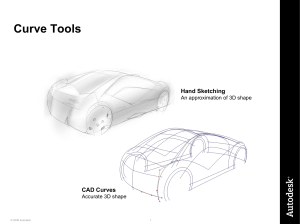
Geometry - ALC - Willmar Public Schools
... Where do I see points, lines, and angles in the real world? What real-life problems could I solve with the knowledge that I have about ...
... Where do I see points, lines, and angles in the real world? What real-life problems could I solve with the knowledge that I have about ...
Curriculum - Pleasantville High School
... How do we solve geometric problems requiring quadratic equations? (factoring only) Review How do we graph quadratic equations on the set of coordinate axes? (1A, 3A, 5A optional) How do we solve quadratic equation graphically? How do we solve a system of quadratic-linear equations graphically? How d ...
... How do we solve geometric problems requiring quadratic equations? (factoring only) Review How do we graph quadratic equations on the set of coordinate axes? (1A, 3A, 5A optional) How do we solve quadratic equation graphically? How do we solve a system of quadratic-linear equations graphically? How d ...
9-12 Geometry
... G.GPE.3 Given the foci, derive the equation of an ellipse, noting that the sum of the distances from the foci to any fixed point on the ellipse is constant, identifying the major and minor axis. G.GPE.3 Given the foci, derive the equation of a hyperbola, noting that the absolute value of the differe ...
... G.GPE.3 Given the foci, derive the equation of an ellipse, noting that the sum of the distances from the foci to any fixed point on the ellipse is constant, identifying the major and minor axis. G.GPE.3 Given the foci, derive the equation of a hyperbola, noting that the absolute value of the differe ...
Standard Geometry-1 Off Semester Pacing Guide 2015
... Understand the differences among supporting evidence, counterexamples, and actual proofs. G.LP.2: Know precise definitions for angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, and plane. Use standard geometric notation. G.PL.5: Explai ...
... Understand the differences among supporting evidence, counterexamples, and actual proofs. G.LP.2: Know precise definitions for angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, and plane. Use standard geometric notation. G.PL.5: Explai ...
Welcome Course: Geometry Teacher: A. Ferraro Contact: AFerraro
... line is perpendicular to the plane determined by them. b. Through a given point there passes one and only one plane perpendicular to a given line. c. Through a given point there passes one and only one line perpendicular to a given plane. d. Two lines perpendicular to the same plane are coplanar e. ...
... line is perpendicular to the plane determined by them. b. Through a given point there passes one and only one plane perpendicular to a given line. c. Through a given point there passes one and only one line perpendicular to a given plane. d. Two lines perpendicular to the same plane are coplanar e. ...
Geometry Exam
... Choose from the terms above to complete each sentence. 1. Two lines are ____________________________ if they intersect to form a right angle. 2. Two angles are____________________________ if their measures have a sum of 90°. 3. When two rays intersect with a common endpoint a(n) ___________________ ...
... Choose from the terms above to complete each sentence. 1. Two lines are ____________________________ if they intersect to form a right angle. 2. Two angles are____________________________ if their measures have a sum of 90°. 3. When two rays intersect with a common endpoint a(n) ___________________ ...
Analytic geometry
In classical mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry, or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry.Analytic geometry is widely used in physics and engineering, and is the foundation of most modern fields of geometry, including algebraic, differential, discrete and computational geometry.Usually the Cartesian coordinate system is applied to manipulate equations for planes, straight lines, and squares, often in two and sometimes in three dimensions. Geometrically, one studies the Euclidean plane (two dimensions) and Euclidean space (three dimensions). As taught in school books, analytic geometry can be explained more simply: it is concerned with defining and representing geometrical shapes in a numerical way and extracting numerical information from shapes' numerical definitions and representations. The numerical output, however, might also be a vector or a shape. That the algebra of the real numbers can be employed to yield results about the linear continuum of geometry relies on the Cantor–Dedekind axiom.