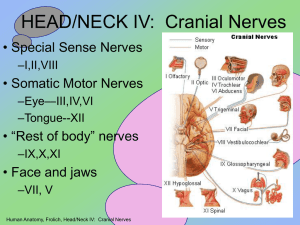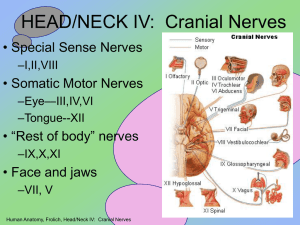
HEAD/NECK IV: Cranial Nerves
... (exits cranial cavity with VIII--internal auditory meatus) • Facial muscles (five branches fan out over face from stylomastoid foramen) ...
... (exits cranial cavity with VIII--internal auditory meatus) • Facial muscles (five branches fan out over face from stylomastoid foramen) ...
HEAD/NECK IV: Cranial Nerves
... (exits cranial cavity with VIII--internal auditory meatus) • Facial muscles (five branches fan out over face from stylomastoid foramen) ...
... (exits cranial cavity with VIII--internal auditory meatus) • Facial muscles (five branches fan out over face from stylomastoid foramen) ...
Concept of pain
... . Pain is negative biological necessity, as its formation is always associated with a change of fundamental homeostatic constants. The most significant of these is the integrity of the containment body (skin, mucous membranes, peritoneum, etc..) And the oxygen level of tissue. In response to damage ...
... . Pain is negative biological necessity, as its formation is always associated with a change of fundamental homeostatic constants. The most significant of these is the integrity of the containment body (skin, mucous membranes, peritoneum, etc..) And the oxygen level of tissue. In response to damage ...
Chapter 12
... Function of Cerebellum Error Control Device - Monitor, Quality Control – Monitors outputs to muscles from motor cortex and sensory signals from receptors – Compares the efferent project plan with execution at motor action site – Considers related factors and makes adjustments ...
... Function of Cerebellum Error Control Device - Monitor, Quality Control – Monitors outputs to muscles from motor cortex and sensory signals from receptors – Compares the efferent project plan with execution at motor action site – Considers related factors and makes adjustments ...
Lab Activity 14 - Portland Community College
... • The cell body of a lower motor neuron is in the spinal cord and its termination is in a skeletal muscle. • The loss of lower motor neurons leads to weakness, twitching of muscle (fasciculation), and loss of muscle mass (muscle atrophy). “Flaccid Paralysis” ...
... • The cell body of a lower motor neuron is in the spinal cord and its termination is in a skeletal muscle. • The loss of lower motor neurons leads to weakness, twitching of muscle (fasciculation), and loss of muscle mass (muscle atrophy). “Flaccid Paralysis” ...
Massage Helps Relieve Muscular Pain
... its own painful input. If left untreated, the resultant ischemia in his hamstrings, and the accompanying postural distortions, may develop into knee, ankle or foot pain as well as dysfunctional biomechanics of any or all of these joints. Sleep patterns may change and activation of other areas of the ...
... its own painful input. If left untreated, the resultant ischemia in his hamstrings, and the accompanying postural distortions, may develop into knee, ankle or foot pain as well as dysfunctional biomechanics of any or all of these joints. Sleep patterns may change and activation of other areas of the ...
Modeling stability in neuron and network function: the role of activity
... the values that are measured from slice and culture experiments in which the natural patterns of activity of a network are altered prior to measurement will differ from those that contribute to network dynamics during behavior. Building models from measured means of a population of neurons with vari ...
... the values that are measured from slice and culture experiments in which the natural patterns of activity of a network are altered prior to measurement will differ from those that contribute to network dynamics during behavior. Building models from measured means of a population of neurons with vari ...
Early Neural Patterning •Neural induction
... -Excess/deficiency of RA causes a shift in Hox gene expression and which then changes the identity of each rhombomere → changes the development of fundamental motor neurons of face and neck -E.g. HoxB1 is only expressed in r4 – if this gene becomes mutated, no facial nerve can form and 2 trigeminal ...
... -Excess/deficiency of RA causes a shift in Hox gene expression and which then changes the identity of each rhombomere → changes the development of fundamental motor neurons of face and neck -E.g. HoxB1 is only expressed in r4 – if this gene becomes mutated, no facial nerve can form and 2 trigeminal ...
Full-Text PDF
... stimulation can offer access to selectivity that is otherwise unobtainable with classic methods. There is a well-defined strength–duration (SD) stimulus space that describes the changing probability of a neuron to fire an action potential in response to a variable stimulus current and pulse width [1 ...
... stimulation can offer access to selectivity that is otherwise unobtainable with classic methods. There is a well-defined strength–duration (SD) stimulus space that describes the changing probability of a neuron to fire an action potential in response to a variable stimulus current and pulse width [1 ...
Spinal Cord - HCC Learning Web
... Formed by the combination of posterior and anterior roots Arrangement of fibers is similar to muscle fibers in a muscle • Endoneurium – connective tissue that wraps around each nerve fiber • Perineurium – connective tissue that surrounds group of nerve fibers forming a fascicle • Epineurium – connec ...
... Formed by the combination of posterior and anterior roots Arrangement of fibers is similar to muscle fibers in a muscle • Endoneurium – connective tissue that wraps around each nerve fiber • Perineurium – connective tissue that surrounds group of nerve fibers forming a fascicle • Epineurium – connec ...
chapter 12 - cerebellum
... Function of Cerebellum Error Control Device - Monitor, Quality Control – Monitors outputs to muscles from motor cortex and sensory signals from receptors – Compares the efferent project plan with execution at motor action site – Considers related factors and makes adjustments ...
... Function of Cerebellum Error Control Device - Monitor, Quality Control – Monitors outputs to muscles from motor cortex and sensory signals from receptors – Compares the efferent project plan with execution at motor action site – Considers related factors and makes adjustments ...
Chapter 14 - MDC Faculty Home Pages
... – Cell locations: axons are in spinal cord tracts; cell bodies are in ganglia, spinal cord gray horns, and brain gray matter – Each pathway is made of a chain of two or more neurons – Pathways are paired: there is a left and a right tract – Most pathways decussate: axons cross midline so brain ...
... – Cell locations: axons are in spinal cord tracts; cell bodies are in ganglia, spinal cord gray horns, and brain gray matter – Each pathway is made of a chain of two or more neurons – Pathways are paired: there is a left and a right tract – Most pathways decussate: axons cross midline so brain ...
autonomic accessory ganglia in nerves reaching organs of the
... their branches running to the urogenital organs of sheep there were concentrations of nerve cells forming ganglia which, due to the area of their occurrence and to differentiate them from the main autonomic ganglia of the abdominal and pelvic cavities, were termed the AAG. There were concentrations ...
... their branches running to the urogenital organs of sheep there were concentrations of nerve cells forming ganglia which, due to the area of their occurrence and to differentiate them from the main autonomic ganglia of the abdominal and pelvic cavities, were termed the AAG. There were concentrations ...
nervous system organization, 022817
... Much of the text material is from, “Principles of Anatomy and Physiology” by Gerald J. Tortora and Bryan Derrickson (2009, 2011, and 2014). I don’t claim authorship. Other sources are noted when they are used. The lecture slides are mapped to the three editions of the textbook based on the color-cod ...
... Much of the text material is from, “Principles of Anatomy and Physiology” by Gerald J. Tortora and Bryan Derrickson (2009, 2011, and 2014). I don’t claim authorship. Other sources are noted when they are used. The lecture slides are mapped to the three editions of the textbook based on the color-cod ...
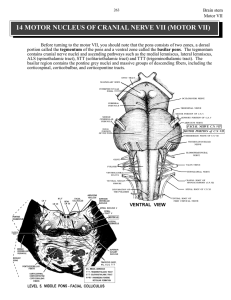
14 MOTOR NUCLEUS OF CRANIAL NERVE VII (MOTOR VII)
... transverse and longitudinal fiber bundles between which are large collections of pontine neurons called the PONTINE GREY (or GRAY). The longitudinal bundles are (1) corticobulbar, (2) corticospinal and, most important for this point, (3) CORTICOPONTINE FIBERS. ...
... transverse and longitudinal fiber bundles between which are large collections of pontine neurons called the PONTINE GREY (or GRAY). The longitudinal bundles are (1) corticobulbar, (2) corticospinal and, most important for this point, (3) CORTICOPONTINE FIBERS. ...
Skeletal System
... sweaty skin; and dilated eyes are signs Also changes in brain wave patterns Its function is to provide the optimal conditions for an appropriate response to some threat (run / see / think) ...
... sweaty skin; and dilated eyes are signs Also changes in brain wave patterns Its function is to provide the optimal conditions for an appropriate response to some threat (run / see / think) ...
AUTONOMIC REFLEX - Semmelweis University
... sympathetic trunk and form the splanchnic nerves, these fibers travel to a prevertebral gaglion 4. some preganglionic axons in the splanchnic nerve innervate chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla ...
... sympathetic trunk and form the splanchnic nerves, these fibers travel to a prevertebral gaglion 4. some preganglionic axons in the splanchnic nerve innervate chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla ...
Osteo-genesis
... system controlling the activity of cardiac muscle, smooth muscles and glands. • It has two components. Sympathetic System and Para-Sympathetic System. Sympathetic system is activated during fight, flight or fright. Parasympathetic system is like the default/background setting. • Both systems have tw ...
... system controlling the activity of cardiac muscle, smooth muscles and glands. • It has two components. Sympathetic System and Para-Sympathetic System. Sympathetic system is activated during fight, flight or fright. Parasympathetic system is like the default/background setting. • Both systems have tw ...
Principles of Extracellular Single
... The problem of a search stimulus is more subtle. Many neurons in the central nervous system have little or no spontaneous activity. In a recent study of hippocampal pyramidal cells, for example, only a tiny minority of the pyramidal cells calculated from anatomical data to be within range of an extr ...
... The problem of a search stimulus is more subtle. Many neurons in the central nervous system have little or no spontaneous activity. In a recent study of hippocampal pyramidal cells, for example, only a tiny minority of the pyramidal cells calculated from anatomical data to be within range of an extr ...
ACTION POTENTIAL THRESHOLD OF HIPPOCAMPAL
... potential between action potentials is expected to in£uence the threshold of subsequent action potentials. We tested this hypothesis by triggering hyperpolarizing current injections (0.1^2 nA for 60 ms) immediately following spontaneous action potentials. Figure 6A shows a spontaneous train of actio ...
... potential between action potentials is expected to in£uence the threshold of subsequent action potentials. We tested this hypothesis by triggering hyperpolarizing current injections (0.1^2 nA for 60 ms) immediately following spontaneous action potentials. Figure 6A shows a spontaneous train of actio ...
Document
... Processing at the Circuit Level • Chains of three neurons (1st, 2nd, and 3rd order) conduct sensory impulses upward to the brain • First-order neurons – soma reside in dorsal root or cranial ganglia, and conduct impulses from the skin to the spinal cord or brain stem • Second-order neurons – soma r ...
... Processing at the Circuit Level • Chains of three neurons (1st, 2nd, and 3rd order) conduct sensory impulses upward to the brain • First-order neurons – soma reside in dorsal root or cranial ganglia, and conduct impulses from the skin to the spinal cord or brain stem • Second-order neurons – soma r ...
For Immediate Release SCIENTIFIC BREAKTHROUGH
... A Genius Solution and New Category in Sports Nutrition: Neuro Muscular Performance BOSTON, MA – June 2, 2016 – Exercise-associated muscle cramps are agonizing. Millions of athletes and fitness enthusiasts suffer from them – even the best trained and most nutritionally-savvy. They’re painful, unpredi ...
... A Genius Solution and New Category in Sports Nutrition: Neuro Muscular Performance BOSTON, MA – June 2, 2016 – Exercise-associated muscle cramps are agonizing. Millions of athletes and fitness enthusiasts suffer from them – even the best trained and most nutritionally-savvy. They’re painful, unpredi ...
Brachial Plexus Surgery: Clinical Analysis of Ten Cases
... degree of weakness of the finger flexors and impaired feeling in the small, ring finger and the medial aspect of the forearm [12]. ...
... degree of weakness of the finger flexors and impaired feeling in the small, ring finger and the medial aspect of the forearm [12]. ...
Unit 4 Sensation & Perception
... long time you will see a visual image that persists after it is removed; the color of the afterimage is the complement. Why? If you stare at something green for a long time you fatigue the green receptors. Then when you state at something white (which contains all colors) the green receptors, which ...
... long time you will see a visual image that persists after it is removed; the color of the afterimage is the complement. Why? If you stare at something green for a long time you fatigue the green receptors. Then when you state at something white (which contains all colors) the green receptors, which ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.