Higher Level Two Tier GCSE Mathematics
... List all the outcomes from mutually exclusive events, e.g. from two coins, and sample space diagrams Write down the probability associated with equally likely events, e.g. the probability of drawing an ace from a pack of cards Know that if the probability of an event occurring is p than the probabil ...
... List all the outcomes from mutually exclusive events, e.g. from two coins, and sample space diagrams Write down the probability associated with equally likely events, e.g. the probability of drawing an ace from a pack of cards Know that if the probability of an event occurring is p than the probabil ...
Geometry practice lesson 9.5 worksheet answers
... Geometry practice lesson 9.5 worksheet answers Geometry practice lesson 9.5 worksheet answers 4. Answers will vary. Possible answers: LESSON 2.4 • Deductive Reasoning 1. No. Explanations will vary. Sample explanation: Because ABC is equilateral,AB BC. Lines and Angles Naming angle pairs (easy) Namin ...
... Geometry practice lesson 9.5 worksheet answers Geometry practice lesson 9.5 worksheet answers 4. Answers will vary. Possible answers: LESSON 2.4 • Deductive Reasoning 1. No. Explanations will vary. Sample explanation: Because ABC is equilateral,AB BC. Lines and Angles Naming angle pairs (easy) Namin ...
2016 Geometry Pacing Guide - Washington County Schools
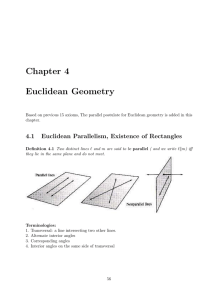
... supplementary angle pairs and use them to solve problems (e.g., solve equations, use in proofs) D.1.c. Identify corresponding, same-side interior, sameside exterior, alternate interior, and alternate exterior angle pairs formed by a pair of parallel lines and a transversal and use these special angl ...
... supplementary angle pairs and use them to solve problems (e.g., solve equations, use in proofs) D.1.c. Identify corresponding, same-side interior, sameside exterior, alternate interior, and alternate exterior angle pairs formed by a pair of parallel lines and a transversal and use these special angl ...
Geometry v. 2016
... CC.2.3.HS.A.6-Verify and apply theorems involving similarity as they relate to plane figures. CC.2.3.HS.A.3--Verify and apply geometric theorems as they relate to geometric figures. CC.2.3.HS.A.11- Apply coordinate geometry to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. CC.2.3.HS.A.14-Apply geome ...
... CC.2.3.HS.A.6-Verify and apply theorems involving similarity as they relate to plane figures. CC.2.3.HS.A.3--Verify and apply geometric theorems as they relate to geometric figures. CC.2.3.HS.A.11- Apply coordinate geometry to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. CC.2.3.HS.A.14-Apply geome ...
Analytic geometry
In classical mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry, or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry.Analytic geometry is widely used in physics and engineering, and is the foundation of most modern fields of geometry, including algebraic, differential, discrete and computational geometry.Usually the Cartesian coordinate system is applied to manipulate equations for planes, straight lines, and squares, often in two and sometimes in three dimensions. Geometrically, one studies the Euclidean plane (two dimensions) and Euclidean space (three dimensions). As taught in school books, analytic geometry can be explained more simply: it is concerned with defining and representing geometrical shapes in a numerical way and extracting numerical information from shapes' numerical definitions and representations. The numerical output, however, might also be a vector or a shape. That the algebra of the real numbers can be employed to yield results about the linear continuum of geometry relies on the Cantor–Dedekind axiom.