Summary version - OnlyOnePlanet Australia
... thoughtfully in reserve design and selection. Major rivers where ecosystems remain substantially intact should be protected. Proposed models of protection for these include the establishment of a four-tiered river classification system, including 'heritage rivers' and 'conservation rivers' for speci ...
... thoughtfully in reserve design and selection. Major rivers where ecosystems remain substantially intact should be protected. Proposed models of protection for these include the establishment of a four-tiered river classification system, including 'heritage rivers' and 'conservation rivers' for speci ...
Basic Ecology Powerpoint BasicEcologyFIB-PPModified
... of the ocean, air, and even rocks. Carbon flows between the atmosphere, land, and ocean in a cycle that encompasses nearly all life and sets the thermostat for Earth's climate. ...
... of the ocean, air, and even rocks. Carbon flows between the atmosphere, land, and ocean in a cycle that encompasses nearly all life and sets the thermostat for Earth's climate. ...
Ecology Name: Date: 1. The diagram below illustrates the
... The dense needles of Douglas r trees can prevent most light from reaching the forest oor. This situation would have the most immediate e ect on A. ...
... The dense needles of Douglas r trees can prevent most light from reaching the forest oor. This situation would have the most immediate e ect on A. ...
Impacts of biological invasions: what`s what and - UNIV-TLSE3
... differ in functional traits from native flora and when those traits drive ecosystem processes [36]. Although invasive plants frequently have traits more associated with rapid resource acquisition than those of natives [37], literature syntheses and meta-analyses often find no large or consistent overa ...
... differ in functional traits from native flora and when those traits drive ecosystem processes [36]. Although invasive plants frequently have traits more associated with rapid resource acquisition than those of natives [37], literature syntheses and meta-analyses often find no large or consistent overa ...
Unit 2 Lesson 7a Bioaccumulation
... functional relationships within and between systems. In its broadest sense, an ecosystem includes environmental, social, and economic elements. The root words of ecosystem are eco, a derivative of the Greek term for house or home, and system, which addresses the relationships and connections between ...
... functional relationships within and between systems. In its broadest sense, an ecosystem includes environmental, social, and economic elements. The root words of ecosystem are eco, a derivative of the Greek term for house or home, and system, which addresses the relationships and connections between ...
Trophic Economics
... community is through the accounting of the energy available for the next level. Producers make great quantities of energy, from which some is used by themselves (growth and metabolism), other is available for the next Trophic Level (exergy) and other is simply lost (entropy). In this way can be dist ...
... community is through the accounting of the energy available for the next level. Producers make great quantities of energy, from which some is used by themselves (growth and metabolism), other is available for the next Trophic Level (exergy) and other is simply lost (entropy). In this way can be dist ...
Ecology Review Sheet
... 17. Explain seasonal turnover in lakes with with winter ice cover (Fig. 50.13). 18. What is a biome? 19. Identify the major aquatic biomes and know their properties. 20. Know both lake and marine zonation. 21. Make sure you know how to read a climograph (Fig. 50.18). 22. Identify the major terrestr ...
... 17. Explain seasonal turnover in lakes with with winter ice cover (Fig. 50.13). 18. What is a biome? 19. Identify the major aquatic biomes and know their properties. 20. Know both lake and marine zonation. 21. Make sure you know how to read a climograph (Fig. 50.18). 22. Identify the major terrestr ...
Ecology and social action
... matter, or the inorganic nutrients derived from it by treatment, at a rate beyond the ecosystem's natural assimilatory capacity). Given these rather primitive but nevertheless meaningful ecological data, we can ask: What constraints does ecology properly place on the relevant social decisions, such ...
... matter, or the inorganic nutrients derived from it by treatment, at a rate beyond the ecosystem's natural assimilatory capacity). Given these rather primitive but nevertheless meaningful ecological data, we can ask: What constraints does ecology properly place on the relevant social decisions, such ...
A Hierarchical Ecological Approach to Conserving Marine
... observe and predict than biotic attributes such as disease. Ecosystem processes such as productivity, however, involve both biotic and abiotic components and therefore have different implications for conservation than strictly abiotic attributes. Water motion for example, is an ecosystem process dri ...
... observe and predict than biotic attributes such as disease. Ecosystem processes such as productivity, however, involve both biotic and abiotic components and therefore have different implications for conservation than strictly abiotic attributes. Water motion for example, is an ecosystem process dri ...
Chapter 9: Ecology Lesson 9.3: Relationships and Interactions in an
... Why are pyramids important in ecology? The classic example of a pyramid is shown here. But the pyramid structure can also represent the decrease in a measured substance from the lowest level on up. In ecology, pyramids model the use of energy from the producers through the ecosystem. What is the sou ...
... Why are pyramids important in ecology? The classic example of a pyramid is shown here. But the pyramid structure can also represent the decrease in a measured substance from the lowest level on up. In ecology, pyramids model the use of energy from the producers through the ecosystem. What is the sou ...
Carrion cycling in food webs: comparisons among terrestrial and
... remain poorly understood due to the difficulties of monitoring free-ranging individuals in benthic ecosystems, and thus scavenging ecology in the deep-sea remains an area of much needed research. Similarly, vertebrate scavenging likely plays an important role in nutrient cycling in other marine envi ...
... remain poorly understood due to the difficulties of monitoring free-ranging individuals in benthic ecosystems, and thus scavenging ecology in the deep-sea remains an area of much needed research. Similarly, vertebrate scavenging likely plays an important role in nutrient cycling in other marine envi ...
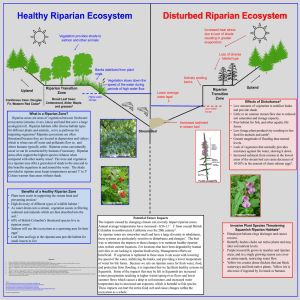
What is a Riparian Zone?
... Squamish. Some of the impacts that may be felt in Squamish are increased winter precipitation resulting in higher winter/spring river flows and lower summer flows which causes a drop in soil moisture, and increased water temperature due to increased sun exposure, which is harmful to fish species. Th ...
... Squamish. Some of the impacts that may be felt in Squamish are increased winter precipitation resulting in higher winter/spring river flows and lower summer flows which causes a drop in soil moisture, and increased water temperature due to increased sun exposure, which is harmful to fish species. Th ...
scientific information needs
... 3 – Determine the feasibility of researching the question within reasonable time and resource constraints. 4 – If the research question was answered, would it facilitate the GBRMPA to better achieve its objectives? For example, would it lead to improvements in the way the Marine Park is managed, or ...
... 3 – Determine the feasibility of researching the question within reasonable time and resource constraints. 4 – If the research question was answered, would it facilitate the GBRMPA to better achieve its objectives? For example, would it lead to improvements in the way the Marine Park is managed, or ...
Nerve activates contraction
... production of nitrogen-containing fertilizer contributes to nitrogenous materials in ecosystems. • The direct product of nitrogen fixation is ammonia, which picks up H + and becomes ammonium in the soil (ammonification), which plants can use. • Certain aerobic bacteria oxidize ammonium into nitrate, ...
... production of nitrogen-containing fertilizer contributes to nitrogenous materials in ecosystems. • The direct product of nitrogen fixation is ammonia, which picks up H + and becomes ammonium in the soil (ammonification), which plants can use. • Certain aerobic bacteria oxidize ammonium into nitrate, ...
Ecology
... when one community replaces another as a result of changing biotic and abiotic factors ...
... when one community replaces another as a result of changing biotic and abiotic factors ...
Ecological Concepts, Principles and Applications
... Biodiversity is the foundation of a vast array of ecosystem services essential for human well-being (see Figure 2).2 Ecosystems support all forms of life, moderate climates, filter water and air, conserve soil and nutrients and control pests. Species (animal and plant) provide us with food, building ...
... Biodiversity is the foundation of a vast array of ecosystem services essential for human well-being (see Figure 2).2 Ecosystems support all forms of life, moderate climates, filter water and air, conserve soil and nutrients and control pests. Species (animal and plant) provide us with food, building ...
Cierra Maszkiewicz Independent Research Annotated Bibliography
... This article explains what mercury is and how it is toxic for aquatic ecosystems. The authors focus primarily on mercury in the environment. However, they touch on how mercury affects not only wildlife, but also humans who consume high levels of mercury. For example, fish are prone to mercury-relate ...
... This article explains what mercury is and how it is toxic for aquatic ecosystems. The authors focus primarily on mercury in the environment. However, they touch on how mercury affects not only wildlife, but also humans who consume high levels of mercury. For example, fish are prone to mercury-relate ...
Lesson 3 Packet - Burnet Middle School
... Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. Each term is used only once. ...
... Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. Each term is used only once. ...
Marine Ecology Progress Series 311:273
... greater depth of sampling is needed before they would be within 95% of the likely diversity. This study illustrates the difficulty in attempting to quantify prokaryotic diversity, even from 1 marine site. One interesting difference between terrestrial and marine systems, however, is that vast though ...
... greater depth of sampling is needed before they would be within 95% of the likely diversity. This study illustrates the difficulty in attempting to quantify prokaryotic diversity, even from 1 marine site. One interesting difference between terrestrial and marine systems, however, is that vast though ...
The Biosphere: Biogeochemical cycling of C,N,P in freshwater and
... in which the H is available as a by-product of fermentation CO2 is found as HCO3• Methanogenesis by CO2 reduction accounts for the limited release of H2 from wetland soils Methanogenic bacteria can only use certain organic substances for acetate splitting • In many cases there is evidence that sulfa ...
... in which the H is available as a by-product of fermentation CO2 is found as HCO3• Methanogenesis by CO2 reduction accounts for the limited release of H2 from wetland soils Methanogenic bacteria can only use certain organic substances for acetate splitting • In many cases there is evidence that sulfa ...
Ecology 1 - New Jersey Institute of Technology
... phytoplankton, that make their own energy from sunlight). Think about how people’s place in the food chain varies – often within a single meal! Numbers of Organisms: In any food web, energy is lost each time one organism eats another. Because of this, there have to be many more plants than there are ...
... phytoplankton, that make their own energy from sunlight). Think about how people’s place in the food chain varies – often within a single meal! Numbers of Organisms: In any food web, energy is lost each time one organism eats another. Because of this, there have to be many more plants than there are ...
Chances and challenges in the conservation of
... obvious to the public than a blue-green algal bloom or the floating corpses from a fish kill. Increasingly, as surface waters become polluted, groundwater resource use is intensifying in many parts of the world, often mining resources faster than they are replenished (Danielopol et al., 2003). We are ...
... obvious to the public than a blue-green algal bloom or the floating corpses from a fish kill. Increasingly, as surface waters become polluted, groundwater resource use is intensifying in many parts of the world, often mining resources faster than they are replenished (Danielopol et al., 2003). We are ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.