ACT Math Preparation Guide
... Function: a set of ordered pairs in which no first component is repeated (an x, abscissa, of the domain is paired with one distinct y, ordinate, of the range). Domain: the set of all first components (x’s or abscissas) of ordered pairs. Range: the set of all second components (y’s or ordinates) of o ...
... Function: a set of ordered pairs in which no first component is repeated (an x, abscissa, of the domain is paired with one distinct y, ordinate, of the range). Domain: the set of all first components (x’s or abscissas) of ordered pairs. Range: the set of all second components (y’s or ordinates) of o ...
Geometry Common Core - Lockland Local Schools
... G-SRT.1. Verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor: A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged. The dilation of a line segment is longer or shorte ...
... G-SRT.1. Verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor: A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged. The dilation of a line segment is longer or shorte ...
Geometry
... c) two secant lines d) a tangent line and a chord. Investigate and apply theorems related to the measure of external angles drawn from a point outside a circle created by two tangent lines, two secant lines, or a tangent and a secant line. Investigate, justify, and apply theorems regarding chords of ...
... c) two secant lines d) a tangent line and a chord. Investigate and apply theorems related to the measure of external angles drawn from a point outside a circle created by two tangent lines, two secant lines, or a tangent and a secant line. Investigate, justify, and apply theorems regarding chords of ...
Learning Target Unit Sheet Course: Geometry Chapter 6: Polygons
... Chapter 6: Polygons and Quadrilaterals __ / Unit_3: Polygons Common Core/Quality Core Standard (s) ...
... Chapter 6: Polygons and Quadrilaterals __ / Unit_3: Polygons Common Core/Quality Core Standard (s) ...
- Orangefield ISD
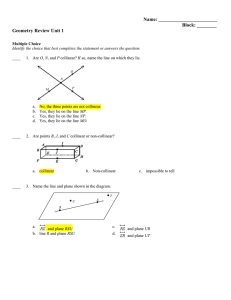
... 19. Line: A line has one dimension. It is usually represented by a straight line with two arrowheads to indicate that the line extends without end in two directions. 20. Line segment: Part of a line that consists of two points, called endpoints, and all points on the line that are between the endpoi ...
... 19. Line: A line has one dimension. It is usually represented by a straight line with two arrowheads to indicate that the line extends without end in two directions. 20. Line segment: Part of a line that consists of two points, called endpoints, and all points on the line that are between the endpoi ...
Analytic geometry
In classical mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry, or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry.Analytic geometry is widely used in physics and engineering, and is the foundation of most modern fields of geometry, including algebraic, differential, discrete and computational geometry.Usually the Cartesian coordinate system is applied to manipulate equations for planes, straight lines, and squares, often in two and sometimes in three dimensions. Geometrically, one studies the Euclidean plane (two dimensions) and Euclidean space (three dimensions). As taught in school books, analytic geometry can be explained more simply: it is concerned with defining and representing geometrical shapes in a numerical way and extracting numerical information from shapes' numerical definitions and representations. The numerical output, however, might also be a vector or a shape. That the algebra of the real numbers can be employed to yield results about the linear continuum of geometry relies on the Cantor–Dedekind axiom.