could be observed. If the neuron responded to more than one type of sensory stimulation it was classified as polysensory. If the neuron did not respond to any of the afore mentioned stimuli it was class ...
... its hands and legs and to put pieces of food into its mouth, after which also chewing and licking could be observed. If the neuron responded to more than one type of sensory stimulation it was classified as polysensory. If the neuron did not respond to any of the afore mentioned stimuli it was class ...
Coding and learning of behavioral sequences
... decreases [24]. Although the onset of firing of different place cells is nicely ordered along the phase axis, the most activated place cells fire longer spike bursts than those that are less excited. This could have a strong influence on synaptic plasticity [25,26]. Spike train adaptation might, how ...
... decreases [24]. Although the onset of firing of different place cells is nicely ordered along the phase axis, the most activated place cells fire longer spike bursts than those that are less excited. This could have a strong influence on synaptic plasticity [25,26]. Spike train adaptation might, how ...
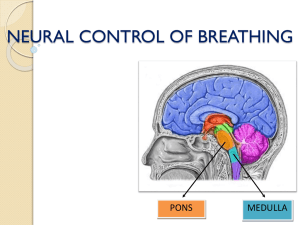
Neural Control of Breathing (By Mohit Chhabra)
... The VRG is responsible for motor control of inspiratory and expiratory muscles during exercise. They are especially important in providing the powerful expiratory signals to the abdominal muscles ...
... The VRG is responsible for motor control of inspiratory and expiratory muscles during exercise. They are especially important in providing the powerful expiratory signals to the abdominal muscles ...
Activity-Dependent Regulation of Potassium Currents in an
... changes in conductances reported here suggest that the conductance densities expressed by each neuron will depend on its history, with an “integration time constant” of several hours. Variability in measured conductances may thus reflect the variability in the activity of the STG before the recordin ...
... changes in conductances reported here suggest that the conductance densities expressed by each neuron will depend on its history, with an “integration time constant” of several hours. Variability in measured conductances may thus reflect the variability in the activity of the STG before the recordin ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... hypothalamus. These cells synapse on inhibitory interneurons (Fig. 9, large red) which project their axons to the medullary RF and the dorsomedial nucleus in the tuberal zone of the hypothalamus. Both the preoptic inhibitory neurons and the dorsomedial nucleus neurons project axons to thermoregulato ...
... hypothalamus. These cells synapse on inhibitory interneurons (Fig. 9, large red) which project their axons to the medullary RF and the dorsomedial nucleus in the tuberal zone of the hypothalamus. Both the preoptic inhibitory neurons and the dorsomedial nucleus neurons project axons to thermoregulato ...
Crapse (2008) Corollary discharge across the animal kingdom
... that is caused by external agents (for example, when something hits you). It is critical for nervous systems to be able to differentiate between these two scenarios. A ubiquitous strategy is to route copies of movement commands to sensory structures. These signals, which are referred to as corollary ...
... that is caused by external agents (for example, when something hits you). It is critical for nervous systems to be able to differentiate between these two scenarios. A ubiquitous strategy is to route copies of movement commands to sensory structures. These signals, which are referred to as corollary ...
Hafiz Noordin Term Paper - Engineering Computing Facility
... Neurons in each of the topographic maps interact in two ways: excitatory and inhibitory. In addition to interactions between maps, there is also a certain amount of lateral interaction between neurons of the same map. This further adds to the complexity of modeling neurons in the cortical map, as th ...
... Neurons in each of the topographic maps interact in two ways: excitatory and inhibitory. In addition to interactions between maps, there is also a certain amount of lateral interaction between neurons of the same map. This further adds to the complexity of modeling neurons in the cortical map, as th ...
What is C. elegans? What are its navigational strategies?
... So dgk-3 is in the right neuron and has known ties to sensory signal transduction.. ...
... So dgk-3 is in the right neuron and has known ties to sensory signal transduction.. ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Lecture Outline Adapted from Martini
... Sensory and Motor Tracts Naming the tracts If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract delivering information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum (in this case) If the tract name ends with “spinal” (as in vestibulospinal), the tract is a motor tract ...
... Sensory and Motor Tracts Naming the tracts If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract delivering information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum (in this case) If the tract name ends with “spinal” (as in vestibulospinal), the tract is a motor tract ...
Neurophysiological foundations of sleep, arousal, awareness and
... and ponto-geniculo-occipital waves can registered following arousal (activation of these structures). This phase is characterised by inhibition of motor neurons (activation of glycinergic intermediate neurons of the spinal cord, which inhibit α motoneurons), activation of the limbic system, increase ...
... and ponto-geniculo-occipital waves can registered following arousal (activation of these structures). This phase is characterised by inhibition of motor neurons (activation of glycinergic intermediate neurons of the spinal cord, which inhibit α motoneurons), activation of the limbic system, increase ...