Unsupervised Learning of Cell Activities in the Associative Cortex of Behaving Monkeys, Using HMM
... from the single cell to the complete network activity. So far, there has been no general method for relating extracellular electrophysiological measured activity of neurons in the associative cortex to the underlying network or the cell-assembly states. It is proposed here to model such data as a pa ...
... from the single cell to the complete network activity. So far, there has been no general method for relating extracellular electrophysiological measured activity of neurons in the associative cortex to the underlying network or the cell-assembly states. It is proposed here to model such data as a pa ...
Feedforward and feedback frequency
... We first consider the local or intralaminar microcircuit, which is the lowest level of the model and may be identified as a set of neurons within a given cortical area and layer. More precisely, we assume a population of pyramidal neurons and a population of inhibitory interneurons at this level. Wi ...
... We first consider the local or intralaminar microcircuit, which is the lowest level of the model and may be identified as a set of neurons within a given cortical area and layer. More precisely, we assume a population of pyramidal neurons and a population of inhibitory interneurons at this level. Wi ...
characterisation of dopamine neurons of the murine ventral
... neurons originating from this region project and receive input from various other brain regions and through several neurotransmitter systems. The attention was concentrated on the excitatory modulation suggested to regulate important functions of synaptic plasticity, which have been associated with ...
... neurons originating from this region project and receive input from various other brain regions and through several neurotransmitter systems. The attention was concentrated on the excitatory modulation suggested to regulate important functions of synaptic plasticity, which have been associated with ...
No Slide Title
... explain how they relate to autonomic effects. – Explain how the ANS controls many target organs through dual innervation. – Explain how control is exerted in the absence of dual innervation. ...
... explain how they relate to autonomic effects. – Explain how the ANS controls many target organs through dual innervation. – Explain how control is exerted in the absence of dual innervation. ...
Multiple Modes of Action Potential Initiation and Propagation in
... and dendrite electrodes (Fig. 2B). In these recording conditions, comparable differences in spike-peak timing between the soma and the dendritic recording site were observed, both for low and high stimulus intensities (n ⫽ 8). This indicates that the whole cell recording conditions had little influe ...
... and dendrite electrodes (Fig. 2B). In these recording conditions, comparable differences in spike-peak timing between the soma and the dendritic recording site were observed, both for low and high stimulus intensities (n ⫽ 8). This indicates that the whole cell recording conditions had little influe ...
Zn2 Slows Down CaV3.3 Gating Kinetics: Implications for
... In addition, Zn2⫹ slowed down channel deactivation but channel recovery from inactivation was only modestly changed. Zn2⫹ also decreased whole cell Ca2⫹ permeability to 45% of control values. In the presence of Zn2⫹, Ca2⫹ currents evoked by mock action potentials were more persistent than in its abs ...
... In addition, Zn2⫹ slowed down channel deactivation but channel recovery from inactivation was only modestly changed. Zn2⫹ also decreased whole cell Ca2⫹ permeability to 45% of control values. In the presence of Zn2⫹, Ca2⫹ currents evoked by mock action potentials were more persistent than in its abs ...
Sliding
... Closing the eye for a brief period causes a shift in the responses towards the non-deprived eye. These shifts in ocular dominance can be easely interpreted as resulting from LTP/D like mechanisms ...
... Closing the eye for a brief period causes a shift in the responses towards the non-deprived eye. These shifts in ocular dominance can be easely interpreted as resulting from LTP/D like mechanisms ...
Zebrafish and motor control over the last decade
... The major motor behaviors and their development have been described in some detail for larval zebrafish (Budick and O'Malley, 2000; Eaton et al., 1977; Saint-Amant and Drapeau, 1998). There is a regular pattern of development with gross body movements followed by the development of rhythmic swimming ...
... The major motor behaviors and their development have been described in some detail for larval zebrafish (Budick and O'Malley, 2000; Eaton et al., 1977; Saint-Amant and Drapeau, 1998). There is a regular pattern of development with gross body movements followed by the development of rhythmic swimming ...
FREE Sample Here
... Rationale: Astrocytes form scar tissue in brain that acts to impede the regrowth of nerve cells. 2.1-37. Myelination of brain nerve axon membranes is accomplished by a. oligodendrocytes. b. microglia. c. astrocytes. d. neurocytes. e. Schwann cells. Difficulty: 1 Question ID: 2.1-37 Page Ref: 37 Topi ...
... Rationale: Astrocytes form scar tissue in brain that acts to impede the regrowth of nerve cells. 2.1-37. Myelination of brain nerve axon membranes is accomplished by a. oligodendrocytes. b. microglia. c. astrocytes. d. neurocytes. e. Schwann cells. Difficulty: 1 Question ID: 2.1-37 Page Ref: 37 Topi ...
Different Subthreshold Mechanisms Underlie Song Selectivity in
... at the base or shoulder of the spike, where the membrane potential described a sharp positive inflection. The amplitudes of spike after hyperpolarizations were measured from the spike shoulder to the trough of the hyperpolarization after the spike. Resting membrane potential was determined by subtra ...
... at the base or shoulder of the spike, where the membrane potential described a sharp positive inflection. The amplitudes of spike after hyperpolarizations were measured from the spike shoulder to the trough of the hyperpolarization after the spike. Resting membrane potential was determined by subtra ...
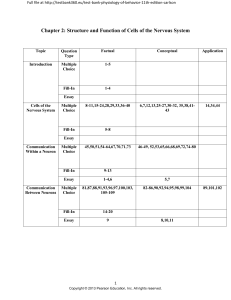
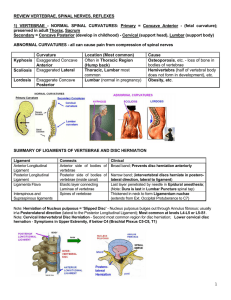
REVIEW VERTEBRAE, SPINAL NERVES, REFLEXES 1
... 7. ____ A 24-year-old-patient is seen for a routine neurological exam. The patient is a medical student who has been studying intensely for Step 1 board (or Final) examinations. Testing of patellar tendon reflexes (deep tendon reflex) shows bilateral, mild hyperreflexia (scored 3). The physician sus ...
... 7. ____ A 24-year-old-patient is seen for a routine neurological exam. The patient is a medical student who has been studying intensely for Step 1 board (or Final) examinations. Testing of patellar tendon reflexes (deep tendon reflex) shows bilateral, mild hyperreflexia (scored 3). The physician sus ...
Glial Signaling Take Home Messages
... a. Monocarboxylate transporters (MCT) move lactate from astrocytes to neurons b. MCT1 expels lactate into the extraneuronal space i. MCT1 is oriented toward exocytosis ii. MCT1 are found in astrocytes c. MCT2 takes up lactate into neurons i. MCT2 are oriented toward endocytosis ii. MCT2 are found in ...
... a. Monocarboxylate transporters (MCT) move lactate from astrocytes to neurons b. MCT1 expels lactate into the extraneuronal space i. MCT1 is oriented toward exocytosis ii. MCT1 are found in astrocytes c. MCT2 takes up lactate into neurons i. MCT2 are oriented toward endocytosis ii. MCT2 are found in ...
The functional asymmetry of auditory cortex is reflected
... of the map. We filled each neuron with a fluorescent marker (Alexa 594) to confirm that the dendritic tree was mostly contained within the slice, and to establish whether spines were present (Fig. 1b, right). All cells analyzed in this study were excitatory, as based on morphology and the presence o ...
... of the map. We filled each neuron with a fluorescent marker (Alexa 594) to confirm that the dendritic tree was mostly contained within the slice, and to establish whether spines were present (Fig. 1b, right). All cells analyzed in this study were excitatory, as based on morphology and the presence o ...
From sensorimotor learning to memory cells in prefrontal and
... cell assemblies distributed over different cortical areas is the neuronal mechanism underlying working memory; the latter proposes changes in calcium levels consequent to stimulation and associated excitability modulation as the critical mechanisms. Although these views are not a priori incompatible ...
... cell assemblies distributed over different cortical areas is the neuronal mechanism underlying working memory; the latter proposes changes in calcium levels consequent to stimulation and associated excitability modulation as the critical mechanisms. Although these views are not a priori incompatible ...
neural representation and the cortical code
... The signal at B1, including all of its noise, is directly transformed into the behavior, so there is a tight correlation between the full signal and the behavioral output. In contrast, the signal at B2 and its noise are not driving behavior, so they will be less well correlated with behavioral outpu ...
... The signal at B1, including all of its noise, is directly transformed into the behavior, so there is a tight correlation between the full signal and the behavioral output. In contrast, the signal at B2 and its noise are not driving behavior, so they will be less well correlated with behavioral outpu ...
Cortex-inspired Developmental Learning for Vision-based Navigation, Attention and Recognition
... behaviors in the challenging task of vision-based navigation, using reinforcement learning and supervised learning jointly. Locally Balanced Incremental Hierarchical Discriminant Regression (LBIHDR) Tree was developed as a cognitive mapping engine to automatically generate internal representations, ...
... behaviors in the challenging task of vision-based navigation, using reinforcement learning and supervised learning jointly. Locally Balanced Incremental Hierarchical Discriminant Regression (LBIHDR) Tree was developed as a cognitive mapping engine to automatically generate internal representations, ...
Heterogeneity of the Population of Command Neurons in the Lamprey
... and Cohen, 1982; Ohta and Grillner, 1989). Earlier experiments have shown that some RS neurons, when stimulated at high frequency, may exert a detectable effect on the output of spinal locomotor networks (Rovainen, 1967; Buchanan and Cohen, 1982). When discharging at normal frequencies, however, onl ...
... and Cohen, 1982; Ohta and Grillner, 1989). Earlier experiments have shown that some RS neurons, when stimulated at high frequency, may exert a detectable effect on the output of spinal locomotor networks (Rovainen, 1967; Buchanan and Cohen, 1982). When discharging at normal frequencies, however, onl ...
Cholinergic Deafferentation of the Entorhinal Cortex in Rats
... represents a familiar stimulus may be maintained in the PFC by the reactivation of the pattern of spikes through recurrent excitatory synaptic transmission. This depends on previous strengthening of excitatory recurrent connections resulting from spike timing-dependent synaptic plasticity. When stim ...
... represents a familiar stimulus may be maintained in the PFC by the reactivation of the pattern of spikes through recurrent excitatory synaptic transmission. This depends on previous strengthening of excitatory recurrent connections resulting from spike timing-dependent synaptic plasticity. When stim ...
PDF
... brightness/contrast and resolution (set at 600 ppi) with the aid of Adobe PhotoShop 6.0 software. To ascertain that postsynaptic structures contacted by human synaptophysin (ⴙ) terminals belonged to the host, rat motor neurons were identified by their morphology and size (>25 m in soma diameter) and ...
... brightness/contrast and resolution (set at 600 ppi) with the aid of Adobe PhotoShop 6.0 software. To ascertain that postsynaptic structures contacted by human synaptophysin (ⴙ) terminals belonged to the host, rat motor neurons were identified by their morphology and size (>25 m in soma diameter) and ...
Complex Biological Systems: When are Simple
... based on concentrations instead of actual counts. A Boolean model would distinguish only between “high” and “low” concentrations. Problem 3: Under what conditions can we trust that the simpler models will make mathematically equivalent predictions to the more elaborate (and biologically more realist ...
... based on concentrations instead of actual counts. A Boolean model would distinguish only between “high” and “low” concentrations. Problem 3: Under what conditions can we trust that the simpler models will make mathematically equivalent predictions to the more elaborate (and biologically more realist ...
Orientation Preference Patterns in Mammalian Visual Cortex: A Wire
... In the intermediate region between Icecube and Pinwheel layouts, we find Wavy Icecube (Figures 2E and 2F) (Braitenberg and Braitenberg, 1979). Bending of the Icecube is the result of attraction between neurons of dissimilar preferred orientations. Again, this layout combines clustering of similarly ...
... In the intermediate region between Icecube and Pinwheel layouts, we find Wavy Icecube (Figures 2E and 2F) (Braitenberg and Braitenberg, 1979). Bending of the Icecube is the result of attraction between neurons of dissimilar preferred orientations. Again, this layout combines clustering of similarly ...
Chapter 16: Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System
... – if nerve maintains background level of activity, can increase or decrease activity ...
... – if nerve maintains background level of activity, can increase or decrease activity ...
Representation of Events in Nerve Nets and Finite Automata
... We shall see later (Section 5.5) that there is no loss of generality in considering the representation, in the case of ·nerve nets, to have the simple form of the firing (or sometimes the non-firing instead) at a certain time of a certain neuron. Por explaining response as due to stimulus., 1 t woul ...
... We shall see later (Section 5.5) that there is no loss of generality in considering the representation, in the case of ·nerve nets, to have the simple form of the firing (or sometimes the non-firing instead) at a certain time of a certain neuron. Por explaining response as due to stimulus., 1 t woul ...
30 Hearing - Semantic Scholar
... motion occurs in the auditory organs of some reptiles and birds. The critical characteristic of the basilar membrane in the mammalian cochlea is that it is not uniform. Instead, the basilar membrane's mechanical properties vary continuously along the cochlea's length. At its apical extreme the human ...
... motion occurs in the auditory organs of some reptiles and birds. The critical characteristic of the basilar membrane in the mammalian cochlea is that it is not uniform. Instead, the basilar membrane's mechanical properties vary continuously along the cochlea's length. At its apical extreme the human ...