Lesson 7.2 - The Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem.notebook
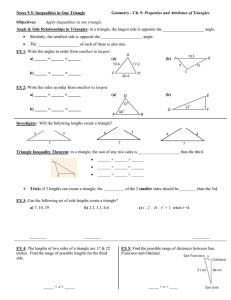
... Lesson 7.2 Converse of Pythagorean Theorem Objective: To use the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if a triangle is a right triangle. ...
... Lesson 7.2 Converse of Pythagorean Theorem Objective: To use the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if a triangle is a right triangle. ...
13b.pdf
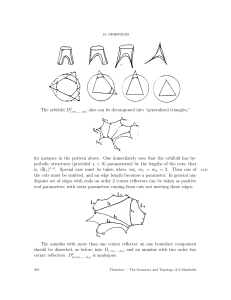
... Proposition 13.4.2. Let O be a two-orbifold. If O is elliptic, then T1 (O) is an elliptic three-orbifold. If O is Euclidean, then T1 (O) is Euclidean. If O is bad, then T S(O) admits an elliptic structure. Proof. The unit tangent bundle T1 (S 2 ) can be identified with the grup SO3 by picking a “bas ...
... Proposition 13.4.2. Let O be a two-orbifold. If O is elliptic, then T1 (O) is an elliptic three-orbifold. If O is Euclidean, then T1 (O) is Euclidean. If O is bad, then T S(O) admits an elliptic structure. Proof. The unit tangent bundle T1 (S 2 ) can be identified with the grup SO3 by picking a “bas ...
Math 367 Homework Assignment 6 due Thursday
... 4. An equilateral triangle is one in which all three sides have equal length. An equiangular triangle is one in which all three angles have equal angle measure. (a) Use the Isosceles Triangle Theorem and its Converse to show that a triangle is equilateral if and only if it is equiangular. In parts ( ...
... 4. An equilateral triangle is one in which all three sides have equal length. An equiangular triangle is one in which all three angles have equal angle measure. (a) Use the Isosceles Triangle Theorem and its Converse to show that a triangle is equilateral if and only if it is equiangular. In parts ( ...