drug elimination ii
... duodenum via common bile duct – excreted into the feces or may be reabsorbed and become systemtically available. This circle is called enterohepatic circulation • Drugs – glucuronide conjugate – hydrolyzed in the gut back to the parent drug by βglucuronidase enzyme present in the intestinal bacteria ...
... duodenum via common bile duct – excreted into the feces or may be reabsorbed and become systemtically available. This circle is called enterohepatic circulation • Drugs – glucuronide conjugate – hydrolyzed in the gut back to the parent drug by βglucuronidase enzyme present in the intestinal bacteria ...
Pharmacogenomics and Personalized Medicine
... Genetic Inheritance: The appearance of deleterious mutations during evolution tend to NOT be inherited for obvious reasons (those that affect growth, reproduction and viability). Our modern existence is the result of millions of years of tolerated (and occasionally beneficial) changes in our genome, ...
... Genetic Inheritance: The appearance of deleterious mutations during evolution tend to NOT be inherited for obvious reasons (those that affect growth, reproduction and viability). Our modern existence is the result of millions of years of tolerated (and occasionally beneficial) changes in our genome, ...
Legislative Advocacy: The Safety of Over-the
... Data on age-specific therapeutic data using modern standards for safety and efficacy that are applicable to children not just adults. ...
... Data on age-specific therapeutic data using modern standards for safety and efficacy that are applicable to children not just adults. ...
Introduction To Pharmacology
... C. Elimination of Drugs. The rate of elimination (disappearance of active drug molecules from the bloodstream or body) is almost always related to termination of pharmacodynamic effect. Therefore, knowledge of plasma concentrations of a drug is important in describing the intensity and duration of a ...
... C. Elimination of Drugs. The rate of elimination (disappearance of active drug molecules from the bloodstream or body) is almost always related to termination of pharmacodynamic effect. Therefore, knowledge of plasma concentrations of a drug is important in describing the intensity and duration of a ...
File
... The manufacture of some drugs results in the formation of a racemic mixture. Explain why it is often preferable to use a method which does not form a racemic mixture, giving one example of such a drug and its effects. ...
... The manufacture of some drugs results in the formation of a racemic mixture. Explain why it is often preferable to use a method which does not form a racemic mixture, giving one example of such a drug and its effects. ...
Introduction-1
... and unintended and that occurs at dose used in man for prophylaxis, diagnosis or therapy of a disease, or for the modification of physiological function”. ...
... and unintended and that occurs at dose used in man for prophylaxis, diagnosis or therapy of a disease, or for the modification of physiological function”. ...
Discussion Continuum 1: Who pays to develop drugs? Introduction
... Once a compound has passed pre-clinical tests (see Info Card A), all the information is sent to the drug regulatory agencies (in each country or in geographical regions), so that they may approve them for carefully controlled tests in humans. Phase I: Tests on healthy volunteers Once approved, a pre ...
... Once a compound has passed pre-clinical tests (see Info Card A), all the information is sent to the drug regulatory agencies (in each country or in geographical regions), so that they may approve them for carefully controlled tests in humans. Phase I: Tests on healthy volunteers Once approved, a pre ...
DNA Day Project 1) Definitions: Drugs
... processes: “translation” and “transcription”.- Transcription (Information stored in RNA and information to make protein).Translation- (starts with ribosomes that reads sequence of mRNA, building blocks (codon) and another RNA (tRNA) assembles amino acids and proteins at the same time. In a given g ...
... processes: “translation” and “transcription”.- Transcription (Information stored in RNA and information to make protein).Translation- (starts with ribosomes that reads sequence of mRNA, building blocks (codon) and another RNA (tRNA) assembles amino acids and proteins at the same time. In a given g ...
Concepts of Pharmacology - Half Life Calculation
... represent the time required for a drug to reach half of its initial concentration after administration • This is because in a single-compartment model elimination is the only process that can alter drug concentration • Intercompartmental distribution cannot occur because there are no other compartme ...
... represent the time required for a drug to reach half of its initial concentration after administration • This is because in a single-compartment model elimination is the only process that can alter drug concentration • Intercompartmental distribution cannot occur because there are no other compartme ...
Concepts of Pharmacology - Half Life Calculation -
... represent the time required for a drug to reach half of its initial concentration after administration • This is because in a single-compartment model elimination is the only process that can alter drug concentration • Intercompartmental distribution cannot occur because there are no other compartme ...
... represent the time required for a drug to reach half of its initial concentration after administration • This is because in a single-compartment model elimination is the only process that can alter drug concentration • Intercompartmental distribution cannot occur because there are no other compartme ...
Medicinal Plants
... • it suppresses prostaglandins and thromboxanes, reducing pain, inflammation and fever • it delays cataract formation However, in children aspirin can interact with chicken pox, leading to a serious disease – Reyes syndrome. The advice is to use acetaminophen (Tylenol) for kids. ...
... • it suppresses prostaglandins and thromboxanes, reducing pain, inflammation and fever • it delays cataract formation However, in children aspirin can interact with chicken pox, leading to a serious disease – Reyes syndrome. The advice is to use acetaminophen (Tylenol) for kids. ...
THE RATIONAL USE OF ANTIDEPRESSANTS COMBINED WITH
... of serotonin reuptake inhibitor plus BDZ; Prolonged use of combined therapy: over 50% of patients have used it for more than one year; Overuse of BDZ exposes patients to dependence, tolerance and fractures; Monotherapy favors the rational use of the medicine better than combined therapy; ...
... of serotonin reuptake inhibitor plus BDZ; Prolonged use of combined therapy: over 50% of patients have used it for more than one year; Overuse of BDZ exposes patients to dependence, tolerance and fractures; Monotherapy favors the rational use of the medicine better than combined therapy; ...
Drug and Chem-informatics Databases - BIDD
... Drug ADME Associated Protein Database (http://bidd.nus.edu.sg/group/admeap/admeap.asp) – A database for facilitating the search for drug Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion associated proteins. It contains information about known drug ADME associated proteins, functions, similarities, su ...
... Drug ADME Associated Protein Database (http://bidd.nus.edu.sg/group/admeap/admeap.asp) – A database for facilitating the search for drug Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion associated proteins. It contains information about known drug ADME associated proteins, functions, similarities, su ...
WebQuest: Drugs, and their effects on the body! Introduction: A drug
... people that are addicted to a drug will build up a tolerance to the drug as the body becomes less and less responsive, requiring more and more of the drug to achieve the desired results. There are actually two type of addiction: ...
... people that are addicted to a drug will build up a tolerance to the drug as the body becomes less and less responsive, requiring more and more of the drug to achieve the desired results. There are actually two type of addiction: ...
View PDF - e-Science Central
... varies in thickness and therefore the matrix dissolves or erodes. The concentration at that chemical compound chains is thought-about disentangled was incontestable to correspond to associate degree abrupt modification within the physics properties of the gel [32]. Showed a relationship between phys ...
... varies in thickness and therefore the matrix dissolves or erodes. The concentration at that chemical compound chains is thought-about disentangled was incontestable to correspond to associate degree abrupt modification within the physics properties of the gel [32]. Showed a relationship between phys ...
NEWER ANTIEPLEPTICS CENTRALLY ACTING MUSCLE
... Acute side effects are mild, mainly nausea, irritability and insomnia, but it occasionally causes severe reactions resulting in aplastic anaemia or hepatitis. For this reason, its recommended use is limited to a form of intractable epilepsy in children (LennoxGastaut syndrome) that is unresponsive t ...
... Acute side effects are mild, mainly nausea, irritability and insomnia, but it occasionally causes severe reactions resulting in aplastic anaemia or hepatitis. For this reason, its recommended use is limited to a form of intractable epilepsy in children (LennoxGastaut syndrome) that is unresponsive t ...
Automation of virtual screening process using the Pipeline Pilot
... Prepare ligands for use in other applications, in particular those that require a 3D coordinates and biological ionization and tautomerization states. When studying receptor-ligand interactions and other areas, it is important to correctly prepare the ligands. Different protonation states, isomers a ...
... Prepare ligands for use in other applications, in particular those that require a 3D coordinates and biological ionization and tautomerization states. When studying receptor-ligand interactions and other areas, it is important to correctly prepare the ligands. Different protonation states, isomers a ...
Gibbs sampler
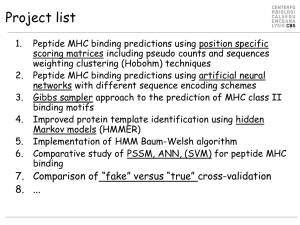
... Peptide MHC binding predictions using position specific scoring matrices including pseudo counts and sequences weighting clustering (Hobohm) techniques Peptide MHC binding predictions using artificial neural networks with different sequence encoding schemes Gibbs sampler approach to the prediction o ...
... Peptide MHC binding predictions using position specific scoring matrices including pseudo counts and sequences weighting clustering (Hobohm) techniques Peptide MHC binding predictions using artificial neural networks with different sequence encoding schemes Gibbs sampler approach to the prediction o ...
Nucleic acid based therapeutic molecules
... zygotic genes in elegans. RNA APP: Amyloid precursor protein; BACE1: Beta-site of APP-cleaving enzyme 1; rAAV: interference (RNAi) is the process recombinant adeno-associated virus; SOD1: Superoxide dismutase 1 of using specific sequence of double stranded RNA (dsRNA) to knockdown the expression fun ...
... zygotic genes in elegans. RNA APP: Amyloid precursor protein; BACE1: Beta-site of APP-cleaving enzyme 1; rAAV: interference (RNAi) is the process recombinant adeno-associated virus; SOD1: Superoxide dismutase 1 of using specific sequence of double stranded RNA (dsRNA) to knockdown the expression fun ...
An Introduction to Pharmacogenomics
... •Matched tissue showed wild type sequence. No mutations seen in 7 nonresponsive cases analysed •Heterozygous mutations seen in 2 cases. Dominant gain of function mutation •Heterologous expression in Cos-7 cells shows mutant receptors (IC50 = 0.015uM) more sensitive to inhibition by gefitinib than wi ...
... •Matched tissue showed wild type sequence. No mutations seen in 7 nonresponsive cases analysed •Heterozygous mutations seen in 2 cases. Dominant gain of function mutation •Heterologous expression in Cos-7 cells shows mutant receptors (IC50 = 0.015uM) more sensitive to inhibition by gefitinib than wi ...
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms, Drug Metabolism and Untoward
... bile or urine. Most Phase I metabolites are conjugated to glucuronide or glutathione. Glucuronidation is the major Phase II conjugation pathway in the body which requires the presence of UDP-glucuronsyltransferases (UGTs). These enzymes catalyze the glucuronidation of drug metabolites using oxygen, ...
... bile or urine. Most Phase I metabolites are conjugated to glucuronide or glutathione. Glucuronidation is the major Phase II conjugation pathway in the body which requires the presence of UDP-glucuronsyltransferases (UGTs). These enzymes catalyze the glucuronidation of drug metabolites using oxygen, ...
Roadrunner Express Winter 2015 Edition
... competition. For example, in the past, the FDA has approved lower-priced drug imports. In addition, the FDA also has the power to work with domestic manufacturers to help them integrate new raw-material resources into their production lines. Currently, those strategies are either not being employed ...
... competition. For example, in the past, the FDA has approved lower-priced drug imports. In addition, the FDA also has the power to work with domestic manufacturers to help them integrate new raw-material resources into their production lines. Currently, those strategies are either not being employed ...
Nanomedicine
... Insulin-dosing is an example of trigger based drug delivery. Insulin therapy for diabetes requires a low baseline release of the drug with peaks after the ingestion of food. ...
... Insulin-dosing is an example of trigger based drug delivery. Insulin therapy for diabetes requires a low baseline release of the drug with peaks after the ingestion of food. ...
PPT here
... 2. Prodrug level must be high enough to generate therapeutic levels of free drug in the target tissue. 3. Prodrug activation at the other sites must be minimal. 4. Prodrugs must be good substrate or possess high binding affinity for tissue associated molecule. 5. It must not be rapidly eliminated fr ...
... 2. Prodrug level must be high enough to generate therapeutic levels of free drug in the target tissue. 3. Prodrug activation at the other sites must be minimal. 4. Prodrugs must be good substrate or possess high binding affinity for tissue associated molecule. 5. It must not be rapidly eliminated fr ...
Drug design
Drug design, sometimes referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and charge to the biomolecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Drug design frequently but not necessarily relies on computer modeling techniques. This type of modeling is often referred to as computer-aided drug design. Finally, drug design that relies on the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biomolecular target is known as structure-based drug design. In addition to small molecules, biopharmaceuticals and especially therapeutic antibodies are an increasingly important class of drugs and computational methods for improving the affinity, selectivity, and stability of these protein-based therapeutics have also been developed.The phrase ""drug design"" is to some extent a misnomer. A more accurate term is ligand design (i.e., design of a molecule that will bind tightly to its target). Although design techniques for prediction of binding affinity are reasonably successful, there are many other properties, such as bioavailability, metabolic half-life, side effects, etc., that first must be optimized before a ligand can become a safe and efficacious drug. These other characteristics are often difficult to predict with rational design techniques. Nevertheless, due to high attrition rates, especially during clinical phases of drug development, more attention is being focused early in the drug design process on selecting candidate drugs whose physicochemical properties are predicted to result in fewer complications during development and hence more likely to lead to an approved, marketed drug. Furthermore, in vitro experiments complemented with computation methods are increasingly used in early drug discovery to select compounds with more favorable ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion) and toxicological profiles.