Invasive Plants
... Invasive plants are recognized worldwide as one of the greatest threats to biodiversity, because of their ability to outcompete native plants. Native vegetation is the cornerstone of healthy habitats and their relationship to other native plant species, soil, and animals is complex and delicate. Whe ...
... Invasive plants are recognized worldwide as one of the greatest threats to biodiversity, because of their ability to outcompete native plants. Native vegetation is the cornerstone of healthy habitats and their relationship to other native plant species, soil, and animals is complex and delicate. Whe ...
Earth as a Living System
... previously had filtered water before it seeped into the aquifer used by Vittel. In response Vittel developed an incentive package for farmers to improve their agricultural practices and consequently reduce water pollution that had affected Vittel's product. This is an example of a Payment for ecosys ...
... previously had filtered water before it seeped into the aquifer used by Vittel. In response Vittel developed an incentive package for farmers to improve their agricultural practices and consequently reduce water pollution that had affected Vittel's product. This is an example of a Payment for ecosys ...
3-acrostic-word-suggestions
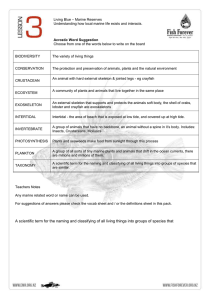
... An animal with hard external skeleton & jointed legs - eg crayfish A community of plants and animals that live together in the same place ...
... An animal with hard external skeleton & jointed legs - eg crayfish A community of plants and animals that live together in the same place ...
Temperate Forest
... important parts of the temperate forest. This is where the forest recycles most of its nutrients. Inside and beneath this leaf litter, thousands of small animals live, like beetles, millipedes, centipedes, and ants. Unseen microscopic creatures such as fungi and bacteria live there, too. All these o ...
... important parts of the temperate forest. This is where the forest recycles most of its nutrients. Inside and beneath this leaf litter, thousands of small animals live, like beetles, millipedes, centipedes, and ants. Unseen microscopic creatures such as fungi and bacteria live there, too. All these o ...
Plant Structure
... vessel; transport water and dissolved substances • Phloem: tubular cells that are stacked to form structures called tubes; move food from where it is made to other parts of the plant where it is used or stored ...
... vessel; transport water and dissolved substances • Phloem: tubular cells that are stacked to form structures called tubes; move food from where it is made to other parts of the plant where it is used or stored ...
“The Classification of Living Things” Video
... Some cause illness strep throat Many are helpful make cheese, yogurt, etc. o Most monerans trap the sun’s energy to make food. o Other bacteria, called Archaebacteria, use a chemical reaction to make food because they live where there is no sunlight (deep ocean floor). Kingdom Protista o M ...
... Some cause illness strep throat Many are helpful make cheese, yogurt, etc. o Most monerans trap the sun’s energy to make food. o Other bacteria, called Archaebacteria, use a chemical reaction to make food because they live where there is no sunlight (deep ocean floor). Kingdom Protista o M ...
Benchmark 3 study guide with answers
... 31. Fennec foxes live in the sandy Sahara Desert and other parts of North Africa. They are cream colored with black tipped tails. They forage for plants but also eat rodents, eggs, reptiles, and insects. ...
... 31. Fennec foxes live in the sandy Sahara Desert and other parts of North Africa. They are cream colored with black tipped tails. They forage for plants but also eat rodents, eggs, reptiles, and insects. ...
Ecology Unit Test Study Guide
... Plants produce their own food using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight (photosynthesis). This is different than ...
... Plants produce their own food using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight (photosynthesis). This is different than ...
Biology Standard SB4 (b)
... Nitrogen is a component of many organic molecules. It forms an essential part of amino acids (which make up proteins) and DNA. Nitrogen is essential for all living cells. What is the nitrogen cycle? Nitrogen is the major component of earth's atmosphere. It enters the food chain by means of nitroge ...
... Nitrogen is a component of many organic molecules. It forms an essential part of amino acids (which make up proteins) and DNA. Nitrogen is essential for all living cells. What is the nitrogen cycle? Nitrogen is the major component of earth's atmosphere. It enters the food chain by means of nitroge ...
1- Autotrophs
... 3- Saprotrophs (Greek: sapros - rotten; trophos - feeder) are also called decomposers or reducers for example, fungi and bacteria. They break down the complex organic compounds in dead matter (plants and animals) into simpler form which can be reused. Decomposers do not ingest their food. Instead th ...
... 3- Saprotrophs (Greek: sapros - rotten; trophos - feeder) are also called decomposers or reducers for example, fungi and bacteria. They break down the complex organic compounds in dead matter (plants and animals) into simpler form which can be reused. Decomposers do not ingest their food. Instead th ...
Gymnosperm Angiosperm
... making trips to the surface in order to breathe. Soon, they start to eat small invertebrates. From then on, their diet becomes increasingly carnivorous, or meat-eating. As they continue to grow, they begin to develop legs and their tails shrink. Amphibians have smooth, moist, thin skin which is cove ...
... making trips to the surface in order to breathe. Soon, they start to eat small invertebrates. From then on, their diet becomes increasingly carnivorous, or meat-eating. As they continue to grow, they begin to develop legs and their tails shrink. Amphibians have smooth, moist, thin skin which is cove ...
Food Webs & Chains
... within it’s community. Includes what it eats, when it eats and where it lives. Coral, plankton, fish ...
... within it’s community. Includes what it eats, when it eats and where it lives. Coral, plankton, fish ...
INSECT – PLANT INTERACTIONS
... RADIATIONS OF PHYTOPHAGOUS INSECTS Hymenoptera – Ancestrally all hymenopterans were phytophagous Basal hymenopterans all eat plants Secondary plant feeding by larval Cynipidae (galls), chalcid wasps (breeding w/in seeds), and assorted other groups like leaf-cutter bees and ants (although leaf-cutte ...
... RADIATIONS OF PHYTOPHAGOUS INSECTS Hymenoptera – Ancestrally all hymenopterans were phytophagous Basal hymenopterans all eat plants Secondary plant feeding by larval Cynipidae (galls), chalcid wasps (breeding w/in seeds), and assorted other groups like leaf-cutter bees and ants (although leaf-cutte ...
PPT
... plants and are used to make plant proteins. Animals make proteins from amino acids derived from plant proteins. •Dead plant and animal tissue is decomposed by bacterial action. Other bacteria in the soil transform nitrogen products to reduce more soil nitrates for plants. ...
... plants and are used to make plant proteins. Animals make proteins from amino acids derived from plant proteins. •Dead plant and animal tissue is decomposed by bacterial action. Other bacteria in the soil transform nitrogen products to reduce more soil nitrates for plants. ...
Chapter 5
... This process in which sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water are used by plants, algae and bacteria to make carbohydrates, oxygen, and water ...
... This process in which sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water are used by plants, algae and bacteria to make carbohydrates, oxygen, and water ...
Communities: How Do Species Interact?
... • A parasite consumes only part of its host, and does not necessarily kill the host. • A “good” parasite would harm its host as little as possible so it would have a place to live. • A predator usually kills its prey and consumes most of the prey’s body. – Use swiftness, intelligence, acute senses ...
... • A parasite consumes only part of its host, and does not necessarily kill the host. • A “good” parasite would harm its host as little as possible so it would have a place to live. • A predator usually kills its prey and consumes most of the prey’s body. – Use swiftness, intelligence, acute senses ...
Trophic Levels in Food Chains and Webs (Chap. 46)
... a previous community had been – more rapid than 1º succession • fields small plants, shrubs forests ...
... a previous community had been – more rapid than 1º succession • fields small plants, shrubs forests ...
ahsge 2 - Auburn City Schools
... food. Predators are consumers that capture and eat other consumers. The prey is the organism that is captured by the ...
... food. Predators are consumers that capture and eat other consumers. The prey is the organism that is captured by the ...
XVII International Botanical Congress – Abstracts
... Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are ubiquitous in nature and associate with the roots of about 75% of all vascular plants. The association is considered to be mutualistic, because the mycorrhiza donates mineral nutrients to the plant in return for a supply of organic carbon. Both of these features mean ...
... Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are ubiquitous in nature and associate with the roots of about 75% of all vascular plants. The association is considered to be mutualistic, because the mycorrhiza donates mineral nutrients to the plant in return for a supply of organic carbon. Both of these features mean ...
Name
... Fill in the diagram below with the Levels of Organization studied in Ecology. Use the terms from the table above. ...
... Fill in the diagram below with the Levels of Organization studied in Ecology. Use the terms from the table above. ...
Herbivore
_grazing_-_20050809.jpg?width=300)
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthparts adapted to rasping or grinding. Horses and other herbivores have wide flat teeth that are adapted to grinding grass, tree bark, and other tough plant material.