What is a predator? Predators
... animals need the flesh of the animals that they kill to survive. Weasels, hawks, wolves, mountain lions, and grizzly bears are all predators. Predators are carnivores, which means their diet consists of meat. Some predators, such as coyotes and bears are also scavengers, meaning they will eat the ca ...
... animals need the flesh of the animals that they kill to survive. Weasels, hawks, wolves, mountain lions, and grizzly bears are all predators. Predators are carnivores, which means their diet consists of meat. Some predators, such as coyotes and bears are also scavengers, meaning they will eat the ca ...
Name____________________ Date__________ Pd
... An organism that gain nutrition by breaking down dead and decaying plants & animals. An organism that uses energy to produce its own food. An organism that consumes both producers and consumers. An organism that eats other consumers. Plants, grass, and trees are examples of this. ...
... An organism that gain nutrition by breaking down dead and decaying plants & animals. An organism that uses energy to produce its own food. An organism that consumes both producers and consumers. An organism that eats other consumers. Plants, grass, and trees are examples of this. ...
First results from an experiment excluding three sizes classes of
... proved that the experimental setup worked. The majority of plant groups did not respond to exclusion of herbivores, supporting our expectation that vegetation responses in tundra are generally too slow to be measured during one growing season. The plant groups with highest growth rates and palatabil ...
... proved that the experimental setup worked. The majority of plant groups did not respond to exclusion of herbivores, supporting our expectation that vegetation responses in tundra are generally too slow to be measured during one growing season. The plant groups with highest growth rates and palatabil ...
Science 10 - SharpSchool
... – This is the interaction between two organisms that is not long lasting and the species do not necessarily live together – Predation – an interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, called the prey. ...
... – This is the interaction between two organisms that is not long lasting and the species do not necessarily live together – Predation – an interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, called the prey. ...
Notes - Academic Workshop
... What are some things that you could do without and still have all of your basic needs met? ____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________ ...
... What are some things that you could do without and still have all of your basic needs met? ____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________ ...
The Chaparral Ecosystem
... diamondback rattlesnake. The rattle snake, carrying a smaller amount of energy from its meal, is then consumed by the red-tailed hawk and its energy is likewise diluted. The Organisms contained within this chain are sorted into levels in the the food chain based on dietary ...
... diamondback rattlesnake. The rattle snake, carrying a smaller amount of energy from its meal, is then consumed by the red-tailed hawk and its energy is likewise diluted. The Organisms contained within this chain are sorted into levels in the the food chain based on dietary ...
Biology: Chapters 3-4
... predation: one creature captures and eats another parasitism: one organism lives in or on another organism mutualism: both species benefit commensalism: one organism benefits, the other is neither helped nor harmed ex: remora ...
... predation: one creature captures and eats another parasitism: one organism lives in or on another organism mutualism: both species benefit commensalism: one organism benefits, the other is neither helped nor harmed ex: remora ...
Chapter 21 The Living Planet (SP09)
... In the areas provided below, describe what this biome is like. Make sure you tell where you might find it, what the temperature and precipitation is like, what kind of plants and animals live here etc. ...
... In the areas provided below, describe what this biome is like. Make sure you tell where you might find it, what the temperature and precipitation is like, what kind of plants and animals live here etc. ...
Plant Volatiles - life.illinois.edu
... Heil et al. (2005) Postsecretory hydrolysis of nectar sucrose and specialization in ant/plant mutualism. Science 308 (5721) Plants provide sugars for which ants have no catabolic enzyme. ...
... Heil et al. (2005) Postsecretory hydrolysis of nectar sucrose and specialization in ant/plant mutualism. Science 308 (5721) Plants provide sugars for which ants have no catabolic enzyme. ...
Chapter 2 - Holden R
... Mosses or ferns grow on larger plants, which provide a habitat, but are not damaged Parasitism- one species benefits and the other is harmed For example: ticks benefit by gaining food and dogs can be harmed by diseases carried by ticks Mutualism- both species benefit For example: ants and acac ...
... Mosses or ferns grow on larger plants, which provide a habitat, but are not damaged Parasitism- one species benefits and the other is harmed For example: ticks benefit by gaining food and dogs can be harmed by diseases carried by ticks Mutualism- both species benefit For example: ants and acac ...
7th Grade - Vernon Independent School District
... Primary Succession- begins in an area that has not been previously occupied by a community (exs-exposed rock); there is no soil Secondary Succession- begins on an area where a community has previously existed; is on soil Pioneer Species- first species to begin growing in an area (moss & ...
... Primary Succession- begins in an area that has not been previously occupied by a community (exs-exposed rock); there is no soil Secondary Succession- begins on an area where a community has previously existed; is on soil Pioneer Species- first species to begin growing in an area (moss & ...
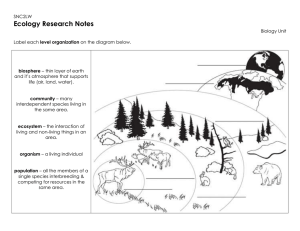
Ecology Study Guide Unit 2 Test on Friday 9-25
... 10. What is the combined portions of Earth called in which all living things exist? 11. All of the members of a particular species that live in the same area are called a(an) 12. What is the original source of almost all the energy in most ecosystems? 13. An organism that cannot make its own food is ...
... 10. What is the combined portions of Earth called in which all living things exist? 11. All of the members of a particular species that live in the same area are called a(an) 12. What is the original source of almost all the energy in most ecosystems? 13. An organism that cannot make its own food is ...
Life Science Study Guide Environment – Everything that surrounds
... Consumers – An organism that cannot make its own food. Consumers eat other organisms. Decomposer – An organism that breaks down dead plants and animals and returns the nutrients to the soil. Bacteria, fungi (mushrooms and yeast), termites, and earthworms are examples of decomposers. Plants then use ...
... Consumers – An organism that cannot make its own food. Consumers eat other organisms. Decomposer – An organism that breaks down dead plants and animals and returns the nutrients to the soil. Bacteria, fungi (mushrooms and yeast), termites, and earthworms are examples of decomposers. Plants then use ...
Animal Kingdom
... Their cells have cell walls. The cells have chloroplasts, the cell parts that use the Sun’s energy to make food. Some protists, such as algae, share characteristics with plants. However, unlike any protist, many members of the plant kingdom have developed an important ability. They can live in dry p ...
... Their cells have cell walls. The cells have chloroplasts, the cell parts that use the Sun’s energy to make food. Some protists, such as algae, share characteristics with plants. However, unlike any protist, many members of the plant kingdom have developed an important ability. They can live in dry p ...
Period - kehsscience.org
... Main Idea: An ecosystem includes both abiotic and biotic factors. Producers provide energy for other organisms in an ecosystem. Complete the following sentences with the correct term from the list below autotrophs eating nonliving abiotic living temperature producers moisture plants animals biotic c ...
... Main Idea: An ecosystem includes both abiotic and biotic factors. Producers provide energy for other organisms in an ecosystem. Complete the following sentences with the correct term from the list below autotrophs eating nonliving abiotic living temperature producers moisture plants animals biotic c ...
The earth rotates on an imaginary line called a(n)
... by breaking down dead organisms. c. They make food for the ...
... by breaking down dead organisms. c. They make food for the ...
AP Study Guide for Behavior/Ecology Unit Test
... Ecological Footprint and comparisons for various countries Chapter 53 – Community Ecology What is meant by a community along with community interactions: Symbiosis (mutualism, parasitism and commensalism) competition, predation, herbivores, importance of carnivores, decomposers/detritivores Trophic ...
... Ecological Footprint and comparisons for various countries Chapter 53 – Community Ecology What is meant by a community along with community interactions: Symbiosis (mutualism, parasitism and commensalism) competition, predation, herbivores, importance of carnivores, decomposers/detritivores Trophic ...
Herbivore
_grazing_-_20050809.jpg?width=300)
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthparts adapted to rasping or grinding. Horses and other herbivores have wide flat teeth that are adapted to grinding grass, tree bark, and other tough plant material.