f19c623c99fc721
... normal reflex in infants, but it is usually associated with a disturbance of the pyramidal tract in children and adults. ...
... normal reflex in infants, but it is usually associated with a disturbance of the pyramidal tract in children and adults. ...
Visually Induced Ocular Torsion
... visual scene enriched with spatial clues important for maintaining posture was found to induce significantly more torsion compared to a scene without spatial clues. The degree of stimuli tilt had no significant effect, nor the stimuli periphery. In the second study, torsional response was shown to d ...
... visual scene enriched with spatial clues important for maintaining posture was found to induce significantly more torsion compared to a scene without spatial clues. The degree of stimuli tilt had no significant effect, nor the stimuli periphery. In the second study, torsional response was shown to d ...
MND Australia International Research Update
... mice in which a protein that is required for RNA editing was deleted. These mice developed a progressive loss of spinal motor neurones, leading to muscle denervation and paralysis. This work provides hard evidence that change to RNA leads to motor neurone death. Disruption in RNA processing has been ...
... mice in which a protein that is required for RNA editing was deleted. These mice developed a progressive loss of spinal motor neurones, leading to muscle denervation and paralysis. This work provides hard evidence that change to RNA leads to motor neurone death. Disruption in RNA processing has been ...
Nervous Tissue - Manasquan Public Schools
... Two Kinds of Nerve Fibers dendrites - neurons usually contain many axons - neurons contain only one ...
... Two Kinds of Nerve Fibers dendrites - neurons usually contain many axons - neurons contain only one ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM PHYSIOLOGY 5 (updated)
... relaxes the lens ligaments lens to become thicker and increase its refractive power the eye focuses on objects nearer than when the eye has less refractive power. As a distant object moves toward the eye, the number of PS impulses impinging on the ciliary muscle must be progressively increased ...
... relaxes the lens ligaments lens to become thicker and increase its refractive power the eye focuses on objects nearer than when the eye has less refractive power. As a distant object moves toward the eye, the number of PS impulses impinging on the ciliary muscle must be progressively increased ...
ecture 23- special senses
... They contain receptors called odorant-binding proteins that match specific odorant particles. They can only be stimulated by water-soluble and lipid-soluble particles that can diffuse through the overlaying mucus. Depolarization is produced the G protein-second messenger mechanism. ...
... They contain receptors called odorant-binding proteins that match specific odorant particles. They can only be stimulated by water-soluble and lipid-soluble particles that can diffuse through the overlaying mucus. Depolarization is produced the G protein-second messenger mechanism. ...
CHAPTER 5: SIMPLE NERVOUS SYSTEMS AND BEHAVIOR
... • Explicit or declarative memory: the recall of information about people, places, and objects, and it requires the medial temporal lobe and the hippocampus. • Implicit or procedural memory: perceptual/motor skills, habits, including classical and operant conditioning, habituation, and sensitization. ...
... • Explicit or declarative memory: the recall of information about people, places, and objects, and it requires the medial temporal lobe and the hippocampus. • Implicit or procedural memory: perceptual/motor skills, habits, including classical and operant conditioning, habituation, and sensitization. ...
Study materials CNS
... glucose blood level and percepted like a positive sensation after food b) HUNGER CENTRE is situated in the lateral HT nucleus, it has the permanent activity which is decreased for some time by stimulation of the satiety centre after food intake c) HYPOTHALAMIC GLUCOSTATIC NEURONS (glucostats) – the ...
... glucose blood level and percepted like a positive sensation after food b) HUNGER CENTRE is situated in the lateral HT nucleus, it has the permanent activity which is decreased for some time by stimulation of the satiety centre after food intake c) HYPOTHALAMIC GLUCOSTATIC NEURONS (glucostats) – the ...
Muscle fiber and motor end plate involvement in the
... was a decrease in the number of synaptic vesicles in the axonal terminals. A comparable reduction in the number of synaptic vesicles was found by us in the limb musculature of the presently studied strain of animals.11 This alteration of the axonal terminal did not seem to be a significant factor in ...
... was a decrease in the number of synaptic vesicles in the axonal terminals. A comparable reduction in the number of synaptic vesicles was found by us in the limb musculature of the presently studied strain of animals.11 This alteration of the axonal terminal did not seem to be a significant factor in ...
Pain pathway
... ascend all the way to terminate in the thalamus. The other two tracts terminate at brainstem levels. Then synapse with: 3rd order neuron – cell body in thalamus, ascend ipsilaterally to project to somatosensory cortex. ...
... ascend all the way to terminate in the thalamus. The other two tracts terminate at brainstem levels. Then synapse with: 3rd order neuron – cell body in thalamus, ascend ipsilaterally to project to somatosensory cortex. ...
File
... 1. How many hours of sleep to you need to get in order to be fully alert? 2. What is the name of your Biological Timing System and how does it change during the teenage years? 3. What analogy does the announcer use for a teen that is trying to function with not enough sleep? 4. What are three daily ...
... 1. How many hours of sleep to you need to get in order to be fully alert? 2. What is the name of your Biological Timing System and how does it change during the teenage years? 3. What analogy does the announcer use for a teen that is trying to function with not enough sleep? 4. What are three daily ...
Spinal Cord/ Reflex Action mainly
... Impulse OUT via ventral root Muscle to carry out response (move hand or foot etc) Brain becomes aware of what has happened ...
... Impulse OUT via ventral root Muscle to carry out response (move hand or foot etc) Brain becomes aware of what has happened ...
Taste and Smell - Liberty Hill High School
... taste buds on epiglottis an pharynx These afferent fibers synapse in medullathalamus gustatory cortex in parietal lobes and fibers to hypothalamus in limbic system ...
... taste buds on epiglottis an pharynx These afferent fibers synapse in medullathalamus gustatory cortex in parietal lobes and fibers to hypothalamus in limbic system ...
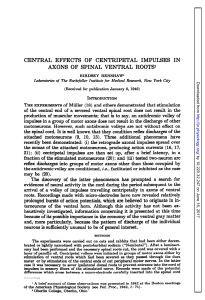
central effects of centripetal impulses in axons of spinal ventral roots
... employed but the action potentials of a second neuron, which discharged 4-5 times, were recorded. At a position intermediate between the two points (records b), small potential changes indicated the activity of both neurons and perhaps of others as well. Current concepts suggest that the repetitive ...
... employed but the action potentials of a second neuron, which discharged 4-5 times, were recorded. At a position intermediate between the two points (records b), small potential changes indicated the activity of both neurons and perhaps of others as well. Current concepts suggest that the repetitive ...
Signaling in large-scale neural networks
... networks. The gap between the constituents and the functional whole is aggravated in large-scale networks because neurons receive signals from a large number of other neurons. For this reason, the activity of individual neurons is rarely directly relatable to singular events in other neurons or in t ...
... networks. The gap between the constituents and the functional whole is aggravated in large-scale networks because neurons receive signals from a large number of other neurons. For this reason, the activity of individual neurons is rarely directly relatable to singular events in other neurons or in t ...
Sodium channel NaV1.9 mutations associated with insensitivity to
... the threshold for excitability of peripheral nociceptive sensory neurons by modulating both the RMP and responses to subthreshold stimuli (14, 15, 17, 23). Voltage-gated sodium channels have been implicated in genetic pain disorders by the discovery of mutations in the genes encoding NaV1.7, NaV1.8, ...
... the threshold for excitability of peripheral nociceptive sensory neurons by modulating both the RMP and responses to subthreshold stimuli (14, 15, 17, 23). Voltage-gated sodium channels have been implicated in genetic pain disorders by the discovery of mutations in the genes encoding NaV1.7, NaV1.8, ...
Chapter 15
... Preganglionic neuron ascends or descends to another ganglion along sympathetic chain before synapsing with postganglionic neuron. An axon may project through a ganglion and synapse with a postglanglionic neuron in one of the prevertebral ganglia. Preganglionic sympathetic fibers synapse on the adren ...
... Preganglionic neuron ascends or descends to another ganglion along sympathetic chain before synapsing with postganglionic neuron. An axon may project through a ganglion and synapse with a postglanglionic neuron in one of the prevertebral ganglia. Preganglionic sympathetic fibers synapse on the adren ...
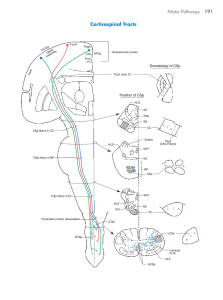
Lecture 3 Figure 1
... Corticonuclear (corticobulbar) fibers arise in the frontal eye fields (areas 6 and 8 in caudal portions of the middle frontal gyrus), the precentral gyrus (somatomotor cortex, area 4), and some originate from the postcentral gyrus (areas 3,1, 2). Fibers from area 4 occupy the genu of the internal caps ...
... Corticonuclear (corticobulbar) fibers arise in the frontal eye fields (areas 6 and 8 in caudal portions of the middle frontal gyrus), the precentral gyrus (somatomotor cortex, area 4), and some originate from the postcentral gyrus (areas 3,1, 2). Fibers from area 4 occupy the genu of the internal caps ...
Communication
... A thick lens gives a clear focus on a near object. This is illustrated by the results as the lens was 13cm away from the screen, compared to the thin lens which was 28cm. This indicates that a thick lens accommodates best when focusing on a near object. Through this experiment links can be drawn bet ...
... A thick lens gives a clear focus on a near object. This is illustrated by the results as the lens was 13cm away from the screen, compared to the thin lens which was 28cm. This indicates that a thick lens accommodates best when focusing on a near object. Through this experiment links can be drawn bet ...
... 3. Identify the cortical regions important for primary gustation 4. Compare and contrast olfaction with other sensory modalities, including its cranial nerve and nature of projection to cortex 5. Discuss how sub-modalities of taste and smell are sorted as they ascend to the cortex 6. Appreciate that ...
Document
... to yield unique patterns of axonal connections. Although NGF controls survival, maturation and axonal projections of nociceptors of different vertebrates, whether the NGF signal is differentially transduced in different species to yield unique features of nociceptor circuits is unclear. Results We i ...
... to yield unique patterns of axonal connections. Although NGF controls survival, maturation and axonal projections of nociceptors of different vertebrates, whether the NGF signal is differentially transduced in different species to yield unique features of nociceptor circuits is unclear. Results We i ...
Nerve activates contraction
... structures plays in nerve cell function. 4.Surround your nerve cell with: astrocytes, microglial cells, and Oligodendrocytes. 5.Explain the supporting role these cells play in nerve tissue ...
... structures plays in nerve cell function. 4.Surround your nerve cell with: astrocytes, microglial cells, and Oligodendrocytes. 5.Explain the supporting role these cells play in nerve tissue ...
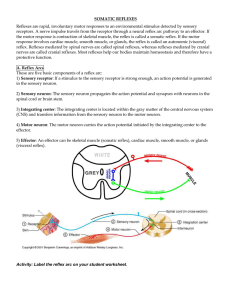
Reflex Activity/Lab
... the motor response is contraction of skeletal muscle, the reflex is called a somatic reflex. If the motor response involves cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, or glands, the reflex is called an autonomic (visceral) reflex. Reflexes mediated by spinal nerves are called spinal reflexes, whereas reflexes m ...
... the motor response is contraction of skeletal muscle, the reflex is called a somatic reflex. If the motor response involves cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, or glands, the reflex is called an autonomic (visceral) reflex. Reflexes mediated by spinal nerves are called spinal reflexes, whereas reflexes m ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.