Chapter 2: Neuroscience
... Helps impulses travel quickly Importance of the myelin sheath is seen in ...
... Helps impulses travel quickly Importance of the myelin sheath is seen in ...
Module 3 - DHS Home
... which mix with negative ions (Chloride-Cl) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mixing of + and – ions (Union of Opposites) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Sodium-Na) while closing the original portal ...
... which mix with negative ions (Chloride-Cl) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mixing of + and – ions (Union of Opposites) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Sodium-Na) while closing the original portal ...
Review Questions for Chapter 1: Studying the Nervous Systems of
... heterotrimeric G-proteins transcription factors immediate early genes 5. The nervous system is known for its plasticity (modifiability), or ability to show enduring changes in response to environmental changes. This typically involves changes in gene expression. Draw a diagram illustrating how neuro ...
... heterotrimeric G-proteins transcription factors immediate early genes 5. The nervous system is known for its plasticity (modifiability), or ability to show enduring changes in response to environmental changes. This typically involves changes in gene expression. Draw a diagram illustrating how neuro ...
A New Mathematics-Inspired Understanding of Breathing and the
... involved. Indeed, neurophysiologists have been conducting intensive investigations of the underlying mechanisms for more than a century. Mathematicians and other brain modelers have gotten into the act and are making profound contributions. For experimentalists, a major focus has been to discover, a ...
... involved. Indeed, neurophysiologists have been conducting intensive investigations of the underlying mechanisms for more than a century. Mathematicians and other brain modelers have gotten into the act and are making profound contributions. For experimentalists, a major focus has been to discover, a ...
PY460: Physiological Psychology
... Note that a low-frequency tone (a) arrives at the ears slightly out of phase. The ear for which the receptors fire first (here the person’s left ear) is interpreted as being closer to the sound. If the difference in phase between the ears is small, then the sound source is close to the center of the ...
... Note that a low-frequency tone (a) arrives at the ears slightly out of phase. The ear for which the receptors fire first (here the person’s left ear) is interpreted as being closer to the sound. If the difference in phase between the ears is small, then the sound source is close to the center of the ...
Topic 6
... Purified molecule of interest is injected into an animal to provoke an immune response (keep in mind these are protein-based molecules, or if smaller, they are coupled to larger proteins). The antibodies that the host animal produces can be collected, purified and tagged with a marker (radioactive, ...
... Purified molecule of interest is injected into an animal to provoke an immune response (keep in mind these are protein-based molecules, or if smaller, they are coupled to larger proteins). The antibodies that the host animal produces can be collected, purified and tagged with a marker (radioactive, ...
Supplement: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... study. Patch pipettes for whole cell axonal recording were filled with a similar intracellular solution, but without fluorescent dye added; these had an impedance of 9-15 MΩ. The pipette was advanced to the cut end of the axon with a positive pressure of about 65 mbar, and guided by switching back a ...
... study. Patch pipettes for whole cell axonal recording were filled with a similar intracellular solution, but without fluorescent dye added; these had an impedance of 9-15 MΩ. The pipette was advanced to the cut end of the axon with a positive pressure of about 65 mbar, and guided by switching back a ...
Take the 10-item multiple choice quiz to check
... prolonged depolarization during the action potential. completion of repolarization before another action potential. that no after-potential occurs. reversal of the direction of propagation of the action potential. that the stimulus is strong enough to elicit a response. ...
... prolonged depolarization during the action potential. completion of repolarization before another action potential. that no after-potential occurs. reversal of the direction of propagation of the action potential. that the stimulus is strong enough to elicit a response. ...
Supplement to: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... study. Patch pipettes for whole cell axonal recording were filled with a similar intracellular solution, but without fluorescent dye added; these had an impedance of 9-15 MΩ. The pipette was advanced to the cut end of the axon with a positive pressure of about 65 mbar, and guided by switching back a ...
... study. Patch pipettes for whole cell axonal recording were filled with a similar intracellular solution, but without fluorescent dye added; these had an impedance of 9-15 MΩ. The pipette was advanced to the cut end of the axon with a positive pressure of about 65 mbar, and guided by switching back a ...
chapter the nervous system and the effects of drugs
... The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps between them, called synapses, which an electri ...
... The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps between them, called synapses, which an electri ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... The principle way neurons communicate is by generating and propagating ACTION POTENTIALS (AP). Only cells with excitable membranes (like muscle cells and neurons) can generate APs. ...
... The principle way neurons communicate is by generating and propagating ACTION POTENTIALS (AP). Only cells with excitable membranes (like muscle cells and neurons) can generate APs. ...
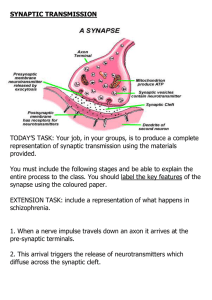
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... 3. When released, the neurotransmitter must be taken up immediately by the post-synaptic neuron, otherwise it will either be re-absorbed by the synaptic terminals from which it was released OR it will be chemically broken down by enzymes in the synaptic ...
... 3. When released, the neurotransmitter must be taken up immediately by the post-synaptic neuron, otherwise it will either be re-absorbed by the synaptic terminals from which it was released OR it will be chemically broken down by enzymes in the synaptic ...
Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
... In sensory cortical areas, neurons are turned to specific stimulus features. In the present paper, the authers investigate the characteristics of the synaptic input that cortical neurons receive to generate their output firing pattern in the visual cortex of mouse. ...
... In sensory cortical areas, neurons are turned to specific stimulus features. In the present paper, the authers investigate the characteristics of the synaptic input that cortical neurons receive to generate their output firing pattern in the visual cortex of mouse. ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... the nervous system, which is the body’s primary communication network. The nervous system gathers and processes information from the environment and allows you to act on the environment. The neuron’s basic task is to communicate with in and with other neurons. ...
... the nervous system, which is the body’s primary communication network. The nervous system gathers and processes information from the environment and allows you to act on the environment. The neuron’s basic task is to communicate with in and with other neurons. ...
Chapter Outline
... there are always more positive ions outside; this accounts for some polarity. g. The large negatively charged proteins in the cytoplasm of the axon also contribute to the resting potential of – 70 mV. 4. Action Potential a. When an axon conducts a nerve impulse, the rapid change in the polarity acro ...
... there are always more positive ions outside; this accounts for some polarity. g. The large negatively charged proteins in the cytoplasm of the axon also contribute to the resting potential of – 70 mV. 4. Action Potential a. When an axon conducts a nerve impulse, the rapid change in the polarity acro ...
PDF
... feature of cortical dynamics. In recent years, another line of research has attracted great interest: the observation of a bimodal distribution of the membrane potential defining up states and down states at the single cell level (Wilson & Kawaguchi, 1996; Steriade, Contreras, & Amzica, 1994; Contre ...
... feature of cortical dynamics. In recent years, another line of research has attracted great interest: the observation of a bimodal distribution of the membrane potential defining up states and down states at the single cell level (Wilson & Kawaguchi, 1996; Steriade, Contreras, & Amzica, 1994; Contre ...
Dorsal Cochlear Nucleus - Neurobiology of Hearing
... The connections between DCN and VCN, and between many other areas of the brain that project to DCN and VCN, demonstrate that we must consider what is going on in the whole brain to really understand how any one area works during real life signal processing and behavior. There remains much to be expl ...
... The connections between DCN and VCN, and between many other areas of the brain that project to DCN and VCN, demonstrate that we must consider what is going on in the whole brain to really understand how any one area works during real life signal processing and behavior. There remains much to be expl ...
Central Nervous System
... Extensions outside the cell body Dendrites – conduct impulses toward the cell body Axons – conduct impulses away from the cell body (only 1!) Axons and Nerve Impulses Axons end in axonal terminals Axonal terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters Axonal terminals are separated fro ...
... Extensions outside the cell body Dendrites – conduct impulses toward the cell body Axons – conduct impulses away from the cell body (only 1!) Axons and Nerve Impulses Axons end in axonal terminals Axonal terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters Axonal terminals are separated fro ...
chapt07_lecture
... C. Classification of Neurons and Nerves 1. Functional classification of neurons – based on direction impulses are conducted a. Sensory neurons: conduct impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS b. Motor neurons: conduct impulses from the CNS to target organs (muscles or glands) c. Association/inte ...
... C. Classification of Neurons and Nerves 1. Functional classification of neurons – based on direction impulses are conducted a. Sensory neurons: conduct impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS b. Motor neurons: conduct impulses from the CNS to target organs (muscles or glands) c. Association/inte ...
10synapse & neurotransmitter
... • EPSPs and IPSPs are graded potential [local]. They can be summated [added]. • Types of Summation 1. Temporal Summation 2. Spatial Summation ...
... • EPSPs and IPSPs are graded potential [local]. They can be summated [added]. • Types of Summation 1. Temporal Summation 2. Spatial Summation ...
Biology 231
... 3) integrating center in brain or spinal cord 4) motor neuron – carries impulse from CNS to an effector 5) effector – part of body that responds to the motor impulse (muscle, gland) the effector’s automatic response to the stimulus is called a reflex knee-jerk reflex – suddenly stretching skeletal m ...
... 3) integrating center in brain or spinal cord 4) motor neuron – carries impulse from CNS to an effector 5) effector – part of body that responds to the motor impulse (muscle, gland) the effector’s automatic response to the stimulus is called a reflex knee-jerk reflex – suddenly stretching skeletal m ...
Powerpoint - Blood Journal
... Orientation of endothelial cell division is regulated by VEGF signaling during blood vessel formation by Gefei Zeng, Sarah M. Taylor, Janet R. McColm, Nicholas C. Kappas, Joseph B. Kearney, Lucy H. Williams, Mary E. Hartnett, and Victoria L. Bautch ...
... Orientation of endothelial cell division is regulated by VEGF signaling during blood vessel formation by Gefei Zeng, Sarah M. Taylor, Janet R. McColm, Nicholas C. Kappas, Joseph B. Kearney, Lucy H. Williams, Mary E. Hartnett, and Victoria L. Bautch ...
Physiology – Excitable Tissue – 11th May 2010
... c. Protoplasmic astrocytes produce substances that are trophic to neurons d. The cell body is always at the dendritic end of the axon 43. Regarding excitation and conduction, select the true statement. a. Excitation may be caused by electrical, chemical or mechanical stimuli b. Action potentials (ne ...
... c. Protoplasmic astrocytes produce substances that are trophic to neurons d. The cell body is always at the dendritic end of the axon 43. Regarding excitation and conduction, select the true statement. a. Excitation may be caused by electrical, chemical or mechanical stimuli b. Action potentials (ne ...
Ch 7 - Nervous system
... its activity. • It signals the body through electrical impulses that communicate with the body cells. • Its signaling and responding abilities are highly specific and rapid. ...
... its activity. • It signals the body through electrical impulses that communicate with the body cells. • Its signaling and responding abilities are highly specific and rapid. ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.