Parasympathetic division
... The parasympathetic division includes visceral motor nuclei in the brain stem associated with four cranial nerves (III, VII, IX, and X). The ganglionic neurons are situated in intramural ganglia or in ganglia closely associated with their target organs. The parasympathetic division innervates ...
... The parasympathetic division includes visceral motor nuclei in the brain stem associated with four cranial nerves (III, VII, IX, and X). The ganglionic neurons are situated in intramural ganglia or in ganglia closely associated with their target organs. The parasympathetic division innervates ...
• Cutis,integument • External covering • Skin+its appendages
... • Types of hair vellus, terminal, club • Phases of growth— anagen, catagen and ...
... • Types of hair vellus, terminal, club • Phases of growth— anagen, catagen and ...
Sensory Motor Approaches with People with Mental Illness Week 5
... – Impact of auditory and visual sensations make the following possible: • Speech and Language: begins with primary level sensory systems and builds on these • Eye-hand Coordination: begins with primary level sensory systems and builds on these with the visual system directing the hand • Visual Perce ...
... – Impact of auditory and visual sensations make the following possible: • Speech and Language: begins with primary level sensory systems and builds on these • Eye-hand Coordination: begins with primary level sensory systems and builds on these with the visual system directing the hand • Visual Perce ...
Spinal Cord - Study Windsor
... 1) a sense of position from the vestibular system, 2) awareness of the position and status of muscles and joints by conscious proprioception and 3) visual input regarding our position. Closing the eyes has only slight effect on the normal individual's stance since the vestibular and conscious pr ...
... 1) a sense of position from the vestibular system, 2) awareness of the position and status of muscles and joints by conscious proprioception and 3) visual input regarding our position. Closing the eyes has only slight effect on the normal individual's stance since the vestibular and conscious pr ...
Questions for entire chapter.
... What is unusual about the vascular arrangement in the kidneys? What and where are the components of the juxtaglomerular apparatus? Which cells secrete renin? What three factors stimulate renin secretion? In what ways does the composition of the glomerular filtrate differ from plasma? Approximately w ...
... What is unusual about the vascular arrangement in the kidneys? What and where are the components of the juxtaglomerular apparatus? Which cells secrete renin? What three factors stimulate renin secretion? In what ways does the composition of the glomerular filtrate differ from plasma? Approximately w ...
Part 1: Multiple choice
... 4. The patellar tendon (knee-jerk) reflex is A. mediated by Golgi tendon organs B. a monosynaptic reflex arc mediated by Ia afferents <––– C. a polysynaptic reflex arc that integrates the input from groups Ia, Ib, and II afferents D. mediated by collaterals of somatosensory afferents E. a volitional ...
... 4. The patellar tendon (knee-jerk) reflex is A. mediated by Golgi tendon organs B. a monosynaptic reflex arc mediated by Ia afferents <––– C. a polysynaptic reflex arc that integrates the input from groups Ia, Ib, and II afferents D. mediated by collaterals of somatosensory afferents E. a volitional ...
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience
... a. Anatomy. We know a lot about what is where. But be careful about labels: neurons in motor cortex sometimes respond to color. Connectivity. We know (more or less) which area is connected to which. We don’t know the wiring diagram at the microscopic level. But we might in a few decades! wij ...
... a. Anatomy. We know a lot about what is where. But be careful about labels: neurons in motor cortex sometimes respond to color. Connectivity. We know (more or less) which area is connected to which. We don’t know the wiring diagram at the microscopic level. But we might in a few decades! wij ...
Polarization theory of motivations, emotions and
... even if the concept of FS is used on the level of systems of organs as qualitative description of their functioning, it practically never happens on the cellular level. ...
... even if the concept of FS is used on the level of systems of organs as qualitative description of their functioning, it practically never happens on the cellular level. ...
Area MST has been thought be involved in heading perception not
... perception of our own movement through space (heading). However, accurate judgments of heading often require integration of visual and nonvisual cues, including vestibular, kinesthetic, and eye movement signals. This sensory integration is complicated by the fact that signals from different modaliti ...
... perception of our own movement through space (heading). However, accurate judgments of heading often require integration of visual and nonvisual cues, including vestibular, kinesthetic, and eye movement signals. This sensory integration is complicated by the fact that signals from different modaliti ...
Osteo-genesis
... • It is part of motor section of Visceral PNS. It is exclusively the motor system controlling the activity of cardiac muscle, smooth muscles and glands. • It has two components. Sympathetic System and Para-Sympathetic System. Sympathetic system is activated during fight, flight or fright. Parasympat ...
... • It is part of motor section of Visceral PNS. It is exclusively the motor system controlling the activity of cardiac muscle, smooth muscles and glands. • It has two components. Sympathetic System and Para-Sympathetic System. Sympathetic system is activated during fight, flight or fright. Parasympat ...
Slide 1 - Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit
... a. Anatomy. We know a lot about what is where. But be careful about labels: neurons in motor cortex sometimes respond to color. Connectivity. We know (more or less) which area is connected to which. We don’t know the wiring diagram at the microscopic level. But we might in a few decades! wij ...
... a. Anatomy. We know a lot about what is where. But be careful about labels: neurons in motor cortex sometimes respond to color. Connectivity. We know (more or less) which area is connected to which. We don’t know the wiring diagram at the microscopic level. But we might in a few decades! wij ...
NEUROTRANSMISSION
... Corty says, “The Junior Scientists solved the last one, so this is up to you. Your mission, should you choose to accept it, is learning about neurotransmission. It’s the process that takes information to and from the brain.” Latisha and Jay look at each other confused and a little concerned. Latisha ...
... Corty says, “The Junior Scientists solved the last one, so this is up to you. Your mission, should you choose to accept it, is learning about neurotransmission. It’s the process that takes information to and from the brain.” Latisha and Jay look at each other confused and a little concerned. Latisha ...
The Role of Voltage Gated Sodium Channels 1
... et al 2001). This means although VGSC 1.9 does not initiate a depolarising upswing of an action potential it does play a role in raising the resting membrane excitability and thus reducing the activation threshold of the nociceptors, which they have been shown to localise. This again suggests a role ...
... et al 2001). This means although VGSC 1.9 does not initiate a depolarising upswing of an action potential it does play a role in raising the resting membrane excitability and thus reducing the activation threshold of the nociceptors, which they have been shown to localise. This again suggests a role ...
Synaptic Responses of Cortical Pyramidal Neurons to Light
... text. Geniculocorticalafferentscontactboth GABAergicnon-pyramidalcells(la) that providefeed-forwardinhibition of pyramidalcells(2) and pyramidalcell apicaldendrites(lb). Therearealsopathwaysfor recurrentinhibition (3), and reciprocalexcitation(4). they form inhibitory terminals onto the somata and p ...
... text. Geniculocorticalafferentscontactboth GABAergicnon-pyramidalcells(la) that providefeed-forwardinhibition of pyramidalcells(2) and pyramidalcell apicaldendrites(lb). Therearealsopathwaysfor recurrentinhibition (3), and reciprocalexcitation(4). they form inhibitory terminals onto the somata and p ...
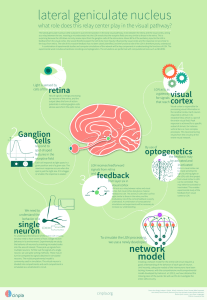
lgn - cinpla
... The lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) is placed in a prominent position in the early visual pathway. It sits between the retina and the visual cortex, acting as a relay between the two. Inserting a microelectrode into the LGN reveals that the receptive fields are very similar to those in the retina. ...
... The lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) is placed in a prominent position in the early visual pathway. It sits between the retina and the visual cortex, acting as a relay between the two. Inserting a microelectrode into the LGN reveals that the receptive fields are very similar to those in the retina. ...
Neurologic Assessment
... Oculomotor response (Cranial nerve III) Size, equality, and roundness of pupils assessed Size measured in millimeters Evaluated for symmetry in size and response to light stimulus Brisk, sluggish, non-reactive Consensual reaction of opposite pupil at same time ...
... Oculomotor response (Cranial nerve III) Size, equality, and roundness of pupils assessed Size measured in millimeters Evaluated for symmetry in size and response to light stimulus Brisk, sluggish, non-reactive Consensual reaction of opposite pupil at same time ...
Outline 10
... o Blood is of critical importance to the brain, but blood is also a source of bacterial toxins and other agents that can _____________ brain tissue o The blood-brain barrier strictly regulates which substances get from the bloodstream into the tissue fluid of the brain o Anything passing from the bl ...
... o Blood is of critical importance to the brain, but blood is also a source of bacterial toxins and other agents that can _____________ brain tissue o The blood-brain barrier strictly regulates which substances get from the bloodstream into the tissue fluid of the brain o Anything passing from the bl ...
Use of rabies virus as a transneuronal tracer of neuronal
... Rabies virus does not spread within the muscle: uptake occurs only at the site of inoculation = importance of complete wound infiltration with rabies antibodies as soon as possible, to prevent virus entry! ...
... Rabies virus does not spread within the muscle: uptake occurs only at the site of inoculation = importance of complete wound infiltration with rabies antibodies as soon as possible, to prevent virus entry! ...
Exercise 5: Synaptic Integration - הפקולטה למדעי הבריאות
... Why is the voltage change in the initial segment so steep? ...
... Why is the voltage change in the initial segment so steep? ...
anatomy and physiology honors
... thick and thin skin C. Dermis components and composition. 1. Sweat glands 2. Sebaceous glands 3. Hair follicles 4. Sensory receptors 5. Fibrous make-up D. Hypodermis composition ...
... thick and thin skin C. Dermis components and composition. 1. Sweat glands 2. Sebaceous glands 3. Hair follicles 4. Sensory receptors 5. Fibrous make-up D. Hypodermis composition ...
Lecture 16
... Leaky integrate and fire neurons Encode each individual spike Time is represented exactly Each spike has an associated time The timing of recent incoming spikes determines whether a neuron will fire • Computationally expensive • Can we do almost as well without encoding every single spike? ...
... Leaky integrate and fire neurons Encode each individual spike Time is represented exactly Each spike has an associated time The timing of recent incoming spikes determines whether a neuron will fire • Computationally expensive • Can we do almost as well without encoding every single spike? ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.