Bowden, Breck (UVM) - Toolik Field Station
... at the scale of a high resolution Earth System Model (ESM) grid cell • NASA/ABoVE: Focus on key process associated with the land surface, and on key interfaces between the land and the coastal ocean and atmospheric boundary layer as they interact with climatemediated terrestrial processes ...
... at the scale of a high resolution Earth System Model (ESM) grid cell • NASA/ABoVE: Focus on key process associated with the land surface, and on key interfaces between the land and the coastal ocean and atmospheric boundary layer as they interact with climatemediated terrestrial processes ...
Ecosystems and Their Services - Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
... These fundamental linkages among organisms and their physical and biological environment constitute an interacting and ever-changing system that is known as an ecosystem. Humans are a component of these ecosystems. Indeed, in many regions they are the dominant organism. Whether dominant or not, howe ...
... These fundamental linkages among organisms and their physical and biological environment constitute an interacting and ever-changing system that is known as an ecosystem. Humans are a component of these ecosystems. Indeed, in many regions they are the dominant organism. Whether dominant or not, howe ...
Ecosystem and Community Interactions
... • Write “job descriptions” for 3 animals and 2 plants – Example: • Oak tree is home to many birds and insects and also provides shades for animals • Woodpecker eats insects ...
... • Write “job descriptions” for 3 animals and 2 plants – Example: • Oak tree is home to many birds and insects and also provides shades for animals • Woodpecker eats insects ...
Sustainable Ecosystems Sustainable Ecosystems
... Ecology is the study of how organisms interact with each other as well as with their environment. A person who studies ecology is called an ecologist. Consider, for example, how an ecologist might study a coral reef. Coral reefs are one of the world’s most important and sensitive ecological systems ...
... Ecology is the study of how organisms interact with each other as well as with their environment. A person who studies ecology is called an ecologist. Consider, for example, how an ecologist might study a coral reef. Coral reefs are one of the world’s most important and sensitive ecological systems ...
Ecosystem Management: Tomorrow`s Approach to
... Ecosystems form the basis for all forms of life support, including provision of food, clean air and water, climate and disease regulation and many others. Biodiversity underpins the health of ecosystems. Appropriate ecosystem management forms the basis for sustainable food security and poverty ...
... Ecosystems form the basis for all forms of life support, including provision of food, clean air and water, climate and disease regulation and many others. Biodiversity underpins the health of ecosystems. Appropriate ecosystem management forms the basis for sustainable food security and poverty ...
Oceans and coastal ecosystems
... proportions for human’s subsistence, development and well-being, as underscored by Rio+20. 2. Recent years has witness a growing recognition in the value of biodiversity and its potential sustainable use to address food security, social and economic growth, and an overall transformation of natural c ...
... proportions for human’s subsistence, development and well-being, as underscored by Rio+20. 2. Recent years has witness a growing recognition in the value of biodiversity and its potential sustainable use to address food security, social and economic growth, and an overall transformation of natural c ...
Introduction to Ecology
... III. Organisms can be categorized by their needs and how they obtain energy. • The sun is the primary source of energy for life on earth. Of all the sun’s energy that hits the earth, only about 1% is used by living things. ...
... III. Organisms can be categorized by their needs and how they obtain energy. • The sun is the primary source of energy for life on earth. Of all the sun’s energy that hits the earth, only about 1% is used by living things. ...
Regeneration of Oak and Northern Hardwood Forests
... high light intensity due to natural gaps and small clearcuts. • Thinning was too light to be effective, and a single burn not only failed to promote oak regeneration but often set back existing regeneration. • Herbicide treatment changed the vegetation markedly and is totally undesirable. • The poor ...
... high light intensity due to natural gaps and small clearcuts. • Thinning was too light to be effective, and a single burn not only failed to promote oak regeneration but often set back existing regeneration. • Herbicide treatment changed the vegetation markedly and is totally undesirable. • The poor ...
Rainforest Complexity
... These frogs are brightly colored and protected from predators by poisonous skin, but their tadpoles are defenseless prey for other creatures like the Tarantula. But tarantula spiders better watch out! The ...
... These frogs are brightly colored and protected from predators by poisonous skin, but their tadpoles are defenseless prey for other creatures like the Tarantula. But tarantula spiders better watch out! The ...
Changes to the Genetic Code (6E)
... transfer matter and energy from one trophic level to another. • Approximately 10% of the available energy in a trophic level is passed on to the next trophic level. The remaining energy, approximately 90%, is used for metabolic functions or dissipated as heat. • Sunlight – radiant energy – is used b ...
... transfer matter and energy from one trophic level to another. • Approximately 10% of the available energy in a trophic level is passed on to the next trophic level. The remaining energy, approximately 90%, is used for metabolic functions or dissipated as heat. • Sunlight – radiant energy – is used b ...
Conservation in the Anthropocene
... Especially worrying to us is the ongoing change in conservation agenda from identifying and protecting sites of high conservation priority to conserving “working landscapes” with extensive human influence. Fourth, if the idea that Earth is already spoiled further permeates the general mindset, monet ...
... Especially worrying to us is the ongoing change in conservation agenda from identifying and protecting sites of high conservation priority to conserving “working landscapes” with extensive human influence. Fourth, if the idea that Earth is already spoiled further permeates the general mindset, monet ...
1.5 A Study of an Ecosystem
... 51. What is meant by a quantitative survey of organisms in a habitat? A survey in which the number of a particular species / organism is counted 52. Ecosystems are subject to changes, both natural and artificial. Mention one of each type of change as it applies to your named ecosystem. Natural: rele ...
... 51. What is meant by a quantitative survey of organisms in a habitat? A survey in which the number of a particular species / organism is counted 52. Ecosystems are subject to changes, both natural and artificial. Mention one of each type of change as it applies to your named ecosystem. Natural: rele ...
Ecosystems Study Sheet
... the level before it. Most of the energy in each level is used at that level. Only a little energy is passed on to the next level. Because each level passes so little energy to the next, the first-level consumers need many producers to support them. In the same way, the second-level consumers need ma ...
... the level before it. Most of the energy in each level is used at that level. Only a little energy is passed on to the next level. Because each level passes so little energy to the next, the first-level consumers need many producers to support them. In the same way, the second-level consumers need ma ...
national unit specification: general information
... It would be preferable if the majority of ecosystems chosen for inclusion were accessible for practical study by the candidates. An introduction on terrestrial ecosystems could include the geological and climatic factors involved in the formation and structure of ecosystems. Outcome 1 A wide range o ...
... It would be preferable if the majority of ecosystems chosen for inclusion were accessible for practical study by the candidates. An introduction on terrestrial ecosystems could include the geological and climatic factors involved in the formation and structure of ecosystems. Outcome 1 A wide range o ...
Ecological Succession
... • The gradual replacement of one plant community by another through natural processes over time ...
... • The gradual replacement of one plant community by another through natural processes over time ...
Letter to Pond Owners - Pender Islands Farmers Institute
... Ignoring the problem will only allow it to worsen. You can help. The Pender Islands Farmers’ Institute and other interested groups are tackling the problem. This summer, amphibian specialist Stan Orchard’s bullfrog-capture team will begin work on North Pender, starting with ponds in the Port Washing ...
... Ignoring the problem will only allow it to worsen. You can help. The Pender Islands Farmers’ Institute and other interested groups are tackling the problem. This summer, amphibian specialist Stan Orchard’s bullfrog-capture team will begin work on North Pender, starting with ponds in the Port Washing ...
Energy Flow - SchoolRack
... an organism’s habitat. • Water – Organisms require water to carry on life’s processes, and water makes up a large part of organisms’ bodies. • Sunlight – Needed for photosynthesis; without it, few organisms can survive. • Oxygen – Can be obtained from the air or from water, and is essential for life ...
... an organism’s habitat. • Water – Organisms require water to carry on life’s processes, and water makes up a large part of organisms’ bodies. • Sunlight – Needed for photosynthesis; without it, few organisms can survive. • Oxygen – Can be obtained from the air or from water, and is essential for life ...
Grade 5 - Northmont City Schools
... which it cannot pass, shadows are formed. As light reaches a new material, it can be absorbed, refracted, reflected or can continue to travel through the new material; one of these interactions may ...
... which it cannot pass, shadows are formed. As light reaches a new material, it can be absorbed, refracted, reflected or can continue to travel through the new material; one of these interactions may ...
Ecology - hudson.edu
... Photosynthesis • Process by which autotrophs harness sunlight in a chemical reaction to change inorganic compounds into energy-rich carbohydrates and oxygen. ...
... Photosynthesis • Process by which autotrophs harness sunlight in a chemical reaction to change inorganic compounds into energy-rich carbohydrates and oxygen. ...
Northern Rockies Ecosystem Types and Descriptions
... temperatures are cold, and high winds are common. Possible tree species include whitebark pine (Pinus albicaulis), alpine larch (Larix lyallii), and limber pine (P. flexilis), but because of very harsh growing conditions, tree heights are often severely stunted. Alpine/subalpine shrubland/meadow The ...
... temperatures are cold, and high winds are common. Possible tree species include whitebark pine (Pinus albicaulis), alpine larch (Larix lyallii), and limber pine (P. flexilis), but because of very harsh growing conditions, tree heights are often severely stunted. Alpine/subalpine shrubland/meadow The ...
This relationship is an example of
... Habitat - The place where an organism lives. A habitat is often thought of as the organism's address. Examples: A lion’s habitat is a savanna. A monkey’s habitat is a rain forest. A cactus’s habitat is in the desert. Niche - An organism’s way of life. A niche is considered to be an organism’s occupa ...
... Habitat - The place where an organism lives. A habitat is often thought of as the organism's address. Examples: A lion’s habitat is a savanna. A monkey’s habitat is a rain forest. A cactus’s habitat is in the desert. Niche - An organism’s way of life. A niche is considered to be an organism’s occupa ...
Ecosystem Integrity - Ecology and Society
... the existence of multiple modes of functioning and the potential for unexpected changes in system behavior. Accordingly, two main variants of ecosystem policies have been derived from this approach. 1) In resource−based systems, such as forests, fisheries, and croplands, decision makers are inclined ...
... the existence of multiple modes of functioning and the potential for unexpected changes in system behavior. Accordingly, two main variants of ecosystem policies have been derived from this approach. 1) In resource−based systems, such as forests, fisheries, and croplands, decision makers are inclined ...
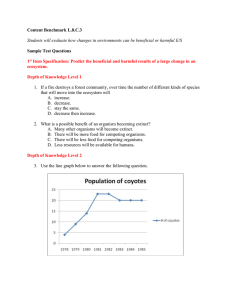
Content Benchmark L.8.C.3 Sample Test Questions
... Increase then decrease Decrease then become stable Decrease until the rabbits are extinct Increase then become stable ...
... Increase then decrease Decrease then become stable Decrease until the rabbits are extinct Increase then become stable ...
Ecosystem ecology - energy flux
... Some of this fixed energy is used to meet plant's energy needs. Some goes into plant growth. Some is stored as non-structural carbohydrates which act as energy sources in roots, seeds, and fruits. Photosynthesis increases plant biomass. Some of this fixed energy is consumed by herbivores, some by de ...
... Some of this fixed energy is used to meet plant's energy needs. Some goes into plant growth. Some is stored as non-structural carbohydrates which act as energy sources in roots, seeds, and fruits. Photosynthesis increases plant biomass. Some of this fixed energy is consumed by herbivores, some by de ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.