Ecological Succession
... is the end result of the succession process • Does not always mean big trees – Grasses in prairies – Cacti in deserts ...
... is the end result of the succession process • Does not always mean big trees – Grasses in prairies – Cacti in deserts ...
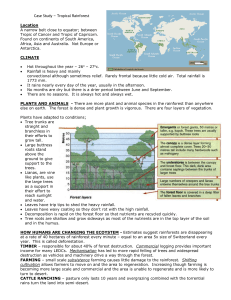
Case Study – Tropical Rainfores
... removed by helicopter because less damage is caused to forest. Sustainable sources - People in MEDCs can help by making sure that any furniture or wood they buy is from a forest where sustainable methods are used. Most products are not marked to show the customer if the wood is produced in this way. ...
... removed by helicopter because less damage is caused to forest. Sustainable sources - People in MEDCs can help by making sure that any furniture or wood they buy is from a forest where sustainable methods are used. Most products are not marked to show the customer if the wood is produced in this way. ...
Living Things Need Energy iI~I
... producers. They do this by using a process called photosynthesis. Most producers are plants, but algae and some bacteria are also producers. Grasses are the main producers in a prairie ecosystem. Examples of producers in other ecosystems include cordgrass and algae in a salt marsh and trees in a for ...
... producers. They do this by using a process called photosynthesis. Most producers are plants, but algae and some bacteria are also producers. Grasses are the main producers in a prairie ecosystem. Examples of producers in other ecosystems include cordgrass and algae in a salt marsh and trees in a for ...
Unit 1 - Cook County Schools
... 4. What are the differences in the main kinds of ecosystems? Content Materials such as nitrogen, water, and carbon are cycled through ecosystems, but energy is not. The energy available to organisms decreases as you move up the food chain. Abiotic factors (precipitation, temperature, and soil) ...
... 4. What are the differences in the main kinds of ecosystems? Content Materials such as nitrogen, water, and carbon are cycled through ecosystems, but energy is not. The energy available to organisms decreases as you move up the food chain. Abiotic factors (precipitation, temperature, and soil) ...
Chapter Summary 4 - Ecology
... dioxide (a ‘greenhouse gas’), due to the burning of fossil fuels, laid down about 350 million years ago. An Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has predicted mostly adverse environmental impacts as a consequence of global warming, triggered by this rising level of carbon dioxide. This is an en ...
... dioxide (a ‘greenhouse gas’), due to the burning of fossil fuels, laid down about 350 million years ago. An Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has predicted mostly adverse environmental impacts as a consequence of global warming, triggered by this rising level of carbon dioxide. This is an en ...
Introduction to Ecology October 7 Ecology
... Nitrogen cycleAtmospheric nitrogen (N2) makes up nearly 78%-80% of air. Organisms can not use it in that form. Lightning and bacteria convert nitrogen into usable forms. ...
... Nitrogen cycleAtmospheric nitrogen (N2) makes up nearly 78%-80% of air. Organisms can not use it in that form. Lightning and bacteria convert nitrogen into usable forms. ...
TAKS Objective 3
... • H Some bacteria are present in aquatic food chains in which fish are secondary ...
... • H Some bacteria are present in aquatic food chains in which fish are secondary ...
Ecology
... • Carnivores - eat animals. • Omnivores - eat both plant and animals. • Detritivores - feed on plant and animal remains and other dead matter ...
... • Carnivores - eat animals. • Omnivores - eat both plant and animals. • Detritivores - feed on plant and animal remains and other dead matter ...
INVASIVE SPECIES 6-8
... Benchmark B: Describe the characteristics of an organism in terms of a combination of inherited traits and recognize reproduction as a characteristic of living organisms essential to the continuation of the species. Grade Seven: Evolutionary Theory 8. Investigate the great diversity among organisms. ...
... Benchmark B: Describe the characteristics of an organism in terms of a combination of inherited traits and recognize reproduction as a characteristic of living organisms essential to the continuation of the species. Grade Seven: Evolutionary Theory 8. Investigate the great diversity among organisms. ...
Communities and Ecosystems
... Energy enters ecosystems in the form of sunlight It is captured by plants and stored in the chemical bonds of sugar (organic matter) Sugar is broken down by all cells to release the stored energy. This process is not completely efficient, and some of the energy is lost as heat. Thus, energy passes t ...
... Energy enters ecosystems in the form of sunlight It is captured by plants and stored in the chemical bonds of sugar (organic matter) Sugar is broken down by all cells to release the stored energy. This process is not completely efficient, and some of the energy is lost as heat. Thus, energy passes t ...
The biosphere - Hillpark Secondary School
... domestic, agricultural and industrial, giving an example of a pollutant from each. The main sources of pollution are agriculture (e.g. excess pesticides and fertilisers cause run off into nearby rivers), industry (carbon particles, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, oil, heavy metals, detergents, r ...
... domestic, agricultural and industrial, giving an example of a pollutant from each. The main sources of pollution are agriculture (e.g. excess pesticides and fertilisers cause run off into nearby rivers), industry (carbon particles, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, oil, heavy metals, detergents, r ...
Document
... Unlike the one-way flow of energy, matter is recycled within and between ecosystems. Water continuously flows between oceans, the atmosphere, and land – sometimes outside organisms and sometimes inside organisms. Every organism needs nutrients to build tissues and carry out life functions. Like wate ...
... Unlike the one-way flow of energy, matter is recycled within and between ecosystems. Water continuously flows between oceans, the atmosphere, and land – sometimes outside organisms and sometimes inside organisms. Every organism needs nutrients to build tissues and carry out life functions. Like wate ...
Ecological Roles and Relationships
... Examples of Producers • Producers include algae, single and multicellular plants, as well as photosynthetic bacteria • Microscopic aquatic algae are called phytoplankton • Some organisms are chemosynthetic, and use chemical and thermal energy from the Earth’s interior to produce their own food ...
... Examples of Producers • Producers include algae, single and multicellular plants, as well as photosynthetic bacteria • Microscopic aquatic algae are called phytoplankton • Some organisms are chemosynthetic, and use chemical and thermal energy from the Earth’s interior to produce their own food ...
6.6.05 The Ecosystem and Human Interference
... to the loss of energy between trophic levels. • Generally, only about 10% of the energy in one trophic level is available to the next trophic level. • This relationship explains why so few carnivores can be supported in a food web. ...
... to the loss of energy between trophic levels. • Generally, only about 10% of the energy in one trophic level is available to the next trophic level. • This relationship explains why so few carnivores can be supported in a food web. ...
Benthos
... • Tilling for crop production • Levees • Logging • Mining • Construction • Runoff • Air and water pollutants • Changing nutrient levels • Releasing toxic chemicals • Introducing non-native species to the ecosystem • Grazing by domestic animals ...
... • Tilling for crop production • Levees • Logging • Mining • Construction • Runoff • Air and water pollutants • Changing nutrient levels • Releasing toxic chemicals • Introducing non-native species to the ecosystem • Grazing by domestic animals ...
Chapter 2 Principles of Ecology
... • ** Descriptive - fur, Carnivora long, canines teeth, fur, warm blooded, feed young milk. • ** Quantitative - how many (International System of measuring; commonly known as SI ...
... • ** Descriptive - fur, Carnivora long, canines teeth, fur, warm blooded, feed young milk. • ** Quantitative - how many (International System of measuring; commonly known as SI ...
Thailand Case Study
... - disaster : frequency and severe cyclone/ typhoon - water resources : intrusion of saltwater, increase salinity of underground water - land use : land use change - socioeconomic and tourism: loss of tourism attraction area ...
... - disaster : frequency and severe cyclone/ typhoon - water resources : intrusion of saltwater, increase salinity of underground water - land use : land use change - socioeconomic and tourism: loss of tourism attraction area ...
Primary productivity
... creates a new land area that is colonized. The first colonists are termed pioneer species. Secondary Succession - an existing community is disrupted and a new one subsequently develops at the site Climax community - community that develops last and remains the longest ...
... creates a new land area that is colonized. The first colonists are termed pioneer species. Secondary Succession - an existing community is disrupted and a new one subsequently develops at the site Climax community - community that develops last and remains the longest ...
What should I know?
... Organisms that eat only animals = CARNIVORES (Ex: lions, owls, snakes) Organisms that eat both plants and animals = OMNIVORES (Ex: bears and most humans) Organisms that break down organic matter = DECOMPOSERS (Ex: bacteria and fungi) Any necessity of life, such as food, water, light, or space = RESO ...
... Organisms that eat only animals = CARNIVORES (Ex: lions, owls, snakes) Organisms that eat both plants and animals = OMNIVORES (Ex: bears and most humans) Organisms that break down organic matter = DECOMPOSERS (Ex: bacteria and fungi) Any necessity of life, such as food, water, light, or space = RESO ...
Document
... Secondary succession is likely to occur a. in a clear-cut deciduous forest. b. on an eroded, bare hillside. c. in an abandoned field. d. in a clear-cut deciduous forest and on an eroded, bare hillside. e. in a clear-cut deciduous forest, on an eroded, bare hillside, and in an abandoned field. Which ...
... Secondary succession is likely to occur a. in a clear-cut deciduous forest. b. on an eroded, bare hillside. c. in an abandoned field. d. in a clear-cut deciduous forest and on an eroded, bare hillside. e. in a clear-cut deciduous forest, on an eroded, bare hillside, and in an abandoned field. Which ...
Name Date ______ Ecological Communities Vocabulary Define
... 6. Complete the food chain below. Fill in each circle with one of the organisms in Word Bank A. Next, identify the role of each type of organism in the food chain by writing a label from Word Bank B on the lines below the circles. Then, use the percentages in Word Bank C to show how much energy is t ...
... 6. Complete the food chain below. Fill in each circle with one of the organisms in Word Bank A. Next, identify the role of each type of organism in the food chain by writing a label from Word Bank B on the lines below the circles. Then, use the percentages in Word Bank C to show how much energy is t ...