Synapses and neuronal signalling
... Local signalling in neurons • Active maintenance of the resting membrane potential • Depolarising and hyperpolarising currents • Input resistance of neurons determines the magnitude of passive changes in membrane potential • Membrane capacitance prolongs the timecourse of signals • Membrane and cyt ...
... Local signalling in neurons • Active maintenance of the resting membrane potential • Depolarising and hyperpolarising currents • Input resistance of neurons determines the magnitude of passive changes in membrane potential • Membrane capacitance prolongs the timecourse of signals • Membrane and cyt ...
Structure of a Neuron Transmission of “Information” Nerve Impulse
... – Across narrow gaps between cells ...
... – Across narrow gaps between cells ...
Nervous System Poster
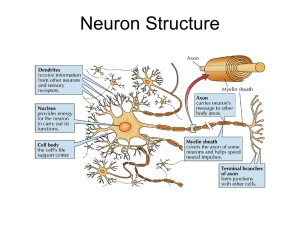
... Essential Knowledge: Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information and produce responses. A. The neuron is the basic structure of the nervous system that reflects function. 1. A typical neuron has a cell body, axon and dendrites. Many axon ...
... Essential Knowledge: Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information and produce responses. A. The neuron is the basic structure of the nervous system that reflects function. 1. A typical neuron has a cell body, axon and dendrites. Many axon ...
Document
... (A) will tend to occur at the negative phase of the sound wave. (B) will tend to occur at the positive phase of the sound wave. (C) will occur equally often at all phases of the sound wave. ...
... (A) will tend to occur at the negative phase of the sound wave. (B) will tend to occur at the positive phase of the sound wave. (C) will occur equally often at all phases of the sound wave. ...
Orexin-A, a peptide that can convince cancer cells to commit suicide
... ways to protect against cancer and to cure it. Just recently researchers found that a small peptide, called orexin-A which can be found in many parts of the body (e.g. gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, kidney, thyroid, lung, testis and placenta) can cause cancer cells to commit suicide. To be able t ...
... ways to protect against cancer and to cure it. Just recently researchers found that a small peptide, called orexin-A which can be found in many parts of the body (e.g. gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, kidney, thyroid, lung, testis and placenta) can cause cancer cells to commit suicide. To be able t ...
Chapter 11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... 1. Electrical impulses carried along the length of axons 2. Always the same regardless of stimulus 3. The underlying functional feature of the nervous system C. Electricity Definitions 1. Voltage (V) a. measure of potential energy generated by separated charge 2. Potential difference a. voltage meas ...
... 1. Electrical impulses carried along the length of axons 2. Always the same regardless of stimulus 3. The underlying functional feature of the nervous system C. Electricity Definitions 1. Voltage (V) a. measure of potential energy generated by separated charge 2. Potential difference a. voltage meas ...
Chapter 5
... channels in a cell membrane Particles move from high concentration to low concentration Example: glucose and salts ...
... channels in a cell membrane Particles move from high concentration to low concentration Example: glucose and salts ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... 4. Proteins along the cell membrane, called Sodium-Potassium Pumps, actively transport Na out of the cell & K into the cell. 5. The build-up of Na outside the cell & K inside the cell makes the Electrochemical Gradient. 6. Because the Na & K ions have different voltages, an electrical differential e ...
... 4. Proteins along the cell membrane, called Sodium-Potassium Pumps, actively transport Na out of the cell & K into the cell. 5. The build-up of Na outside the cell & K inside the cell makes the Electrochemical Gradient. 6. Because the Na & K ions have different voltages, an electrical differential e ...
Neural Control II
... – Electrical synapses – involve direct cytoplasmic connections between the two cells formed by gap junctions; the gap junctions allow ion currents to continue; relatively rare in vertebrates – Chemical synapses – electrical impulses must be converted to a chemical signal that crosses the synapse; mo ...
... – Electrical synapses – involve direct cytoplasmic connections between the two cells formed by gap junctions; the gap junctions allow ion currents to continue; relatively rare in vertebrates – Chemical synapses – electrical impulses must be converted to a chemical signal that crosses the synapse; mo ...
Chapter 2
... Sodium ions are concentrated on the outside of the axon membrane. Potassium ions are concentrated on the inside of the axon membrane. Ion channels are closed. The inside of the axon membrane is more negative that is the outside. ...
... Sodium ions are concentrated on the outside of the axon membrane. Potassium ions are concentrated on the inside of the axon membrane. Ion channels are closed. The inside of the axon membrane is more negative that is the outside. ...
Lecture 1 - Microbiology Intro
... – Intelligently converse with microbiologists, geologists, environmental scientists and engineers about the role microorganisms play in the cycling of elements – Use several techniques to identify and characterize microorganisms in any environment – Relate microbial physiology, genetics, cell struct ...
... – Intelligently converse with microbiologists, geologists, environmental scientists and engineers about the role microorganisms play in the cycling of elements – Use several techniques to identify and characterize microorganisms in any environment – Relate microbial physiology, genetics, cell struct ...
3. Facilitated Diffusion (Assisted diffusion) 4. Diffusion Through Ion
... __channel proteins________ which are usually __specific _____ for one type of ion ions are _charged__________ so… o they’re __insoluble_____ in lipids o they can’t get through the __nonpolar interior ______________ of membrane some ion channels are always open; others open and close (gated channels) ...
... __channel proteins________ which are usually __specific _____ for one type of ion ions are _charged__________ so… o they’re __insoluble_____ in lipids o they can’t get through the __nonpolar interior ______________ of membrane some ion channels are always open; others open and close (gated channels) ...
CT1
... 3. If a sodium ion (Na+) is being transported across the cell membrane into an area of higher concentration, the SPECIFIC transport process being used is _____uniport________________. 4. When a cell is exporting wastes, it is performing the steps of metabolism called __respiration________ and __excr ...
... 3. If a sodium ion (Na+) is being transported across the cell membrane into an area of higher concentration, the SPECIFIC transport process being used is _____uniport________________. 4. When a cell is exporting wastes, it is performing the steps of metabolism called __respiration________ and __excr ...
chart answers - Wilson`s Web Page
... DNA and histone proteins that carry the instructions for the synthesis of proteins (histone proteins help package DNA and play a role in the regulation of the expression of genes) ...
... DNA and histone proteins that carry the instructions for the synthesis of proteins (histone proteins help package DNA and play a role in the regulation of the expression of genes) ...
Structures and Functions Lecture 2
... fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft occurs • Higher impulse frequency more released ...
... fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft occurs • Higher impulse frequency more released ...
with the concentration gradient.
... Cell Membrane Structure 2. 3 types of proteins a. Channel Proteins – provides a passageway for molecules to enter and leaved the cell. b. Receptor Proteins – Receive chemical signals from the other cells. c. Marker Proteins – Identifies the cell – lets the body know where the cell is supposed to be ...
... Cell Membrane Structure 2. 3 types of proteins a. Channel Proteins – provides a passageway for molecules to enter and leaved the cell. b. Receptor Proteins – Receive chemical signals from the other cells. c. Marker Proteins – Identifies the cell – lets the body know where the cell is supposed to be ...
Nervous System
... understanding of the stimulus; determines size, texture, and relationship of parts Visual and auditory areas: receives visual information from the retinas Olfactory, gustatory, and vestibular cortices: receives information related to pitch, rhythm, and loudness ...
... understanding of the stimulus; determines size, texture, and relationship of parts Visual and auditory areas: receives visual information from the retinas Olfactory, gustatory, and vestibular cortices: receives information related to pitch, rhythm, and loudness ...
Electrochemical Impulse
... receptors exist in your skin and organs that can change membrane potential due to environmental changes. These receptors will open channels allowing cations like sodium into the cell body. ...
... receptors exist in your skin and organs that can change membrane potential due to environmental changes. These receptors will open channels allowing cations like sodium into the cell body. ...
Nervous System Period 7 - Mercer Island School District
... there is a sudden change in the voltage across the wall of the axon, caused by the movement of ions in and out of the neuron The speed of nerve impulses varies enormously in different types of neuron. The fastest travel at about 250 mph Neurons that need to transmit electrical signals quickly are sh ...
... there is a sudden change in the voltage across the wall of the axon, caused by the movement of ions in and out of the neuron The speed of nerve impulses varies enormously in different types of neuron. The fastest travel at about 250 mph Neurons that need to transmit electrical signals quickly are sh ...
Neurobiology of the Senses
... 5 The Na+ channels close when cGMP detaches. The membrane’s permeability to Na+ decreases, and the rod hyperpolarizes. ...
... 5 The Na+ channels close when cGMP detaches. The membrane’s permeability to Na+ decreases, and the rod hyperpolarizes. ...
paper
... Amplitude of somatosensory cortical evoked potentials is correlated with spontaneous activity of spinal neurons in the cat E. Manjarrez, G. Rojas-Piloni, L. Martinez, D. Vazquez, D. Velez, I. Mendez, A. Flores Neuroscience Letters 323(2002):187-190 ...
... Amplitude of somatosensory cortical evoked potentials is correlated with spontaneous activity of spinal neurons in the cat E. Manjarrez, G. Rojas-Piloni, L. Martinez, D. Vazquez, D. Velez, I. Mendez, A. Flores Neuroscience Letters 323(2002):187-190 ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.