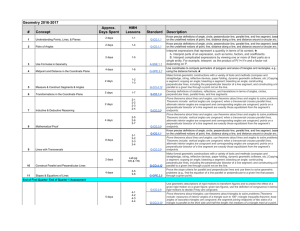
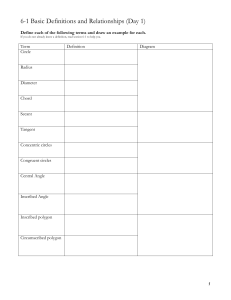
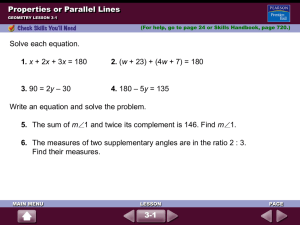
SMSG Geometry Summary
... 2. Definition. Two intersecting sets, each of which is either a line, a ray or a segment, are perpendicular if the two lines which contain them determine a right angle. 3. Definition. If the sum of the measures of two angles is 90, then the angles are called complementary, and each of them is called ...
... 2. Definition. Two intersecting sets, each of which is either a line, a ray or a segment, are perpendicular if the two lines which contain them determine a right angle. 3. Definition. If the sum of the measures of two angles is 90, then the angles are called complementary, and each of them is called ...
Geometry Honors - Belvidere School District
... Unit Summary: Identify points, lines, planes, angles, and their relationships. Measure segments, angles, and polygons using a variety of methods. Introduce the terms and symbols of geometry. Make conjectures about vertical angles, linear pairs of angles, midpoints, and distance. Explore these proper ...
... Unit Summary: Identify points, lines, planes, angles, and their relationships. Measure segments, angles, and polygons using a variety of methods. Introduce the terms and symbols of geometry. Make conjectures about vertical angles, linear pairs of angles, midpoints, and distance. Explore these proper ...
A diagonal - Berkeley City College
... interior angle is right. We can also try to prove that its diagonals are congruent. To prove that a parallelogram is a rhombus, we need to prove that its four sides are congruent. We can also try to prove that its diagonals are perpendicular. To prove that a parallelogram is a square, we need to pro ...
... interior angle is right. We can also try to prove that its diagonals are congruent. To prove that a parallelogram is a rhombus, we need to prove that its four sides are congruent. We can also try to prove that its diagonals are perpendicular. To prove that a parallelogram is a square, we need to pro ...
Riemannian connection on a surface

For the classical approach to the geometry of surfaces, see Differential geometry of surfaces.In mathematics, the Riemannian connection on a surface or Riemannian 2-manifold refers to several intrinsic geometric structures discovered by Tullio Levi-Civita, Élie Cartan and Hermann Weyl in the early part of the twentieth century: parallel transport, covariant derivative and connection form . These concepts were put in their final form using the language of principal bundles only in the 1950s. The classical nineteenth century approach to the differential geometry of surfaces, due in large part to Carl Friedrich Gauss, has been reworked in this modern framework, which provides the natural setting for the classical theory of the moving frame as well as the Riemannian geometry of higher-dimensional Riemannian manifolds. This account is intended as an introduction to the theory of connections.