* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry - ALC - Willmar Public Schools
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic geometry wikipedia , lookup
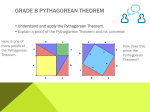
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Willmar Public Schools Curriculum Map Subject Area Week 1 Mathematics--ALC Content Points, Lines, and Angles in the Plane Course Name Standards Addressed Know and apply properties of geometric figures to solve real-world and mathematical problems and to logically justify results in geometry. Construct logical arguments, based on axioms, definitions and theorems, to prove theorems and other results in geometry. 2 Parallel Lines and Transversals Know and apply properties of geometric figures to solve real-world and mathematical problems and to logically justify results in geometry. 3 Constructions Construct logical arguments, based on axioms, definitions and theorems, to prove theorems and other results in geometry. Geometry Skills/Benchmarks Know and apply properties of angles, including corresponding, exterior, interior, vertical, complementary and supplementary angles, to solve problems and logically justify results. Use properties of polygons— including quadrilaterals and regular polygons—to define them, classify them, solve problems and logically justify results. Date Essential Questions Where do I see points, lines, and angles in the real world? What real-life problems could I solve with the knowledge that I have about angle relationships? 5/6/2009 Assessments Unit Test Geometer’s Sketchpad Projects Use technology tools to examine theorems, make and test conjectures, perform constructions and develop mathematical reasoning skills in multi-step problems. The tools may include compass and straight edge, dynamic geometry software, design. software or Internet applets. Know and apply properties of parallel and perpendicular lines, including properties of angles formed by a transversal, to solve problems and logically justify results. Know and apply properties of angles, including corresponding, exterior, interior, vertical, complementary and supplementary angles, to solve problems and logically justify results. Use technology tools to examine theorems, make and test conjectures, perform constructions and develop mathematical What role has investigation using technology played in my understanding of parallel lines and the angles formed by transversals? Unit Test Geometer’s Sketchpad Projects Willmar Public Schools Curriculum Map reasoning skills in multi-step problems. The tools may include compass and straight edge, dynamic geometry software, design. software or Internet applets. Know and apply properties of geometric figures to solve real-world and mathematical problems and to logically justify results in geometry. Know and apply properties of parallel and perpendicular lines, including properties of angles formed by a transversal, to solve problems and logically justify results. How can compasses, straightedges, and geometry software be used to test conjectures and investigate theorems? Unit test Geometer’s Sketchpad Projects Constructions Understand the roles of axioms, definitions, undefined terms and theorems in logical arguments. Construct logical arguments, based on axioms, definitions and theorems, to prove theorems and other results in geometry. 4 Construct logical arguments and write proofs of theorems and other results in geometry, including proofs by contradiction. Express proofs in a form that clearly justifies the reasoning, such as twocolumn proofs, paragraph proofs, flow charts or illustrations. Use technology tools to examine theorems, make and test conjectures, perform constructions and develop mathematical reasoning skills in multi-step problems. The tools may include compass and straight edge, dynamic geometry software, design software or Internet applets. Triangle Properties and Proofs Know and apply properties of geometric figures to solve real-world and mathematical problems and to logically justify results in geometry. Know and apply properties of equilateral, isosceles and scalene triangles to solve problems and logically justify results. Solve real-world and mathematical geometric problems using algebraic methods. Use algebra to solve geometric problems unrelated to coordinate geometry, such as solving for an unknown length in a figure involving similar triangles, or using How could the knowledge of the properties of triangles help a person plan a central location to build a laundry room on a college campus? Unit Test Geometer’s Sketchpad Projects Map Activity Willmar Public Schools Curriculum Map the Pythagorean Theorem to obtain a quadratic equation for a length in a geometric figure. Understand the roles of axioms, definitions, undefined terms and theorems in logical arguments. Construct logical arguments, based on axioms, definitions and theorems, to prove theorems and other results in geometry. 5 Construct logical arguments and write proofs of theorems and other results in geometry, including proofs by contradiction. Express proofs in a form that clearly justifies the reasoning, such as twocolumn proofs, paragraph proofs, flow charts or illustrations. Use technology tools to examine theorems, make and test conjectures, perform constructions and develop mathematical reasoning skills in multi-step problems. The tools may include compass and straight edge, dynamic geometry software, design software or Internet applets. Quadrilaterals and Special Polygons Unit Test How can mathematical modeling and the properties of polygons be used to answer questions that arise in real-life? Investigations Projects Know and apply properties of geometric figures to solve real-world and mathematical problems and to logically justify results in geometry. Solve real-world and mathematical geometric problems using algebraic methods. 6 Circle Properties and Proofs Calculate measurements of plane and solid geometric figures; know that physical measurements depend on the choice of a unit and that they are approximations. Use properties of polygons— including quadrilaterals and regular polygons—to define them, classify them, solve problems and logically justify results. Use algebra to solve geometric problems unrelated to coordinate geometry, such as solving for an unknown length in a figure involving similar triangles, or using the Pythagorean Theorem to obtain a quadratic equation for a length in a geometric figure. Compose and decompose two- and three-dimensional figures; use decomposition to determine the perimeter, area, surface area and volume of various figures. Willmar Public Schools Curriculum Map Construct logical arguments, based on axioms, definitions and theorems, to prove theorems and other results in geometry. Know and apply properties of geometric figures to solve real-world and mathematical problems and to logically justify results in geometry. Solve real-world and mathematical geometric problems using algebraic methods. Construct logical arguments and write proofs of theorems and other results in geometry, including proofs by contradiction. Express proofs in a form that clearly justifies the reasoning, such as twocolumn proofs, paragraph proofs, flow charts or illustrations. Use technology tools to examine theorems, make and test conjectures, perform constructions and develop mathematical reasoning skills in multi-step problems. The tools may include compass and straight edge, dynamic geometry software, design software or Internet applets. Know and apply properties of a circle to solve problems and logically justify results. Unit Test How can the properties of circles help calculate the areas of oddly-shaped curved figures? Investigations Know the equation for the graph of a circle with radius r and center (h, k), (x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2, and justify this equation using the Pythagorean Theorem and properties of translations. Use coordinate geometry to represent and analyze line segments and polygons, including determining lengths, midpoints and slopes of line segments. 7 Coordinate Geometry Solve real-world and mathematical geometric problems using algebraic methods. Use algebra to solve geometric problems unrelated to coordinate geometry, such as solving for an unknown length in a figure involving similar triangles, or using the Pythagorean Theorem to obtain a quadratic equation for a length in a geometric figure. Three straight bike trails in a park you are designing intersect to form a triangle. Where would be the best place to build a first aid station so that it is equidistant from the three bike trails? Unit Test Project Willmar Public Schools Curriculum Map 8 9 The Pythagorean Theorem Know and apply properties of geometric figures to solve real-world and mathematical problems and to logically justify results in geometry. Understand and apply the fact that the effect of a scale factor k on length, area and volume is to multiply each by k, k2 and k3, respectively. Know and apply properties of geometric figures to solve real-world and mathematical problems and to logically justify results in geometry. Know and apply properties of congruent and similar figures to solve problems and logically justify results. Transformations, Similarity, and Proportion Trigonometry Know and apply properties of right triangles, including properties of 45-45-90 and 30-60-90 triangles, to solve problems and logically justify results. Calculate measurements of plane and solid geometric figures; know that physical measurements depend on the choice of a unit and that they are approximations. How can the Pythagorean theorem be used to find the distance between two locations? Solve real-world and mathematical geometric problems using algebraic methods. Unit Test Map Activity What effect does doubling the length, width, and/or height have on a straight line, a square, or a cube? How can one find the height of an object without measuring it directly? Understand how the properties of similar right triangles allow the trigonometric ratios to be defined, and determine the sine, cosine and tangent of an acute angle in a right triangle. Solve real-world and mathematical geometric problems using algebraic methods. 10 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse to solve problems and logically justify results. Unit Test Project Use numeric, graphic and symbolic representations of transformations in two dimensions, such as reflections, translations, scale changes and rotations about the origin by multiples of 90˚, to solve problems involving figures on a coordinate grid. Apply the trigonometric ratios sine, cosine and tangent to solve problems, such as determining lengths and areas in right triangles and in figures that can be decomposed into right triangles. Know how to use calculators, tables or other technology to What is the relationship between the sides of similar triangles? How can the trigonometric ratios be used to find the missing angles and/or sides in right triangles? Unit Test Willmar Public Schools Curriculum Map evaluate trigonometric ratios. Use calculators, tables or other technologies in connection with the trigonometric ratios to find angle measures in right triangles in various contexts. 11 Calculate measurements of plane and solid geometric figures; know that physical measurements depend on the choice of a unit and that they are approximations. Compose and decompose two- and three-dimensional figures; use decomposition to determine the perimeter, area, surface area and volume of various figures. Area Calculate measurements of plane and solid geometric figures; know that physical measurements depend on the choice of a unit and that they are approximations. 12 Volume Determine the surface area and volume of pyramids, cones and spheres. Use measuring devices or formulas as appropriate. How can I determine how much material I will need to cover the surfaces in my home? Unit Test Project Determine the surface area and volume of pyramids, cones and spheres. Use measuring devices or formulas as appropriate. Understand that quantities associated with physical measurements must be assigned units; apply such units correctly in expressions, equations and problem solutions that involve measurements; and convert between measurement systems. How much “stuff” can I fit inside different closed solids? Unit Test Project