Resource 43
... given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). G-GPE.5. Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems (e.g., find the equ ...
... given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). G-GPE.5. Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems (e.g., find the equ ...
Resource 37
... Understand and apply theorems about circles G-C.1. Prove that all circles are similar. G-C.2. Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; ...
... Understand and apply theorems about circles G-C.1. Prove that all circles are similar. G-C.2. Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; ...
Geometry
... intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius, and define the radian measure of the angle as the constant of proportionality; derive the formula for the area of a sector ...
... intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius, and define the radian measure of the angle as the constant of proportionality; derive the formula for the area of a sector ...
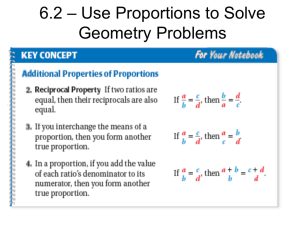
6.2 – Use Proportions to Solve Geometry Problems
... Tower is Dallas, TX. The actual building is 560 feet tall. Your model is 10 inches tall, and the diameter of the dome on your scale model is ...
... Tower is Dallas, TX. The actual building is 560 feet tall. Your model is 10 inches tall, and the diameter of the dome on your scale model is ...
Clever Catch - American Educational Products
... Two non-vertical lines are perpendicular if the product of their slopes is equal to _______. ...
... Two non-vertical lines are perpendicular if the product of their slopes is equal to _______. ...
HS Geometry - Catalina Foothills School District
... Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, and conversely, rectangles are parallelograms with congruent diagonals. CFSD.G-CO.11 Prove, and use theorems about trapezoids, kites ...
... Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, and conversely, rectangles are parallelograms with congruent diagonals. CFSD.G-CO.11 Prove, and use theorems about trapezoids, kites ...
Section 2-6 Proving Geometric Relationships With Solutions Gordon
... Use the diagram and the given angle measure to find the other three angle measures. 4. Find the value of w ...
... Use the diagram and the given angle measure to find the other three angle measures. 4. Find the value of w ...
Analytic geometry
In classical mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry, or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry.Analytic geometry is widely used in physics and engineering, and is the foundation of most modern fields of geometry, including algebraic, differential, discrete and computational geometry.Usually the Cartesian coordinate system is applied to manipulate equations for planes, straight lines, and squares, often in two and sometimes in three dimensions. Geometrically, one studies the Euclidean plane (two dimensions) and Euclidean space (three dimensions). As taught in school books, analytic geometry can be explained more simply: it is concerned with defining and representing geometrical shapes in a numerical way and extracting numerical information from shapes' numerical definitions and representations. The numerical output, however, might also be a vector or a shape. That the algebra of the real numbers can be employed to yield results about the linear continuum of geometry relies on the Cantor–Dedekind axiom.