Biological Neurons and Neural Networks, Artificial Neurons
... The human brain is extremely energy efficient, using approximately 10-16 joules per operation per second, whereas the best computers today use around 10-6 joules ...
... The human brain is extremely energy efficient, using approximately 10-16 joules per operation per second, whereas the best computers today use around 10-6 joules ...
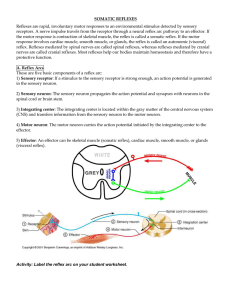
Reflex Activity/Lab
... the motor response is contraction of skeletal muscle, the reflex is called a somatic reflex. If the motor response involves cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, or glands, the reflex is called an autonomic (visceral) reflex. Reflexes mediated by spinal nerves are called spinal reflexes, whereas reflexes m ...
... the motor response is contraction of skeletal muscle, the reflex is called a somatic reflex. If the motor response involves cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, or glands, the reflex is called an autonomic (visceral) reflex. Reflexes mediated by spinal nerves are called spinal reflexes, whereas reflexes m ...
INTRODUCTION - Faculty & Staff Webpages
... – Autonomic sensory neurons are associated with interoceptors. – Autonomic sensory input is not consciously perceived. • The ANS also receives sensory input from somatic senses and special sensory neurons. • The autonomic motor neurons regulate visceral activities by either increasing (exciting) or ...
... – Autonomic sensory neurons are associated with interoceptors. – Autonomic sensory input is not consciously perceived. • The ANS also receives sensory input from somatic senses and special sensory neurons. • The autonomic motor neurons regulate visceral activities by either increasing (exciting) or ...
22_LectureSlides
... • Feed-forward control-predictive – Response anticipates stimulus – More timely, but depends on practice ...
... • Feed-forward control-predictive – Response anticipates stimulus – More timely, but depends on practice ...
Culture of primary rat hippocampal neurons
... by such species is the suspect of many human maladies, including aging, neurodegenerative disorders, and diabetes (Wallace 2005). Many important aspects of neural function are mediated by local signals that impinge on only one part of the cell. For example, growth cones at the tips of axons are sens ...
... by such species is the suspect of many human maladies, including aging, neurodegenerative disorders, and diabetes (Wallace 2005). Many important aspects of neural function are mediated by local signals that impinge on only one part of the cell. For example, growth cones at the tips of axons are sens ...
Feedback — Exam
... strengthens/weakens as a function of the timing of prevs. postsynaptic spikes (STDP). Mark the correct sentences. When the pre synaptic cell fires a spike immediately after the post synaptic cell – no change in the synaptic strength When the postsynaptic spike fires before the pre-synaptic spike, th ...
... strengthens/weakens as a function of the timing of prevs. postsynaptic spikes (STDP). Mark the correct sentences. When the pre synaptic cell fires a spike immediately after the post synaptic cell – no change in the synaptic strength When the postsynaptic spike fires before the pre-synaptic spike, th ...
Name Nervous System Questions 1. When a neuron is at its resting
... A. the inside of the cell is positively charged relative to the outside. B. sodium-potassium pumps transport sodium ions into the cell. C. gated sodium channels are open. D. sodium-potassium pumps transport both sodium and potassium ions out of the cell. E. there are more potassium ions inside the n ...
... A. the inside of the cell is positively charged relative to the outside. B. sodium-potassium pumps transport sodium ions into the cell. C. gated sodium channels are open. D. sodium-potassium pumps transport both sodium and potassium ions out of the cell. E. there are more potassium ions inside the n ...
Irregular persistent activity induced by synaptic excitatory feedback
... Brunel and Wang, 2001), though not very robustly. However, these models do not account for the high irregularity shown in the experiments. While high irregularity can be obtained robustly in the baseline period, provided inhibition is sufficiently strong, because neurons receive synaptic inputs that ...
... Brunel and Wang, 2001), though not very robustly. However, these models do not account for the high irregularity shown in the experiments. While high irregularity can be obtained robustly in the baseline period, provided inhibition is sufficiently strong, because neurons receive synaptic inputs that ...
Eds., M. Kawaguchi, K. Misaki, H. Sato, T. Yokokawa, T.... and S. Tanabe, pp. 41–48.
... In the freshwater goby embryo, the position of craniofacial peripheral nerves (ON, OC, nV, nVII-X, nALL) was identical to the other vertebrates (Kuratani and Horigome, 2000; Murakami and Watanabe, 2009). Furthermore, the topological distribution of the identified tracts of longitudinal and transvers ...
... In the freshwater goby embryo, the position of craniofacial peripheral nerves (ON, OC, nV, nVII-X, nALL) was identical to the other vertebrates (Kuratani and Horigome, 2000; Murakami and Watanabe, 2009). Furthermore, the topological distribution of the identified tracts of longitudinal and transvers ...
An Introduction to the ANS and Higher
... Two divisions have opposing effects on heart function 1. Parasympathetic division • Acetylcholine released by postganglionic fibers slows heart rate 2. Sympathetic division • NE released by varicosities accelerates heart rate • Balance between two divisions • Autonomic tone is present • Releases sma ...
... Two divisions have opposing effects on heart function 1. Parasympathetic division • Acetylcholine released by postganglionic fibers slows heart rate 2. Sympathetic division • NE released by varicosities accelerates heart rate • Balance between two divisions • Autonomic tone is present • Releases sma ...
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... The gray matter in the center surrounds the central core Looks like a butterfly ...
... The gray matter in the center surrounds the central core Looks like a butterfly ...
Biology Nervous System - Educational Research Center
... − the nervous system and the endocrine system are related such that both achieve communication among different body organs. − the speed of propagation depends on external factors such as temperature, alcohol, drugs and certain medicines. − the striated contractile muscle fibers of the skeletal muscl ...
... − the nervous system and the endocrine system are related such that both achieve communication among different body organs. − the speed of propagation depends on external factors such as temperature, alcohol, drugs and certain medicines. − the striated contractile muscle fibers of the skeletal muscl ...
Neurobiology of learning
... inactive, isolated mice did. These results were observed in mice of all ages. ...
... inactive, isolated mice did. These results were observed in mice of all ages. ...
File
... Imagine running a sprint. After you finish running, you will need a period of time (ARP) to calm down before you will run again. After you completely recover, you can run again, but you will need some more intense motivation (RRP), because you don’t really feel like sprinting again. ...
... Imagine running a sprint. After you finish running, you will need a period of time (ARP) to calm down before you will run again. After you completely recover, you can run again, but you will need some more intense motivation (RRP), because you don’t really feel like sprinting again. ...
25. Organ of balance and hearing
... direction and rate at which movement occurs (Figure 15-15) Depends on the functioning of the cristae ampullaris, located in the ampulla of each semicircular duct Cupula: gelatinous cap where the hair cells of cristae are ...
... direction and rate at which movement occurs (Figure 15-15) Depends on the functioning of the cristae ampullaris, located in the ampulla of each semicircular duct Cupula: gelatinous cap where the hair cells of cristae are ...
neural control of respiration
... Skeletal muscles provide the motive force for respiration. Unlike cardiac or smooth muscle, they have no rhythmic "beat" of their own; they depend entirely on the nervous system for a stimulus to contract. Two separate neural systems control respiration: (1) Voluntary control originates in cerebral ...
... Skeletal muscles provide the motive force for respiration. Unlike cardiac or smooth muscle, they have no rhythmic "beat" of their own; they depend entirely on the nervous system for a stimulus to contract. Two separate neural systems control respiration: (1) Voluntary control originates in cerebral ...
Nervous Systems II PPT
... ◦ Nuclei = groupings of neuronal call bodies ◦ Tracts = groupings of neuronal axons ...
... ◦ Nuclei = groupings of neuronal call bodies ◦ Tracts = groupings of neuronal axons ...
Chapter-01
... Nerve cells or receptors that are capable of receiving stimuli from within the body and external environment are located in sense organs and in other different organs. Receptors are modified neurons. They are of different types. Rods and cones in the eye, sound receptors in the ear, taste receptors ...
... Nerve cells or receptors that are capable of receiving stimuli from within the body and external environment are located in sense organs and in other different organs. Receptors are modified neurons. They are of different types. Rods and cones in the eye, sound receptors in the ear, taste receptors ...
Chapter 13 *Lecture PowerPoint The Spinal Cord,
... • Spinal cord communicates with the rest of the body by way of spinal nerves • Nerve—a cordlike organ composed of numerous nerve fibers (axons) bound together by connective tissue – Mixed nerves contain both afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) fibers ...
... • Spinal cord communicates with the rest of the body by way of spinal nerves • Nerve—a cordlike organ composed of numerous nerve fibers (axons) bound together by connective tissue – Mixed nerves contain both afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) fibers ...
Synaptic Competition during the Reformation of a Neuromuscular Map
... Previous work from our laboratory and those of others has shown that the spinal motor neuron pools of some muscles re-establish a topographic map after their innervation has been interrupted (Brown and Hardman, 1987; Hardman and Brown, 1987; Laskowski and Sanes, 1988; DeSantis et al., 1992; Grow et ...
... Previous work from our laboratory and those of others has shown that the spinal motor neuron pools of some muscles re-establish a topographic map after their innervation has been interrupted (Brown and Hardman, 1987; Hardman and Brown, 1987; Laskowski and Sanes, 1988; DeSantis et al., 1992; Grow et ...
Diapositive 1 - Andrei Gorea, Ph
... 4. Perception corresponds to the activity of a small selection from the very numerous high-level neurons, each of which corresponds to a pattern of external events of the order of complexity of the events symbolized by a word [grand-mother cells]. 5. High impulse frequency in such neurons correspond ...
... 4. Perception corresponds to the activity of a small selection from the very numerous high-level neurons, each of which corresponds to a pattern of external events of the order of complexity of the events symbolized by a word [grand-mother cells]. 5. High impulse frequency in such neurons correspond ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.