Nervous Sytem notes HS Spring
... axon, with each portion of the axon undergoing depolarization then repolarization. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers, the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This “jumping” from node-to-node is called saltatory condu ...
... axon, with each portion of the axon undergoing depolarization then repolarization. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers, the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This “jumping” from node-to-node is called saltatory condu ...
Unit IV-D Outline
... 1. Functions of Regulation a. regulation - responses to a wide variety of changes that take place both inside and outside the body of the organism must be controlled in amount and directed to the right place b. coordination – responses to a wide variety of changes that take place both inside and out ...
... 1. Functions of Regulation a. regulation - responses to a wide variety of changes that take place both inside and outside the body of the organism must be controlled in amount and directed to the right place b. coordination – responses to a wide variety of changes that take place both inside and out ...
Nervous System - Uplift Education
... ◦ A quick switch in voltage potential (charge difference) across the membrane that travels all the way along the axon of the neuron ◦ Occurs due to flow of ions across the membrane ◦ All – or - nothing ...
... ◦ A quick switch in voltage potential (charge difference) across the membrane that travels all the way along the axon of the neuron ◦ Occurs due to flow of ions across the membrane ◦ All – or - nothing ...
Fundamentals of Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... going to skeletal muscles and Visceral Motor – going to smooth or cardiac muscles. Inter-neurons receive information from sensory neurons and integrate it, interpret the meaning and pass instructions to motor neurons to act. Neurons (on basis # of appendages) Multipolar Neurons – many dendrites and ...
... going to skeletal muscles and Visceral Motor – going to smooth or cardiac muscles. Inter-neurons receive information from sensory neurons and integrate it, interpret the meaning and pass instructions to motor neurons to act. Neurons (on basis # of appendages) Multipolar Neurons – many dendrites and ...
The Nervous System
... Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system Action Potential: a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulati ...
... Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system Action Potential: a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulati ...
neuron and nervous system
... Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system Action Potential: a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulati ...
... Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system Action Potential: a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulati ...
Lecture 12
... Lecture 12: Sensory Receptors and Special Senses I. General Terms A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. ...
... Lecture 12: Sensory Receptors and Special Senses I. General Terms A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. ...
CHAPTER NINE: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... i. An increase in membrane potential ii. Inside of the membrane becomes more negative than the resting potential iii. Reduces the probability of producing a nerve impulse c. Occur when a stimulus causes gated ion channels to open d. Decrease in magnitude with distance as ions flow and diffuse throug ...
... i. An increase in membrane potential ii. Inside of the membrane becomes more negative than the resting potential iii. Reduces the probability of producing a nerve impulse c. Occur when a stimulus causes gated ion channels to open d. Decrease in magnitude with distance as ions flow and diffuse throug ...
Phases
... The positive feedback of the rising phase slows At the peak of the action potential, the sodium permeability is maximized and the membrane voltage Vm is nearly equal to the sodium equilibrium voltage ENa. However, the same raised voltage that opened the sodium channels initially also slowly shuts th ...
... The positive feedback of the rising phase slows At the peak of the action potential, the sodium permeability is maximized and the membrane voltage Vm is nearly equal to the sodium equilibrium voltage ENa. However, the same raised voltage that opened the sodium channels initially also slowly shuts th ...
Lab 8: Muscle and Nervous Tissue
... locate a cluster of sensory neuron cell bodies. You may also note bundles of nerve fibers passing among groups of neuron cell bodies. Sketch and Label this 2. Sensory Neuron Cell Bodies 7. Obtain a prepared slide of neuroglial cells. Search and locate some darkly stained Astrocytes with numerous lon ...
... locate a cluster of sensory neuron cell bodies. You may also note bundles of nerve fibers passing among groups of neuron cell bodies. Sketch and Label this 2. Sensory Neuron Cell Bodies 7. Obtain a prepared slide of neuroglial cells. Search and locate some darkly stained Astrocytes with numerous lon ...
13.1- neurons
... which acts as insulation for the axons. - The myelin sheath acts as insulation by preventing the loss of charged ions from the nerve cell. ...
... which acts as insulation for the axons. - The myelin sheath acts as insulation by preventing the loss of charged ions from the nerve cell. ...
Nerve and muscle signalling
... • The frequency of spikes within a trains usually encodes the intensity of the sensation or instruction • Trains of spikes are usually interspersed by periods of silence ...
... • The frequency of spikes within a trains usually encodes the intensity of the sensation or instruction • Trains of spikes are usually interspersed by periods of silence ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses Quiz Answers
... a) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axon ...
... a) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axon ...
Nerve Pathways Practice Sheet
... Fill-in-the-Blanks The nervous system is a connection of many different (1) _____________________ (nerve cells). These nerves form pathways that send messages all over the body, in many different directions. (2) ________ neurons detect specific kinds of environmental stimuli, (3) ___________________ ...
... Fill-in-the-Blanks The nervous system is a connection of many different (1) _____________________ (nerve cells). These nerves form pathways that send messages all over the body, in many different directions. (2) ________ neurons detect specific kinds of environmental stimuli, (3) ___________________ ...
Chapter 33
... chemically gated potassium channel. When opened, potassium ions leave the cell which increases the negative charge and inhibits the start of an action potential. ...
... chemically gated potassium channel. When opened, potassium ions leave the cell which increases the negative charge and inhibits the start of an action potential. ...
Slide ()
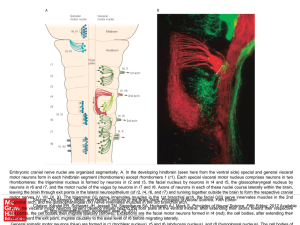
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
Action Potential Neurons at Work
... What happens during depolarization? Which channel is open/closed and where are ions moving? The inside receives an influx of Na+ ions and the sodium ion channel is open. ...
... What happens during depolarization? Which channel is open/closed and where are ions moving? The inside receives an influx of Na+ ions and the sodium ion channel is open. ...
Nervous System
... Difference in permeability of resting membrane to potassium ions versus sodium ions Resting membrane much more permeable to potassium ions than to sodium ions • Results in slightly more net potassium ion diffusion than sodium ion diffusion • Neuron stays inactive and polarized at its resting potenti ...
... Difference in permeability of resting membrane to potassium ions versus sodium ions Resting membrane much more permeable to potassium ions than to sodium ions • Results in slightly more net potassium ion diffusion than sodium ion diffusion • Neuron stays inactive and polarized at its resting potenti ...
Histology05-NerveTissue
... in conscious sensations, but others do not. However, they are not considered part of the autonomic nervous system, which is entirely ...
... in conscious sensations, but others do not. However, they are not considered part of the autonomic nervous system, which is entirely ...
ppt
... drawing of the synapse where this toxin acts. 3. How will it affect individual action potentials and muscular contraction? (Draw effects on other side of ...
... drawing of the synapse where this toxin acts. 3. How will it affect individual action potentials and muscular contraction? (Draw effects on other side of ...
20-NervousSystem
... membrane of a resting neuron is generated by different concentrations of Na+, K+, and Cl ...
... membrane of a resting neuron is generated by different concentrations of Na+, K+, and Cl ...
C13 Lesson 2 extra credit
... 1. How are a stimulus and a response related? 2. How do the three different types of neurons function? 3. What is a nerve net? How many specialized neurons does a nerve net include? 4. What are the three functions of a brain? 5. How are animals with many sense organs able to process many stimuli at ...
... 1. How are a stimulus and a response related? 2. How do the three different types of neurons function? 3. What is a nerve net? How many specialized neurons does a nerve net include? 4. What are the three functions of a brain? 5. How are animals with many sense organs able to process many stimuli at ...
Motor Neuron
... – Found in neural pathways in the central nervous system – Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
... – Found in neural pathways in the central nervous system – Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
Nervous and Endocrine System
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
Exam
... is bathed on its inner surface (the side facing the brain) by cerebrospinal fluid sends protrusions through the dural wall of the superior sagittal sinus is continuous with the perineurium of the spinal nerves closely follows every contour of the brain surface, including cortical sulci lies between ...
... is bathed on its inner surface (the side facing the brain) by cerebrospinal fluid sends protrusions through the dural wall of the superior sagittal sinus is continuous with the perineurium of the spinal nerves closely follows every contour of the brain surface, including cortical sulci lies between ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.