Biology Pre-Learning Check
... Summarize the relationship between the climatic zone and the resultant biomes. (This includes explaining the nature of the rainfall and temperature of the mid-latitude climatic zone that supports the deciduous forest.) Explain climate and weather patterns associated with certain geographic locations ...
... Summarize the relationship between the climatic zone and the resultant biomes. (This includes explaining the nature of the rainfall and temperature of the mid-latitude climatic zone that supports the deciduous forest.) Explain climate and weather patterns associated with certain geographic locations ...
Do Now
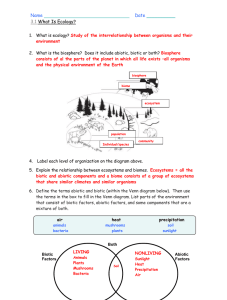
... 2. Organisms die. 3. Nitrification:Organisms in the soil (nitrogen fixing bacteria) convert ammonia into nitrogen compounds (nitrites then nitrates). Nitrates will be used by plants. 4. Nitrogen Fixation: Conversion of nitrogen from atmosphere into ammonia Ex. Lightening bolts. 5. Denitrification: t ...
... 2. Organisms die. 3. Nitrification:Organisms in the soil (nitrogen fixing bacteria) convert ammonia into nitrogen compounds (nitrites then nitrates). Nitrates will be used by plants. 4. Nitrogen Fixation: Conversion of nitrogen from atmosphere into ammonia Ex. Lightening bolts. 5. Denitrification: t ...
Analytical Biochemistry 11:
... amino acid was involved but reduced recoveries wcrc observed when less than 40 mg was supplied. Under these conditions, the action of ninhydrin is not completely specific for a-amino nitrogen: thus y-amino-n-butyric acid yields almost all its nitrogen as ammonia. Citrulline and glutamine produce mor ...
... amino acid was involved but reduced recoveries wcrc observed when less than 40 mg was supplied. Under these conditions, the action of ninhydrin is not completely specific for a-amino nitrogen: thus y-amino-n-butyric acid yields almost all its nitrogen as ammonia. Citrulline and glutamine produce mor ...
Amino Acid Metabolism 1 Key Concepts
... fixation, or oxidized to nitrate (NO3-) by atmospheric lightning, before it can be used by other liver organisms. Nitrogen fixation in nature is carried out by certain types of soil bacteria that live in both the soil and aquatic environments. Rhizobium is an example of a nitrogen-fixing soil bacter ...
... fixation, or oxidized to nitrate (NO3-) by atmospheric lightning, before it can be used by other liver organisms. Nitrogen fixation in nature is carried out by certain types of soil bacteria that live in both the soil and aquatic environments. Rhizobium is an example of a nitrogen-fixing soil bacter ...
Biosphere VOCAB QUIZ Name _____ All the organisms that live in a
... _____ all the different populations that live together in a certain area _____ the parts of the planet (from about 8 km above the Earth’s surface down to 11 km below the ocean’s surface) including land, water or atmosphere in which all life exists _____ group of organisms so similar to one another t ...
... _____ all the different populations that live together in a certain area _____ the parts of the planet (from about 8 km above the Earth’s surface down to 11 km below the ocean’s surface) including land, water or atmosphere in which all life exists _____ group of organisms so similar to one another t ...
Chapter 4 Outline
... a. Specialized bacteria convert gaseous nitrogen to ammonia in nitrogen fixation. b. Special bacteria convert ammonia in the soil to nitrite ions and nitrate ions; the latter is used by plants as a nutrient. This process is nitrification. c. Decomposer bacteria convert detritus into ammonia and wate ...
... a. Specialized bacteria convert gaseous nitrogen to ammonia in nitrogen fixation. b. Special bacteria convert ammonia in the soil to nitrite ions and nitrate ions; the latter is used by plants as a nutrient. This process is nitrification. c. Decomposer bacteria convert detritus into ammonia and wate ...
Ch 4 Outline
... a. Specialized bacteria convert gaseous nitrogen to ammonia in nitrogen fixation. b. Special bacteria convert ammonia in the soil to nitrite ions and nitrate ions; the latter is used by plants as a nutrient. This process is nitrification. c. Decomposer bacteria convert detritus into ammonia and wate ...
... a. Specialized bacteria convert gaseous nitrogen to ammonia in nitrogen fixation. b. Special bacteria convert ammonia in the soil to nitrite ions and nitrate ions; the latter is used by plants as a nutrient. This process is nitrification. c. Decomposer bacteria convert detritus into ammonia and wate ...
Chapter 4 Ecosystems: What are They and How Do They Work
... a. Specialized bacteria convert gaseous nitrogen to ammonia in nitrogen fixation. b. Special bacteria convert ammonia in the soil to nitrite ions and nitrate ions; the latter is used by plants as a nutrient. This process is nitrification. c. Decomposer bacteria convert detritus into ammonia and wate ...
... a. Specialized bacteria convert gaseous nitrogen to ammonia in nitrogen fixation. b. Special bacteria convert ammonia in the soil to nitrite ions and nitrate ions; the latter is used by plants as a nutrient. This process is nitrification. c. Decomposer bacteria convert detritus into ammonia and wate ...
Ch 3-4 study guide ANSWERS
... 12. Human processes mainly contribute to the A. release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. B. decrease of the total amount of carbon found on Earth. C. depletion of carbon dioxide reserves in the atmosphere. D. increase in the amount of carbon contained in rock materials. ...
... 12. Human processes mainly contribute to the A. release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. B. decrease of the total amount of carbon found on Earth. C. depletion of carbon dioxide reserves in the atmosphere. D. increase in the amount of carbon contained in rock materials. ...
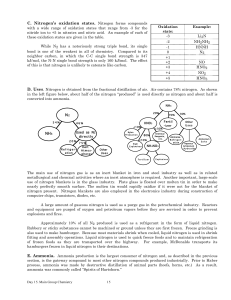
Nitrogen`s oxidation states
... and N2O5 . The trademark of their chemistry is their ability to interconvert so it is difficult to study any one pure oxide. All of these oxides are acid anhydrides. Nitrous oxide, N2O. The proper IUPAC name N2O is dinitrogen monoxide, however its common name, nitrous oxide, is widely used. It is al ...
... and N2O5 . The trademark of their chemistry is their ability to interconvert so it is difficult to study any one pure oxide. All of these oxides are acid anhydrides. Nitrous oxide, N2O. The proper IUPAC name N2O is dinitrogen monoxide, however its common name, nitrous oxide, is widely used. It is al ...
Impacts of air pollution on terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem on
... Economic growth may result in elevated atmospheric emissions of sulphur, nitrogen, and heavy metals. These atmospheric pollutants may have an impact on surrounding ecosystems, as they can travel far from their sources and be deposited throughout the region. Increased sulphur and nitrogen deposition ...
... Economic growth may result in elevated atmospheric emissions of sulphur, nitrogen, and heavy metals. These atmospheric pollutants may have an impact on surrounding ecosystems, as they can travel far from their sources and be deposited throughout the region. Increased sulphur and nitrogen deposition ...
Drip Irrigation Improves N Efficiency
... Soil N. Most soil N is tied up in complex forms in organic matter and is unavailable to the plant. The rate at which these complex forms are broken down into plant-available forms is constantly changing, controlled by a series of interactions of crop residues, soil microbes, soil moisture, and tempe ...
... Soil N. Most soil N is tied up in complex forms in organic matter and is unavailable to the plant. The rate at which these complex forms are broken down into plant-available forms is constantly changing, controlled by a series of interactions of crop residues, soil microbes, soil moisture, and tempe ...
Available
... is coupled to the formation of NADH. In addition, when fumarate is converted back to aspartate, the malate dehydrogenase reaction used to convert malate to oxaloacetate generates a mole of NADH. These two moles of NADH, thus, are oxidized in the mitochondria yielding 6 moles of ATP. ...
... is coupled to the formation of NADH. In addition, when fumarate is converted back to aspartate, the malate dehydrogenase reaction used to convert malate to oxaloacetate generates a mole of NADH. These two moles of NADH, thus, are oxidized in the mitochondria yielding 6 moles of ATP. ...
Organism
... together into food webs Who eats whom? A species may weave into web at more than one level Example: omnivores eat both consumers & producers bears humans eating meat? eating plants? ...
... together into food webs Who eats whom? A species may weave into web at more than one level Example: omnivores eat both consumers & producers bears humans eating meat? eating plants? ...
Chapter 3 Ecosystems What Are They and How Do They Work
... c. Nitrification, when NH4+ is not taken up by plants, if further converted by other bacteria to nitrite and then nitrate, easily taken up by plant roots. 4. Plants and animals return nitrogen rich compounds as waste, cast-off particles, and dead bodies. a. Ammonification by specialized decomposing ...
... c. Nitrification, when NH4+ is not taken up by plants, if further converted by other bacteria to nitrite and then nitrate, easily taken up by plant roots. 4. Plants and animals return nitrogen rich compounds as waste, cast-off particles, and dead bodies. a. Ammonification by specialized decomposing ...
B_Division_Virginia_Regional_Ecology_Test_2009
... a) Its need to find different foods to eat b) The change in an abiotic factor in its environment c) Its need to find a new habitat d) The change in a biotic factor in its environment ...
... a) Its need to find different foods to eat b) The change in an abiotic factor in its environment c) Its need to find a new habitat d) The change in a biotic factor in its environment ...
Lecture III.1. Bacteria and Archaea.
... fellow bacteria are busily producing EPS from which they and you benefit. Why shouldn’t you produce less EPS than the others? After all, EPS is metabolically expensive, and the energy saved could be used to increase your rate of cell division and therefore the numbers of your descendants. Give two p ...
... fellow bacteria are busily producing EPS from which they and you benefit. Why shouldn’t you produce less EPS than the others? After all, EPS is metabolically expensive, and the energy saved could be used to increase your rate of cell division and therefore the numbers of your descendants. Give two p ...
macromolecules
... c. Smaller units are called monomers d. Monomers join together to form larger ...
... c. Smaller units are called monomers d. Monomers join together to form larger ...
Study Guide for Exam 3
... What are the two main pathways in the carbon cycle that cycles carbon between the atmosphere and biosphere? What are the organic and inorganic forms of carbon in the carbon cycle? What is nitrogen fixation? Why is it important? What are the biological and industrial forms of nitrogen fixation? What ...
... What are the two main pathways in the carbon cycle that cycles carbon between the atmosphere and biosphere? What are the organic and inorganic forms of carbon in the carbon cycle? What is nitrogen fixation? Why is it important? What are the biological and industrial forms of nitrogen fixation? What ...
Proteins
... Human nutrition: important sources of Protein (bean, soybean, pea, peanut, etc.) Oil (soybean, peanut, etc.) Also, legumes are the major nitrogen fixers Legumes have nitrogen-fixing bacteria in their roots, in a symbiotic relationship Bacteria take Nitrogen from air, and make it usable for the plant ...
... Human nutrition: important sources of Protein (bean, soybean, pea, peanut, etc.) Oil (soybean, peanut, etc.) Also, legumes are the major nitrogen fixers Legumes have nitrogen-fixing bacteria in their roots, in a symbiotic relationship Bacteria take Nitrogen from air, and make it usable for the plant ...
Basic Principle in Plant Physiology
... Fixation • Nitrogen is needed for amino acids, nucleotides • Atmospheric N2 is the ultimate source of biological nitrogen • Nitrogen fixation: a few bacteria possess nitrogenase which can reduce N2 to ammonia • Nitrogen is recycled in nature through the nitrogen cycle ...
... Fixation • Nitrogen is needed for amino acids, nucleotides • Atmospheric N2 is the ultimate source of biological nitrogen • Nitrogen fixation: a few bacteria possess nitrogenase which can reduce N2 to ammonia • Nitrogen is recycled in nature through the nitrogen cycle ...
Dynamics of Ecosystems
... decomposers do not kill producers or prey. Fungi actually release enzymes and the breakdown occurs outside of their cells. They subsequently absorb nutrients. ...
... decomposers do not kill producers or prey. Fungi actually release enzymes and the breakdown occurs outside of their cells. They subsequently absorb nutrients. ...
Cycles of Matter - Brookwood High School
... 6. Ammonia (NH3), nitrate ions (NO3-), and nitrite ions(NO2-) are found in wastes produced by organisms 7. These compounds taken up by producers to make proteins ...
... 6. Ammonia (NH3), nitrate ions (NO3-), and nitrite ions(NO2-) are found in wastes produced by organisms 7. These compounds taken up by producers to make proteins ...
Document
... – Carbon is emitted by the burning of fossil fuels. – Some carbon is stored for long periods of time in areas called carbon sinks. carbon dioxide in air combustion ...
... – Carbon is emitted by the burning of fossil fuels. – Some carbon is stored for long periods of time in areas called carbon sinks. carbon dioxide in air combustion ...
Nitrogen cycle

The nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen is converted between its various chemical forms. This transformation can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. The majority of Earth's atmosphere (78%) is nitrogen, making it the largest pool of nitrogen. However, atmospheric nitrogen has limited availability for biological use, leading to a scarcity of usable nitrogen in many types of ecosystems. The nitrogen cycle is of particular interest to ecologists because nitrogen availability can affect the rate of key ecosystem processes, including primary production and decomposition. Human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, use of artificial nitrogen fertilizers, and release of nitrogen in wastewater have dramatically altered the global nitrogen cycle.