Ecology Big Ideas
... average annual CO2 concentration. CO2 levels are recorded in parts per million (ppm). This is the number of CO2 molecules in every one million molecules of the atmosphere. Study this graph and answer the questions below it. 1. What conclusions can be drawn from this graph? ...
... average annual CO2 concentration. CO2 levels are recorded in parts per million (ppm). This is the number of CO2 molecules in every one million molecules of the atmosphere. Study this graph and answer the questions below it. 1. What conclusions can be drawn from this graph? ...
Chapter 10 Babbey
... • Plants use carbon dioxide gas to make sugar and oxygen. • Animals use oxygen and sugar to make carbon dioxide gas. ...
... • Plants use carbon dioxide gas to make sugar and oxygen. • Animals use oxygen and sugar to make carbon dioxide gas. ...
Nutrient Removal by Crops in North Carolina | NC State Extension
... losses of 50 percent because of leaching, volatilization, or denitrification. Consequently, crop removal values reflect a minimum amount of nitrogen required because they do not account for nitrogen losses. Legumes produce most of their own nitrogen through a symbiotic, or beneficial, relationship w ...
... losses of 50 percent because of leaching, volatilization, or denitrification. Consequently, crop removal values reflect a minimum amount of nitrogen required because they do not account for nitrogen losses. Legumes produce most of their own nitrogen through a symbiotic, or beneficial, relationship w ...
Amino Acid Catabolism
... ary considerably, but all amino acids are degraded to one of seven metabolites: ...
... ary considerably, but all amino acids are degraded to one of seven metabolites: ...
26.4 The ureo cyde
... deamination also has produced ammonia, however. And ammonia, even in low concentrations, is especially toxic to brain cells and can result in coma and death. A Closer Look Hyperammonemia examines some reasons for this toxicity. It is important that ammonia be removed from the body-This is accomplish ...
... deamination also has produced ammonia, however. And ammonia, even in low concentrations, is especially toxic to brain cells and can result in coma and death. A Closer Look Hyperammonemia examines some reasons for this toxicity. It is important that ammonia be removed from the body-This is accomplish ...
Ecology Stations - Wheatmore Science
... 1. Name one producer in this food web. 2. Name one secondary consumer in this food web. 3. If grasshoppers were removed from this ecosystem, what organism(s) would starve? 4. Which trophic level does the rabbit occupy? 5. How many organisms consume the flowering shrub? 6. Which will have greater bio ...
... 1. Name one producer in this food web. 2. Name one secondary consumer in this food web. 3. If grasshoppers were removed from this ecosystem, what organism(s) would starve? 4. Which trophic level does the rabbit occupy? 5. How many organisms consume the flowering shrub? 6. Which will have greater bio ...
Chapter 3
... convert this organic material from their death into simpler nitrogen-containing inorganic compounds like ammonia (NH3) and ammonium (NH4+). ...
... convert this organic material from their death into simpler nitrogen-containing inorganic compounds like ammonia (NH3) and ammonium (NH4+). ...
Lecture_12
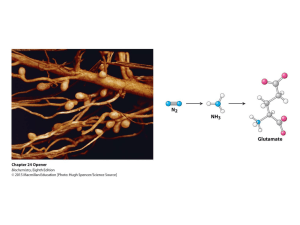
... Three key problems must be addressed to synthesize amino acids. 1. The inert N2 must be converted into an accessible from of nitrogen, usually NH3. 2. All the amino acids except glycine are chiral. Stereochemical control must yield only the L amino acids. 3. The amounts of the individual amino acid ...
... Three key problems must be addressed to synthesize amino acids. 1. The inert N2 must be converted into an accessible from of nitrogen, usually NH3. 2. All the amino acids except glycine are chiral. Stereochemical control must yield only the L amino acids. 3. The amounts of the individual amino acid ...
File - SCT JJ`s Sciences
... 7. All models are probably involved and succession may not often reach the same final potential natural community. 45.3 Dynamics of an Ecosystem In an ecosystem, populations interact among themselves and with the physical environment. A. Autotrophs 1. Autotrophs capture energy (e.g., sunlight) and ...
... 7. All models are probably involved and succession may not often reach the same final potential natural community. 45.3 Dynamics of an Ecosystem In an ecosystem, populations interact among themselves and with the physical environment. A. Autotrophs 1. Autotrophs capture energy (e.g., sunlight) and ...
STATION 1: BIOTIC vs. ABIOTIC
... FOOD CHAINS, FOOD WEBS, ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS Analyze the flow of energy through food chains, food webs and ecological pyramids and answer the questions on your review sheet. ...
... FOOD CHAINS, FOOD WEBS, ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS Analyze the flow of energy through food chains, food webs and ecological pyramids and answer the questions on your review sheet. ...
5.1.1 Relationships
... food and break them down into materials which can be recycled for use by other organisms. Bacteria and fungi in the soil are very important because they return nutrients to the soil when they decompose dead animals and plants. The highly important cycle operating in this process is the nitrogen cycl ...
... food and break them down into materials which can be recycled for use by other organisms. Bacteria and fungi in the soil are very important because they return nutrients to the soil when they decompose dead animals and plants. The highly important cycle operating in this process is the nitrogen cycl ...
5.1.1 Relationships
... food and break them down into materials which can be recycled for use by other organisms. Bacteria and fungi in the soil are very important because they return nutrients to the soil when they decompose dead animals and plants. The highly important cycle operating in this process is the nitrogen cycl ...
... food and break them down into materials which can be recycled for use by other organisms. Bacteria and fungi in the soil are very important because they return nutrients to the soil when they decompose dead animals and plants. The highly important cycle operating in this process is the nitrogen cycl ...
NON-SYMBIOTIC NITROGEN FIXATION IN TROPICAL SOILS 1
... description of Azotobacter chroococcum. and Azotobacter agilis by Beijerinck in 1901. These studíes seem appropriate because the proof of nitrogen fixation in amounts of economical importance could expIam (1) the lacic of plant response to nitrogenous fertilizer, (2) the recuperation of soils left u ...
... description of Azotobacter chroococcum. and Azotobacter agilis by Beijerinck in 1901. These studíes seem appropriate because the proof of nitrogen fixation in amounts of economical importance could expIam (1) the lacic of plant response to nitrogenous fertilizer, (2) the recuperation of soils left u ...
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
... The ammonium ion is assimilated into an amino acid through glutamate and glutamine Most amino acids obtain their α–amino group from glutamate by transamination. The sidechain nitrogen of glutamine is the nitrogen source for the sidechain nitrogens of tryptophan and histidine. ...
... The ammonium ion is assimilated into an amino acid through glutamate and glutamine Most amino acids obtain their α–amino group from glutamate by transamination. The sidechain nitrogen of glutamine is the nitrogen source for the sidechain nitrogens of tryptophan and histidine. ...
Technical Data Sheet Yeast Extract 19512
... Fine pale-yellow powder easily soluble in water. Yeast Extract contains a mix of peptides, free amino acids, purine and pyrimidine bases and hydrosoluble vitamins of B group. ...
... Fine pale-yellow powder easily soluble in water. Yeast Extract contains a mix of peptides, free amino acids, purine and pyrimidine bases and hydrosoluble vitamins of B group. ...
Amino Acid Catabolism - Chemistry Courses: About
... Nitrogen fixation • Bacteria • Nitrogenase • Costly—16 ATP per N2 molecule ...
... Nitrogen fixation • Bacteria • Nitrogenase • Costly—16 ATP per N2 molecule ...
Amino Acid Catabolism - Chemistry Courses: About
... Nitrogen fixation • Bacteria • Nitrogenase • Costly—16 ATP per N2 molecule ...
... Nitrogen fixation • Bacteria • Nitrogenase • Costly—16 ATP per N2 molecule ...
Objective 8: TSWBAT describe the cycling of
... • Life on earth depends on the recycling of essential chemical elements • Atoms present in the complex molecules of an organism at its time of death are returned as simpler compounds to the atmosphere, water, or soil by the actions of decomposers • This decomposition replenished the pools of inorgan ...
... • Life on earth depends on the recycling of essential chemical elements • Atoms present in the complex molecules of an organism at its time of death are returned as simpler compounds to the atmosphere, water, or soil by the actions of decomposers • This decomposition replenished the pools of inorgan ...
A GENOMIC ANALYSIS OF Paenibacillus macerans
... More notably, P. macerans has the ability to fix nitrogen that is very beneficial towards crops productivity. Biological nitrogen fixers accounted for supplying nearly 60 % of world’s new ammonia source annually (Schlesinger, 1991). It is vital to harness research understanding on biological nitroge ...
... More notably, P. macerans has the ability to fix nitrogen that is very beneficial towards crops productivity. Biological nitrogen fixers accounted for supplying nearly 60 % of world’s new ammonia source annually (Schlesinger, 1991). It is vital to harness research understanding on biological nitroge ...
Name
... Nitrogen gas is common in the atmosphere, but most living things cannot use nitrogen gas in their cells. Organisms need nitrogen in a more chemically reactive form. Certain types of bacteria can use nitrogen from the atmosphere. Such nitrogen-fixing bacteria produce ammonia. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria ...
... Nitrogen gas is common in the atmosphere, but most living things cannot use nitrogen gas in their cells. Organisms need nitrogen in a more chemically reactive form. Certain types of bacteria can use nitrogen from the atmosphere. Such nitrogen-fixing bacteria produce ammonia. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria ...
Lab 11
... Results (What are the results observed?) – Include only the key assays, not every test that was performed. In cases where multiple assays were employed to determine one characteristic, only one type of assay ...
... Results (What are the results observed?) – Include only the key assays, not every test that was performed. In cases where multiple assays were employed to determine one characteristic, only one type of assay ...
Nitrogen and Sulfur - School of Plant, Environmental and Soil
... genera of bacteria involved. These form nodules on roots of legumes. The symbiosis is specific between legume and bacteria species. To ensure root nodulation one can inoculate if the right species is not present. ...
... genera of bacteria involved. These form nodules on roots of legumes. The symbiosis is specific between legume and bacteria species. To ensure root nodulation one can inoculate if the right species is not present. ...
Alkaloid
... nitrogen that can be used by all organisms. Just as carbon fixation can be performed by only certain organisms (eg. photosynthetic), nitrogen fixation is performed only by a small number of bacterial species, including symbiotic bacteria (Rhizobium) in the roots of leguminous plants. As you might pr ...
... nitrogen that can be used by all organisms. Just as carbon fixation can be performed by only certain organisms (eg. photosynthetic), nitrogen fixation is performed only by a small number of bacterial species, including symbiotic bacteria (Rhizobium) in the roots of leguminous plants. As you might pr ...
Nitrogen cycle

The nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen is converted between its various chemical forms. This transformation can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. The majority of Earth's atmosphere (78%) is nitrogen, making it the largest pool of nitrogen. However, atmospheric nitrogen has limited availability for biological use, leading to a scarcity of usable nitrogen in many types of ecosystems. The nitrogen cycle is of particular interest to ecologists because nitrogen availability can affect the rate of key ecosystem processes, including primary production and decomposition. Human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, use of artificial nitrogen fertilizers, and release of nitrogen in wastewater have dramatically altered the global nitrogen cycle.