L3_fnl_Plankton Food Web_TEACHER
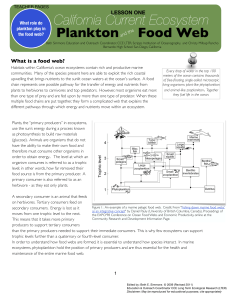
... Plants, the “primary producers” in ecosystems, use the sun’s energy during a process known as photosynthesis to build raw materials (glucose). Animals are organisms that do not have the ability to make their own food and therefore must consume other organisms in order to obtain energy. The level at ...
... Plants, the “primary producers” in ecosystems, use the sun’s energy during a process known as photosynthesis to build raw materials (glucose). Animals are organisms that do not have the ability to make their own food and therefore must consume other organisms in order to obtain energy. The level at ...
Biodiversity Outcomes Framework
... They also understand how biological resources meet their basic needs for food and shelter and create jobs for thousands of people who work in fisheries, forestry, agriculture and tourism. ...
... They also understand how biological resources meet their basic needs for food and shelter and create jobs for thousands of people who work in fisheries, forestry, agriculture and tourism. ...
Biodiversity, ecosystem thresholds, resilience and forest degradation
... instead dominated by only a few species, or if it should be a closed canopy forest but is actually open or savannah, then the state has changed. These would be considered negative changes in state, as they degrade the forest, from a biodiversity perspective and from a production perspective, and wou ...
... instead dominated by only a few species, or if it should be a closed canopy forest but is actually open or savannah, then the state has changed. These would be considered negative changes in state, as they degrade the forest, from a biodiversity perspective and from a production perspective, and wou ...
Chapter 20
... Scientists carried out an investigation into the interaction between different species of organisms. The table below shows the numbers of two different species of beetles on the same tree. The beetles were given a constant source of food throughout the investigation. Number of beetles ...
... Scientists carried out an investigation into the interaction between different species of organisms. The table below shows the numbers of two different species of beetles on the same tree. The beetles were given a constant source of food throughout the investigation. Number of beetles ...
A food web perspective on large herbivore community limitation
... The exceptional diversity of large mammals in African savannas provides an ideal opportunity to explore the relative importance of top-down and bottom-up controls of large terrestrial herbivore communities. Recent work has emphasized the role of herbivore and carnivore body size in shaping these tro ...
... The exceptional diversity of large mammals in African savannas provides an ideal opportunity to explore the relative importance of top-down and bottom-up controls of large terrestrial herbivore communities. Recent work has emphasized the role of herbivore and carnivore body size in shaping these tro ...
Document
... mammals than on bacterial communities across the globe, yet the success of a project may be dependent on appropriate soil bacteria being present. • We know that animals often play key roles in structuring ecosystems. However, the majority of restoration efforts are focused on plant communities. • In ...
... mammals than on bacterial communities across the globe, yet the success of a project may be dependent on appropriate soil bacteria being present. • We know that animals often play key roles in structuring ecosystems. However, the majority of restoration efforts are focused on plant communities. • In ...
New Zealand`s Naturally Uncommon Ecosystems
... Abstract: We provide an overview of naturally uncommon ecosystems in New Zealand. Terrestrial ecosystems that were rare before humans colonised New Zealand often have highly specialised and diverse assemblages of flora and fauna, characterised by endemic and rare species. A national-scale typology p ...
... Abstract: We provide an overview of naturally uncommon ecosystems in New Zealand. Terrestrial ecosystems that were rare before humans colonised New Zealand often have highly specialised and diverse assemblages of flora and fauna, characterised by endemic and rare species. A national-scale typology p ...
a wide range of insect herbivores thus preventing many potential
... Managing ecosystem services in broadacre landscapes: what are the appropriate spatial scales? which appeared in the Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 48 (12): 1549-1559. It is one of a suite of papers published in this special edition of ...
... Managing ecosystem services in broadacre landscapes: what are the appropriate spatial scales? which appeared in the Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 48 (12): 1549-1559. It is one of a suite of papers published in this special edition of ...
The effects of disturbance on trophic levels, food webs
... in the aftermath of natural disturbance, while human disturbances are mostly associated with habitat loss and therefore recovery is not possible. In light of the number and significance of the ecosystem services that we rely on, preserving intact trophic structures will ensure we can continue to r ...
... in the aftermath of natural disturbance, while human disturbances are mostly associated with habitat loss and therefore recovery is not possible. In light of the number and significance of the ecosystem services that we rely on, preserving intact trophic structures will ensure we can continue to r ...
An experimental field mesocosm system to study multiple
... (2016). Multiple-stressor effects on stream invertebrates: DNA barcoding reveals contrasting responses of cryptic mayfly species. Ecological Indicators, 61, 159-169. ...
... (2016). Multiple-stressor effects on stream invertebrates: DNA barcoding reveals contrasting responses of cryptic mayfly species. Ecological Indicators, 61, 159-169. ...
Ecosystem Services - Digital Library Of The Commons
... is unrecognised and undervalued, which results in destruction of ecosystems. We discuss why this formulation has attracted ecologists and summarise the resultant contributions to research, particularly to the understanding of indirect or regulating services. We then outline three sets of weaknesses ...
... is unrecognised and undervalued, which results in destruction of ecosystems. We discuss why this formulation has attracted ecologists and summarise the resultant contributions to research, particularly to the understanding of indirect or regulating services. We then outline three sets of weaknesses ...
Community ecology and dynamics
... of P from litter and decreased activity of microbial decomposers. Proportion of fungi relative to bacteria increases. Fungal-based food webs retain nutrients better than bacterial-based food webs. Nutrient cycling thus becomes more closed & essential nutrients, especially P, become less available. S ...
... of P from litter and decreased activity of microbial decomposers. Proportion of fungi relative to bacteria increases. Fungal-based food webs retain nutrients better than bacterial-based food webs. Nutrient cycling thus becomes more closed & essential nutrients, especially P, become less available. S ...
Biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning: emerging issues and
... aquatic environments are small, and the high viscosity of water (compared to air) means that primary producers and consumers are often highly mobile and at the same time constrained and entrained by the medium as a result of water movements. The frequency and intensity of physical disturbance is lik ...
... aquatic environments are small, and the high viscosity of water (compared to air) means that primary producers and consumers are often highly mobile and at the same time constrained and entrained by the medium as a result of water movements. The frequency and intensity of physical disturbance is lik ...
Science GRADE: Biology TIMELINE: 4 th Quarter
... populations to become better adapted to their environment. ...
... populations to become better adapted to their environment. ...
American Samoa Archipelago - Western Pacific Fishery Council
... that can rapidly address new scientific information and changes in environmental conditions or human use patterns. 3. To improve public and government awareness and understanding of the marine environment in order to reduce unsustainable human impacts and foster support for responsible stewardship. ...
... that can rapidly address new scientific information and changes in environmental conditions or human use patterns. 3. To improve public and government awareness and understanding of the marine environment in order to reduce unsustainable human impacts and foster support for responsible stewardship. ...
Reference Sites in Ecological Restoration
... topographic positions in the landscape when the restoration site is an isolated fragment. Usually more than one reference site is considered when seeking guidance in the design of a restoration. These can be multiple sites that are similar in successional stage, structure, and function which provide ...
... topographic positions in the landscape when the restoration site is an isolated fragment. Usually more than one reference site is considered when seeking guidance in the design of a restoration. These can be multiple sites that are similar in successional stage, structure, and function which provide ...
Effects of stocking-up freshwater food webs
... Bottom-up control: resource regulation of growth and production typically beginning with biogeochemical control of photosynthesis Diel: daily, referring to events that recur at intervals of 24 hours or less with no connotation of either daytime or nighttime. Epilithion: biofilm (bacteria, algae) tha ...
... Bottom-up control: resource regulation of growth and production typically beginning with biogeochemical control of photosynthesis Diel: daily, referring to events that recur at intervals of 24 hours or less with no connotation of either daytime or nighttime. Epilithion: biofilm (bacteria, algae) tha ...
alteration of ecosystem nitrogen dynamics by exotic plants: a case
... Nitrogen cycling is an ecosystem function that may be particularly sensitive to changes in species composition. Species may affect ecosystem nitrogen (hereafter, N) cycling and storage by influencing rates of N input (e.g., N fixation; Vitousek et al. 1987, Musil and Midgley 1990, Witkowski 1991, St ...
... Nitrogen cycling is an ecosystem function that may be particularly sensitive to changes in species composition. Species may affect ecosystem nitrogen (hereafter, N) cycling and storage by influencing rates of N input (e.g., N fixation; Vitousek et al. 1987, Musil and Midgley 1990, Witkowski 1991, St ...
A2 level Biology Revision Notes - A
... 2. Period of r____ g_____ where the ever-increasing number of individuals continue to reproduce. The population size doubles during each interval of time 3. Period when population growth d_______ until its size remains more or less s_____. The decline may be due to food supply limiting numbers or to ...
... 2. Period of r____ g_____ where the ever-increasing number of individuals continue to reproduce. The population size doubles during each interval of time 3. Period when population growth d_______ until its size remains more or less s_____. The decline may be due to food supply limiting numbers or to ...
Ecological Dynamics on Yellowstone`s Northern Range
... major or irreversible changes in processes, ecosystem conditions, or population numbers? Theory and field studies have shown that some ecological systems change abruptly from one relatively stable state to another. In these situations, simply removing the factor or factors that caused change may not ...
... major or irreversible changes in processes, ecosystem conditions, or population numbers? Theory and field studies have shown that some ecological systems change abruptly from one relatively stable state to another. In these situations, simply removing the factor or factors that caused change may not ...
the functioning of marine ecosystems
... et al., 1997). Ecosystems carry out a diverse array of processes that provide both goods and services to humans. It also becomes important to understand what impacts an ecosystem can tolerate before major structural changes occur, and how reversible these changes are. In this respect, improved under ...
... et al., 1997). Ecosystems carry out a diverse array of processes that provide both goods and services to humans. It also becomes important to understand what impacts an ecosystem can tolerate before major structural changes occur, and how reversible these changes are. In this respect, improved under ...
I. Ch 8 plant health FINAL copy
... habitat both above ground and in the soil. Ecological approaches call for designing the field and farm to take advantage of the inherent strengths of natural systems. Most of this is done prior to, and during, planting a crop and has the goal of preventing problems from developing by contributing t ...
... habitat both above ground and in the soil. Ecological approaches call for designing the field and farm to take advantage of the inherent strengths of natural systems. Most of this is done prior to, and during, planting a crop and has the goal of preventing problems from developing by contributing t ...
What is ecology?
... The Nonliving Environment • Abiotic factors- the nonliving parts of an organism’s environment. • Examples include air currents, temperature, moisture, light, and soil. • Abiotic factors affect an organism’s life. copyright cmassengale ...
... The Nonliving Environment • Abiotic factors- the nonliving parts of an organism’s environment. • Examples include air currents, temperature, moisture, light, and soil. • Abiotic factors affect an organism’s life. copyright cmassengale ...
Assembly history dictates ecosystem functioning
... Community assembly history is increasingly recognized as a fundamental determinant of community structure. However, little is known as to how assembly history may affect ecosystem functioning via its effect on community structure. Using wood-decaying fungi as a model system, we provide experimental ...
... Community assembly history is increasingly recognized as a fundamental determinant of community structure. However, little is known as to how assembly history may affect ecosystem functioning via its effect on community structure. Using wood-decaying fungi as a model system, we provide experimental ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.























