Chapter 12 - Nervous Tissue
... _____________ (to +30 mV) as sodium channels open to allow Na+ ions to move into the neuron 3. An action potential is generated via an influx of ___ ions along the entire length of the axon 4. After depolarization, ______________ occurs as Na+ channels close and K+ channels open: ___ moves out of th ...
... _____________ (to +30 mV) as sodium channels open to allow Na+ ions to move into the neuron 3. An action potential is generated via an influx of ___ ions along the entire length of the axon 4. After depolarization, ______________ occurs as Na+ channels close and K+ channels open: ___ moves out of th ...
Exercise 5: Synaptic Integration - הפקולטה למדעי הבריאות
... The EPSP occuring first will now be closest to the cell soma. Will this sequence of EPSPs cause an action potential to initiate? ...
... The EPSP occuring first will now be closest to the cell soma. Will this sequence of EPSPs cause an action potential to initiate? ...
Cognitive neuroscience lecture
... Sodium ions are concentrated on the outside of the axon membrane. Potassium ions are concentrated on the inside of the axon membrane. Ion channels are closed. The inside of the axon membrane is more negative that is the outside. ...
... Sodium ions are concentrated on the outside of the axon membrane. Potassium ions are concentrated on the inside of the axon membrane. Ion channels are closed. The inside of the axon membrane is more negative that is the outside. ...
Look at brain imaging article.
... neuroscience. We highlight some recent progress and the challenges that remain. central theme of biology is the relation between the structure and function of things. By structure, we mean the physical form of something, a property that humans can apprehend by touch (if the object is big enough) or ...
... neuroscience. We highlight some recent progress and the challenges that remain. central theme of biology is the relation between the structure and function of things. By structure, we mean the physical form of something, a property that humans can apprehend by touch (if the object is big enough) or ...
23 Comp Review 1
... proteins inside of cells, and proteins are made of amino acids, most of which have a negative charge. Because proteins are negatively charged, the inside layer of the cell membrane has a negative charge. • Outside of the cell, there are many electrolytes, especially sodium (Na+), which have a positi ...
... proteins inside of cells, and proteins are made of amino acids, most of which have a negative charge. Because proteins are negatively charged, the inside layer of the cell membrane has a negative charge. • Outside of the cell, there are many electrolytes, especially sodium (Na+), which have a positi ...
Resistive communications based on neuristors
... We can use the neuristor M to achieve this communication as it is shown in figure 6. To begin conduction, a potential is generated near the cell body portion of the axon, here the Vin of the Q transistor. But whereas an electrical signal in an electronic device occurs because electrons move along a ...
... We can use the neuristor M to achieve this communication as it is shown in figure 6. To begin conduction, a potential is generated near the cell body portion of the axon, here the Vin of the Q transistor. But whereas an electrical signal in an electronic device occurs because electrons move along a ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology I
... Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. The purchaser may make back-up copies for his/her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The Publishers assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages caused by the use of theses programs or from the use of the ...
... Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. The purchaser may make back-up copies for his/her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The Publishers assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages caused by the use of theses programs or from the use of the ...
The Nervous System
... Cells of the Nervous System Neurons/nerve cells: receive stimuli and transmit action potentials (send and receive information) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and two extensions Dendrites: shorter, more numerous, and receives information (Action Potentials) Axons: single, long “fiber” whic ...
... Cells of the Nervous System Neurons/nerve cells: receive stimuli and transmit action potentials (send and receive information) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and two extensions Dendrites: shorter, more numerous, and receives information (Action Potentials) Axons: single, long “fiber” whic ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Axonal growth during development. Cell adhesion molecules. Cell adhesion. Regulation of growth cones. Biochemical properties of axonal growth. Axon regeneration. Neurotrophic factors: Types and actions. Trk receptors for neurotrophins. Action of steroid hormones in the development of the nervous sys ...
... Axonal growth during development. Cell adhesion molecules. Cell adhesion. Regulation of growth cones. Biochemical properties of axonal growth. Axon regeneration. Neurotrophic factors: Types and actions. Trk receptors for neurotrophins. Action of steroid hormones in the development of the nervous sys ...
Chapter 13 - Los Angeles City College
... Ca++ channels in postsynaptic membrane. Increases the # of AMPA receptors, increasing ability to depolarize. Diffusion of Ca++ may activate NO, stimulating release of more glutamate. ...
... Ca++ channels in postsynaptic membrane. Increases the # of AMPA receptors, increasing ability to depolarize. Diffusion of Ca++ may activate NO, stimulating release of more glutamate. ...
Ionic Mechanism of the Slow Afterdepolarization Induced by
... of the medial prefrontal cortex with the use of patch clamp or conventional sharp microelectrode recording techniques. For standard intracellular recording sharp microelectrodes were pulled from 1.2-mm OD omega-dot glass (Friedrich and Dimmock, Millville, NJ) with a Flaming-Brown horizontal puller ( ...
... of the medial prefrontal cortex with the use of patch clamp or conventional sharp microelectrode recording techniques. For standard intracellular recording sharp microelectrodes were pulled from 1.2-mm OD omega-dot glass (Friedrich and Dimmock, Millville, NJ) with a Flaming-Brown horizontal puller ( ...
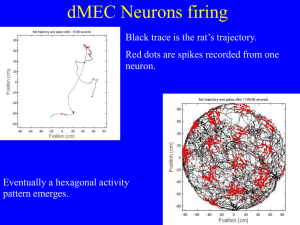
How grid cells neurons encode rat position
... spatial activity patterns non-invasively. • High temporal and spatial resolution is desirable. • No single technology currently satisfies both of these requirements. • By combining data from different modalities, the shortcomings of individual techniques can be overcome. ...
... spatial activity patterns non-invasively. • High temporal and spatial resolution is desirable. • No single technology currently satisfies both of these requirements. • By combining data from different modalities, the shortcomings of individual techniques can be overcome. ...
The Origins of Two-State Spontaneous Membrane Potential
... Natick, MA), or both, to block inward currents attributable to voltagesensitive sodium or calcium currents, respectively. Intracellular recordings were obtained using a conventional active bridge amplifier, digitized (usually at 4 kHz), and stored digitally for later analysis. Electrodes were tested ...
... Natick, MA), or both, to block inward currents attributable to voltagesensitive sodium or calcium currents, respectively. Intracellular recordings were obtained using a conventional active bridge amplifier, digitized (usually at 4 kHz), and stored digitally for later analysis. Electrodes were tested ...
membrane potential
... Concept 37.3: Action potentials are the signals conducted by axons Researchers can record the changes in membrane potential when a neuron responds to a stimulus Changes in membrane potential occur because neurons contain gated ion channels that open or close in response to stimuli ...
... Concept 37.3: Action potentials are the signals conducted by axons Researchers can record the changes in membrane potential when a neuron responds to a stimulus Changes in membrane potential occur because neurons contain gated ion channels that open or close in response to stimuli ...
Building Blocks File
... is impermeable to MOST dissolved substances ie these cannot get in or out easily • BUT the cell membrane is permeable to some substances ie it has what is called selective permeability LCSC06 | Biosciences for SLT ...
... is impermeable to MOST dissolved substances ie these cannot get in or out easily • BUT the cell membrane is permeable to some substances ie it has what is called selective permeability LCSC06 | Biosciences for SLT ...
glandular epithelium
... • Membrane epithelium becomes glandular epithelium when it invaginates / involutes into the tissue layer / layers below, forming a gland • There are two main types of gland. They are exocrine and endocrine. ...
... • Membrane epithelium becomes glandular epithelium when it invaginates / involutes into the tissue layer / layers below, forming a gland • There are two main types of gland. They are exocrine and endocrine. ...
Self Assessment Chapter 11 part 2 - CM
... • Refractory period – period of time, after neuron has generated an action potential, when neuron cannot be stimulated to generate another action potential; can be divided into two phases (Figure 11.17): • Absolute refractory period – when no additional stimulus (no matter how strong) is able to pro ...
... • Refractory period – period of time, after neuron has generated an action potential, when neuron cannot be stimulated to generate another action potential; can be divided into two phases (Figure 11.17): • Absolute refractory period – when no additional stimulus (no matter how strong) is able to pro ...
Figure 8.1b
... • Held in place by a suspensory ligament attached to the ciliary body • The lens focuses light on the retina of the eye • It is elastic and can change shape to focus images at different distances • Contraction of the smooth muscles of the cilliary body makes the lens thicker or thinner • With age th ...
... • Held in place by a suspensory ligament attached to the ciliary body • The lens focuses light on the retina of the eye • It is elastic and can change shape to focus images at different distances • Contraction of the smooth muscles of the cilliary body makes the lens thicker or thinner • With age th ...
Slide 1
... FIGURE 18.7 (A) Schematic representation of the major steps in the developmental PCD pathway of neurons in the nematode worm C. elegans. Both fly and mammalian homologues have been identified supporting the hypothesis that mechanisms of PCD are evolutionarily conserved. The mammalian homologues are ...
... FIGURE 18.7 (A) Schematic representation of the major steps in the developmental PCD pathway of neurons in the nematode worm C. elegans. Both fly and mammalian homologues have been identified supporting the hypothesis that mechanisms of PCD are evolutionarily conserved. The mammalian homologues are ...
Project synopsis on
... Electroencephalography (EEG) is an electrophysiological monitoring method to record electrical activity of the brain. It is typically noninvasive, with the electrodes placed along the scalp, although invasive electrodes are sometimes used in specific applications. EEG measures voltage fluctuations r ...
... Electroencephalography (EEG) is an electrophysiological monitoring method to record electrical activity of the brain. It is typically noninvasive, with the electrodes placed along the scalp, although invasive electrodes are sometimes used in specific applications. EEG measures voltage fluctuations r ...
Nervous System - healthsciencesMBIT
... Each vessel contains a very some quantity of a chemical compound called a neurotransmitter After the nerve impulse arrives at the synaptic knob neurotransmitters molecules are released from the vesicles into the synaptic cleft ...
... Each vessel contains a very some quantity of a chemical compound called a neurotransmitter After the nerve impulse arrives at the synaptic knob neurotransmitters molecules are released from the vesicles into the synaptic cleft ...
neural progenitor cells
... NPCs are a great choice for investigators looking to reduce the time from initial culture to experiment readout, as they eliminate the 4 to 8 weeks for iPSCs to differentiate into NPCs. ATCC NPCs are derived from a collection of well characterized, integration-free reprogrammed iPSCs. The single don ...
... NPCs are a great choice for investigators looking to reduce the time from initial culture to experiment readout, as they eliminate the 4 to 8 weeks for iPSCs to differentiate into NPCs. ATCC NPCs are derived from a collection of well characterized, integration-free reprogrammed iPSCs. The single don ...
Shaping dendrites with machinery borrowed from
... of sensory cells Because epithelia form the interface between an organism and its environment, it is not surprising that they have been modified to generate most sense organs. Sensory cells such as photoreceptors, auditory hair cells, gustatory cells, olfactory receptor neurons, and skin receptors, ...
... of sensory cells Because epithelia form the interface between an organism and its environment, it is not surprising that they have been modified to generate most sense organs. Sensory cells such as photoreceptors, auditory hair cells, gustatory cells, olfactory receptor neurons, and skin receptors, ...
Test 3
... 1. List the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system, and describe their relationship to each other. Nervous system, CNS, PNS, Somatic, ANS. Sensory, integration, motor 2. Describe the types of glial cells, Schwann, oligodendrocyte 3. Explain the physiological characteristics of mat ...
... 1. List the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system, and describe their relationship to each other. Nervous system, CNS, PNS, Somatic, ANS. Sensory, integration, motor 2. Describe the types of glial cells, Schwann, oligodendrocyte 3. Explain the physiological characteristics of mat ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.