* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ch 03 geometry parallel lines
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Group action wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
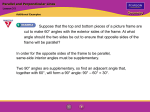
Some terms… • Parallel lines • Skew lines • Parallel planes Transversal and types of angles • Transversal • Corresponding angles • Alternate exterior angles • Alternate interior angles • Consecutive interior angles (same side 1 3 2 4 5 6 7 8 Parallel and perpendicular • Parallel Postulate • Perpendicular Postulate • Theorem: If two lines intersect to form a linear pair of congruent angles, then the lines are perpendicular • Theorem: If two sides of two adjacent acute angles are perpendicular, then the angles are complementary • Theorem: If two lines are perpendicular, then they intersect to form four right angles angle pairs you already know • What angle pairs do you already know? 1 3 Linear Pairs (measures are supplementary) • Translated into a formula 5 7 2 4 6 8 m 1 + m 2 = 180 Vertical Angles (measures are congruent) • Translated into a Linear Pairs and Vertical Angles do not give you parallel lines! formula Parallel lines and angle pairs Corresponding Angles Postulate () Translated into a formula m 1 = m 5 m 3 = m 7 m 8 = m 4 m6 = m 2 1 Alternate Exterior Angle Theorem () Translated into a formula m 1 = m 8 m 2 = m 7 Alternate Interior Angles Postulate () Translated into a formula m 4 = m 5 m 3 = m 6 Consecutive Interior Angles Theorem (180) Translated into a formula m 3 + m 5 = 180 m 4 + m 6 = 180 3 5 7 4 6 8 2 Parallel lines and angle pairs • Consecutive Angles Theorem (180) 1 Translated into a formula 3 m 3 + m 5 = 180 m 3 + m 5 = 180 5 7 4 6 8 2 Examples from Class Work Linear Pairs (180) Vertical Angles () Corresponding Angles Postulate () Alternate Exterior Angle Theorem () Alternate Interior Angle Theorem () 83 + Consecutive Interior Angles Theorem (180) -83 180 3. 3 1 83 x (y – 13 ) 83 = y – 13 +13 +13 96 = y What are these angles to each x =other? -83 x = 97 What are these angles to each other? Slope and parallel lines • What conclusion can you draw about slopes of parallel lines? • What part of y = mx + b would be the same? • What would be different? Slope and Perpendicular lines • What conclusion can you draw about slopes of perpendicular lines? • What part of y = mx + b would be the same? • What would be different?