Applying Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation to the Study of Spike Timing Dependent Plasticity in Neural Networks
... physiologically accurate than the similar, but more complex, Hodgkin Huxley model, the FN model’s simplicity to implement and accurate mimicking of general neural spiking behavior make it an ideal first choice for the purposes of generating a neural micro-network. The specific FN model used here was ...
... physiologically accurate than the similar, but more complex, Hodgkin Huxley model, the FN model’s simplicity to implement and accurate mimicking of general neural spiking behavior make it an ideal first choice for the purposes of generating a neural micro-network. The specific FN model used here was ...
A lineage-related reciprocal inhibition circuitry for sensory
... Figure 1. Structural organisation of the central complex and ellipsoid body. (a) Cartoon of adult Drosophila brain showing central complex ground pattern (PB, protocerebral bridge; FB, fan-shaped body; EB, ellipsoid body; NO, noduli; LAL, lateral accessory lobes MB, mushroom bodies are shown for ori ...
... Figure 1. Structural organisation of the central complex and ellipsoid body. (a) Cartoon of adult Drosophila brain showing central complex ground pattern (PB, protocerebral bridge; FB, fan-shaped body; EB, ellipsoid body; NO, noduli; LAL, lateral accessory lobes MB, mushroom bodies are shown for ori ...
Data Visualization Optimization Computational Modeling of Perception
... a single lateral excitation stage. The reasons for this are twofold. First, data visualizations are typically viewed in an exploratory manner, thus we seek to model perception in the moments after viewing, before steadystate activity is reached. Second, calculating the neural activity until steady s ...
... a single lateral excitation stage. The reasons for this are twofold. First, data visualizations are typically viewed in an exploratory manner, thus we seek to model perception in the moments after viewing, before steadystate activity is reached. Second, calculating the neural activity until steady s ...
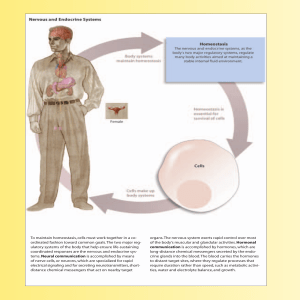
To maintain homeostasis, cells must work together in a co
... ❚ Electrical signals are produced by changes in ion movement across the plasma membrane. Changes in membrane potential are brought about by changes in ion movement across the membrane. For example, if the net inward flow of positively charged ions increases compared to the resting state, the membran ...
... ❚ Electrical signals are produced by changes in ion movement across the plasma membrane. Changes in membrane potential are brought about by changes in ion movement across the membrane. For example, if the net inward flow of positively charged ions increases compared to the resting state, the membran ...
Document
... characterize excitatory and inhibitory motor neurons in the human gastric sling and clasp fibers, their location, structure, responses, and how they affect that area of the body and potential complications that may arise there. Often times, there is a discrepancy with the cell signaling that takes p ...
... characterize excitatory and inhibitory motor neurons in the human gastric sling and clasp fibers, their location, structure, responses, and how they affect that area of the body and potential complications that may arise there. Often times, there is a discrepancy with the cell signaling that takes p ...
Dopamine
... than in control conditions. Moreover, the relationship between DA neuron firing and release was altered. Thus, although there was no significant correlation between DA cell population burst firing and DA release in control rats, there was a significant correlation between burst firing in the remaini ...
... than in control conditions. Moreover, the relationship between DA neuron firing and release was altered. Thus, although there was no significant correlation between DA cell population burst firing and DA release in control rats, there was a significant correlation between burst firing in the remaini ...
18
... By Mojtaba Solgi How does the human brain make sense of the 3D world while its visual input, the retinal images, are only two-dimensional? There are multiple depth-cues exploited by the brain to create a 3D model of the world. Despite the importance of this subject both for scientists and engineers, ...
... By Mojtaba Solgi How does the human brain make sense of the 3D world while its visual input, the retinal images, are only two-dimensional? There are multiple depth-cues exploited by the brain to create a 3D model of the world. Despite the importance of this subject both for scientists and engineers, ...
Adaptive Behavior - Server users.dimi.uniud.it
... interactions among neuromodulators, receptors, synapses, and neurons. Although the neuromodulators diffuse freely to the other neurons in a net, they can specifically influence synapses by using specific interactions with the receptors on the synapses. Only those synapses that have an appropriate re ...
... interactions among neuromodulators, receptors, synapses, and neurons. Although the neuromodulators diffuse freely to the other neurons in a net, they can specifically influence synapses by using specific interactions with the receptors on the synapses. Only those synapses that have an appropriate re ...
Neural analysis of sound frequency in insects
... are 4–5 times larger than those evoked by ultrasound, suggesting that cricket-like frequencies excite more receptors(44)(Fig. 3A). A difference in CAP amplitude could also arise, however, if extracellular potentials were larger for low-frequency receptors, as would be the case if they had larger-dia ...
... are 4–5 times larger than those evoked by ultrasound, suggesting that cricket-like frequencies excite more receptors(44)(Fig. 3A). A difference in CAP amplitude could also arise, however, if extracellular potentials were larger for low-frequency receptors, as would be the case if they had larger-dia ...
PAPER Glucosensing neurons do more than just sense glucose
... as the hypothalamus, locus coeruleus, basal ganglia, limbic system and nucleus tractus solitarius. The ability to sense and regulate glucose metabolism is critical because of glucose’s primacy as a metabolic substrate for neural function. Most neurons use glucose as an energy substrate, but glucosen ...
... as the hypothalamus, locus coeruleus, basal ganglia, limbic system and nucleus tractus solitarius. The ability to sense and regulate glucose metabolism is critical because of glucose’s primacy as a metabolic substrate for neural function. Most neurons use glucose as an energy substrate, but glucosen ...
Proceedings of 2014 BMI the Third International Conference on
... On one hand neuroscience is rich in data and poor in theory. On the other hand, many computer scientists are busy with engineering inspired methods, not motivated by brain in ...
... On one hand neuroscience is rich in data and poor in theory. On the other hand, many computer scientists are busy with engineering inspired methods, not motivated by brain in ...
Associative memory properties of multiple cortical modules
... and mean firing rates in certain conditions which are plausible in the cortex. Although a better description of associative recurrent networks which, for example, allows the inclusion of attractors corresponding to spontaneous activity states and of realistic values for the mean firing rates of the ...
... and mean firing rates in certain conditions which are plausible in the cortex. Although a better description of associative recurrent networks which, for example, allows the inclusion of attractors corresponding to spontaneous activity states and of realistic values for the mean firing rates of the ...
Axons break in animals lacking β-spectrin
... nerve processes (that were initially normal) were later found to be broken. In some cases, we observed neurons that broke, regrew, and then broke again at a later time point (Fig. 3 C). Subsequent breaks occur at different locations along the axon. Although breaks are most easily observed in the com ...
... nerve processes (that were initially normal) were later found to be broken. In some cases, we observed neurons that broke, regrew, and then broke again at a later time point (Fig. 3 C). Subsequent breaks occur at different locations along the axon. Although breaks are most easily observed in the com ...
Chapter 49 and 50 Presentations-Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
... control which you have over whole muscles. There are two basic ways in which graded muscle contractions are controlled by the nervous system. 1. By varying the number of muscle fibers that contract. 2. By varying the rate at which the fibers are ...
... control which you have over whole muscles. There are two basic ways in which graded muscle contractions are controlled by the nervous system. 1. By varying the number of muscle fibers that contract. 2. By varying the rate at which the fibers are ...
Brain Oscillations Control Timing of Single
... A growing body of animal research suggests that neurons represent information not only in terms of their firing rates but also by varying the timing of spikes relative to neuronal oscillations. Although researchers have argued that this temporal coding is critical in human memory and perception, no ...
... A growing body of animal research suggests that neurons represent information not only in terms of their firing rates but also by varying the timing of spikes relative to neuronal oscillations. Although researchers have argued that this temporal coding is critical in human memory and perception, no ...
Self-Organizing Feature Maps with Lateral Connections: Modeling
... a erent (input) connections to the cortex. The self-organizing process is driven by external input [4, 20, 19], and appears to be based on correlated (i.e. cooccurring) neuronal activity and the resulting cooperation and competition between neurons [19, 18]. In addition to the a erent connections, t ...
... a erent (input) connections to the cortex. The self-organizing process is driven by external input [4, 20, 19], and appears to be based on correlated (i.e. cooccurring) neuronal activity and the resulting cooperation and competition between neurons [19, 18]. In addition to the a erent connections, t ...
The Nervous System
... five times more abundant than neurons. In common usage, supporting cells are collectively called neuroglia, or simply glial cells (from the Middle Greek glia = glue). Unlike neurons, which do not divide mitotically (except for particular neural stem cells; chapter 8, section 8.1), glial cells are ab ...
... five times more abundant than neurons. In common usage, supporting cells are collectively called neuroglia, or simply glial cells (from the Middle Greek glia = glue). Unlike neurons, which do not divide mitotically (except for particular neural stem cells; chapter 8, section 8.1), glial cells are ab ...
Neural computations associated with goal
... situations and have found that BOLD activity in the medial orbitofrontal cortex (mOFC) correlates with behavioral measures of stimulus values [11-‐13]. These findings are consistent with monkey neurophysiology stu ...
... situations and have found that BOLD activity in the medial orbitofrontal cortex (mOFC) correlates with behavioral measures of stimulus values [11-‐13]. These findings are consistent with monkey neurophysiology stu ...
video slide - Plattsburgh State Faculty and Research Web Sites
... Conduction of Action Potentials • An action potential can be used to transmit a signal because the action potential can “travel” long distances by regenerating itself along the length of the axon. • At the site where the action potential is generated, the electrical current depolarizes the neighbor ...
... Conduction of Action Potentials • An action potential can be used to transmit a signal because the action potential can “travel” long distances by regenerating itself along the length of the axon. • At the site where the action potential is generated, the electrical current depolarizes the neighbor ...
Sensory Adaptation and Short Term Plasticity as Bayesian
... adaptation phenomena measured in primary visual cortex. First, using a simulation of a single synapse, we illustrate that estimating presynaptic excitability and normalizing postsynaptic responses by these estimates makes neural output more stable (Fig 2). That is, we show that using an excitability ...
... adaptation phenomena measured in primary visual cortex. First, using a simulation of a single synapse, we illustrate that estimating presynaptic excitability and normalizing postsynaptic responses by these estimates makes neural output more stable (Fig 2). That is, we show that using an excitability ...
6 - Coach Eikrem's Website
... Review and Assessment True or False? 1. The gyri divide the brain into 4 regions. 2. The hypothalamus regulates blood pressure. 3. The meninges has 3 layers. 4. The cerebellum coordinates balance. 5. The pons is also called the interbrain. ...
... Review and Assessment True or False? 1. The gyri divide the brain into 4 regions. 2. The hypothalamus regulates blood pressure. 3. The meninges has 3 layers. 4. The cerebellum coordinates balance. 5. The pons is also called the interbrain. ...
Online Textbook Worksheets
... _____ 2. Sensory neurons carry nerve impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands. _____ 3. The peripheral nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. _____ 4. The myelin sheath is similar to the plastic that encases an electrical cord. _____ 5. The somatic nervous system con ...
... _____ 2. Sensory neurons carry nerve impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands. _____ 3. The peripheral nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. _____ 4. The myelin sheath is similar to the plastic that encases an electrical cord. _____ 5. The somatic nervous system con ...
Cognition without a Neural Code: How a Folded Electromagnetic Fields
... support of TNGS shows coordination between areas separated by 10 cm or more (Gaetz et al. 1998; Srinivasan et al. 1999). With a maximum conduction velocity in lightly myelinated neurons of 8 m/s, five round-trips along 10 cm of axon take 125 ms. Next, there is the membrane constant, the time a neuro ...
... support of TNGS shows coordination between areas separated by 10 cm or more (Gaetz et al. 1998; Srinivasan et al. 1999). With a maximum conduction velocity in lightly myelinated neurons of 8 m/s, five round-trips along 10 cm of axon take 125 ms. Next, there is the membrane constant, the time a neuro ...
nervous system
... Cranial Nerves – emerge through cranial foramina of the skull.Reptiles, birds, and mammals have only 12 pairs of these. Spinal Nerves – emerge through intervertebral foramina. The number of spinal nerves is directly related to the number of segments in the trunk and tail of vertebrae. e.g, number of ...
... Cranial Nerves – emerge through cranial foramina of the skull.Reptiles, birds, and mammals have only 12 pairs of these. Spinal Nerves – emerge through intervertebral foramina. The number of spinal nerves is directly related to the number of segments in the trunk and tail of vertebrae. e.g, number of ...
Neural computations associated with goal-directed choice
... (a) Illustration of the main components of the diffusion model of perceptual decision-making. Evidence E in favor of a decision can be strong (black) or weak (gray) and is integrated over time. A decision is made when a common threshold is reached. (b) Illustration of the main components of the urge ...
... (a) Illustration of the main components of the diffusion model of perceptual decision-making. Evidence E in favor of a decision can be strong (black) or weak (gray) and is integrated over time. A decision is made when a common threshold is reached. (b) Illustration of the main components of the urge ...