1 APES Benchmark Study Guide Chapter 1
... Concept 5-2: Some species develop adaptations that allow them to reduce or avoid competition with other species for resources. Concept 5-3: No population can continue to grow indefinitely because of limitations on resources and because of competition among species for those resources. Concept 5-4: T ...
... Concept 5-2: Some species develop adaptations that allow them to reduce or avoid competition with other species for resources. Concept 5-3: No population can continue to grow indefinitely because of limitations on resources and because of competition among species for those resources. Concept 5-4: T ...
General Concepts and Biogeochemistry
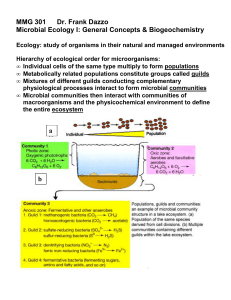
... macroorganisms and the physicochemical environment to define the entire ecosystem ...
... macroorganisms and the physicochemical environment to define the entire ecosystem ...
soil biota, soil systems, and processes
... Soils may be viewed as the organizing centers for terrestrial ecosystems. Major functions such as ecosystem production, respiration, and nutrient recycling are controlled by the rates at which nutrients are released by ...
... Soils may be viewed as the organizing centers for terrestrial ecosystems. Major functions such as ecosystem production, respiration, and nutrient recycling are controlled by the rates at which nutrients are released by ...
New England Forest Ecology
... Adaptations; how and why species adapt The vernal pool habitat is a fast-changing, freshwater habitat with species adapted to survive periods of drought. A vernal pool forms when impermeable soils underlying the topsoil allow pools to form in depressions during winter rains. The pools fill up during ...
... Adaptations; how and why species adapt The vernal pool habitat is a fast-changing, freshwater habitat with species adapted to survive periods of drought. A vernal pool forms when impermeable soils underlying the topsoil allow pools to form in depressions during winter rains. The pools fill up during ...
Required information: 1. Common and Scientific Name of Species 2
... Ecology Project Rubric Assignment: Find all the information about the organism as shown below. ...
... Ecology Project Rubric Assignment: Find all the information about the organism as shown below. ...
MICROORGANISMS
... Diseases are controlled by: Sterilization (high heat) Disinfectants Vaccines Antibiotics ...
... Diseases are controlled by: Sterilization (high heat) Disinfectants Vaccines Antibiotics ...
1 Everything Is Connected
... What Is the Web of Life? All organisms, or living things, are linked together in the web of life. In this web, energy and resources pass between organisms and their surroundings. The study of how different organisms interact with one another and their environment is ecology. An alligator may hunt al ...
... What Is the Web of Life? All organisms, or living things, are linked together in the web of life. In this web, energy and resources pass between organisms and their surroundings. The study of how different organisms interact with one another and their environment is ecology. An alligator may hunt al ...
Ecological Succession - Hatboro
... the newly altered environment is often optimal for some other species of plant or animal. Under the changed conditions of the environment, the previously dominant species may fail and another species may become ascendant. Ecological succession may also occur when the conditions of an environment sud ...
... the newly altered environment is often optimal for some other species of plant or animal. Under the changed conditions of the environment, the previously dominant species may fail and another species may become ascendant. Ecological succession may also occur when the conditions of an environment sud ...
Name______________________________________
... 9. ____________________ the community of organisms in an area and the nonliving parts of the area 10. ___________________ all the different populations in an area ...
... 9. ____________________ the community of organisms in an area and the nonliving parts of the area 10. ___________________ all the different populations in an area ...
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning
... the combined biological activities of many species, and it is often not possible to determine the relative contributions of individual species to ecosystem processes. Species within groups such as grazing mammals, large predators, perennial grasses, or nitrogen-fixing microbes may therefore be funct ...
... the combined biological activities of many species, and it is often not possible to determine the relative contributions of individual species to ecosystem processes. Species within groups such as grazing mammals, large predators, perennial grasses, or nitrogen-fixing microbes may therefore be funct ...
Food Web Background
... Every living organism needs energy to sustain life. Organisms within a community depend on one another for food to create energy. The simplest of these feeding relationships is referred to as a food chain. A food chain is a linear arrangement of at least three organisms in which each uses the organi ...
... Every living organism needs energy to sustain life. Organisms within a community depend on one another for food to create energy. The simplest of these feeding relationships is referred to as a food chain. A food chain is a linear arrangement of at least three organisms in which each uses the organi ...
Food Chains - Mr. White`s Page
... The ultimate source of energy (for most ecosystems) is the sun The ultimate fate of energy in ecosystems is for it to be lost as heat, metabolism, reproduction, etc.. Energy and nutrients are passed from organism to organism through the food chain as one organism eats ...
... The ultimate source of energy (for most ecosystems) is the sun The ultimate fate of energy in ecosystems is for it to be lost as heat, metabolism, reproduction, etc.. Energy and nutrients are passed from organism to organism through the food chain as one organism eats ...
Food Chains
... The ultimate source of energy (for most ecosystems) is the sun The ultimate fate of energy in ecosystems is for it to be lost as heat, metabolism, reproduction, etc.. ...
... The ultimate source of energy (for most ecosystems) is the sun The ultimate fate of energy in ecosystems is for it to be lost as heat, metabolism, reproduction, etc.. ...
BIOL4_Revision checklist - gale-force-glyn
... How is ATP made during the lightdependent reaction? What is the role of photolysis in the lightdependent reaction? How are chloroplasts adapted to carry out the light-dependent ...
... How is ATP made during the lightdependent reaction? What is the role of photolysis in the lightdependent reaction? How are chloroplasts adapted to carry out the light-dependent ...
Ecology
... Choose suitable terms from the list below that most closely match each of the following descriptions: population; producers; competition; predation; community; symbiosis; decomposers; parasitism (a) A situation in which one organism lives on or in a second species, feeding on it and causing it harm. ...
... Choose suitable terms from the list below that most closely match each of the following descriptions: population; producers; competition; predation; community; symbiosis; decomposers; parasitism (a) A situation in which one organism lives on or in a second species, feeding on it and causing it harm. ...
Study Guide A Answer Key
... 5. The low pH of _________________ can affect ecosystems by slowing the growth of plants and damaging fish habitat. ...
... 5. The low pH of _________________ can affect ecosystems by slowing the growth of plants and damaging fish habitat. ...
Everything is connected!
... A biotic factor is any living component that affects another organism, including animals that consume the organism in question, and the living food that the organism consumes. Each biotic factor needs energy to do work and food for proper growth. Biotic factors include human influence. Biot ...
... A biotic factor is any living component that affects another organism, including animals that consume the organism in question, and the living food that the organism consumes. Each biotic factor needs energy to do work and food for proper growth. Biotic factors include human influence. Biot ...
Fauna of the Northern hardwood forest
... types in the area, what type of hardwood forest it was. We concluded that it was a Northern hardwood forest and then we found what animals were excepted to inhabit that type of forest. In our observations of the ecosystems in Centennial Woods we did not see as many animals as we predicted. This is b ...
... types in the area, what type of hardwood forest it was. We concluded that it was a Northern hardwood forest and then we found what animals were excepted to inhabit that type of forest. In our observations of the ecosystems in Centennial Woods we did not see as many animals as we predicted. This is b ...
SOL 4.5 – Living Systems
... The plants and animals that are found in a particular location are referred to as an ecosystem. These plants and animals depend on each other to survive. In a delicate balance, these life forms help to sustain one another in regular patterns. Disruptions to an ecosystem can be disastrous to all orga ...
... The plants and animals that are found in a particular location are referred to as an ecosystem. These plants and animals depend on each other to survive. In a delicate balance, these life forms help to sustain one another in regular patterns. Disruptions to an ecosystem can be disastrous to all orga ...
Challenges and Opportunities
... does not address ecosystems recovery or biodiversity in the pillars it supports. 9. Climate change offers opportunities for renewed focus on ecosystems recovery both as part of climate resilience and of low carbon growth/carbon sequestration and the community of practice should take advantage of thi ...
... does not address ecosystems recovery or biodiversity in the pillars it supports. 9. Climate change offers opportunities for renewed focus on ecosystems recovery both as part of climate resilience and of low carbon growth/carbon sequestration and the community of practice should take advantage of thi ...
Organism
... Organisms, Habitat & Niche • Organisms are individual living things; organisms need energy and matter from the environment • Habitat is the place a plant or animal lives • Niche is the role an organism plays in the environment ...
... Organisms, Habitat & Niche • Organisms are individual living things; organisms need energy and matter from the environment • Habitat is the place a plant or animal lives • Niche is the role an organism plays in the environment ...
File - Nevada Challenger
... many ways that life is interconnected. The show’s final segment focuses on how humans have influenced Habitat Earth. The human species’ appetite for energy and food are unraveling ecological networks that have existed for millions of years, in addition to creating new global connections between Eart ...
... many ways that life is interconnected. The show’s final segment focuses on how humans have influenced Habitat Earth. The human species’ appetite for energy and food are unraveling ecological networks that have existed for millions of years, in addition to creating new global connections between Eart ...
Review for Environmental Systems Fall Final Exam 2015
... Why did hunter-gatherers have such a low environmental impact? They were small in population size and wandered from place to place looking for food. They were not in on spot long enough to cause harm. How much time have we spent as a hunter gatherer type of society verses an agricultural society? We ...
... Why did hunter-gatherers have such a low environmental impact? They were small in population size and wandered from place to place looking for food. They were not in on spot long enough to cause harm. How much time have we spent as a hunter gatherer type of society verses an agricultural society? We ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.