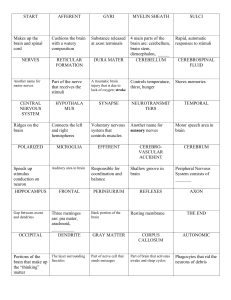
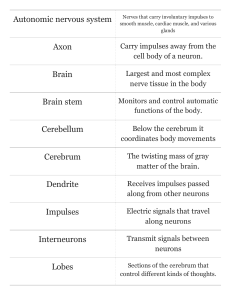
Nervous System Chap49
... takes information away from cell body. It branches at the end into terminal knobs. A terminal knob secretes a chemical called Neurotransmitter in the gap to the next neuron or muscle membrane. Most common neurotransmitter secreted is Acetylcholine. 10. Resting Potential: is when a nerve fiber has m ...
... takes information away from cell body. It branches at the end into terminal knobs. A terminal knob secretes a chemical called Neurotransmitter in the gap to the next neuron or muscle membrane. Most common neurotransmitter secreted is Acetylcholine. 10. Resting Potential: is when a nerve fiber has m ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 16. Stimulating a nerve cell increases the permeability of the membrane to ___sodium________ ions. ...
... 16. Stimulating a nerve cell increases the permeability of the membrane to ___sodium________ ions. ...
Chapter 11: Nervous System
... Ions flow along their chemical gradient when they move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Ions flow along their electrical gradient when they move toward an area of opposite charge Electrochemical gradient – the electrical and ...
... Ions flow along their chemical gradient when they move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Ions flow along their electrical gradient when they move toward an area of opposite charge Electrochemical gradient – the electrical and ...
Chapter 11: Nervous System
... Ions flow along their chemical gradient when they move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Ions flow along their electrical gradient when they move toward an area of opposite charge Electrochemical gradient – the electrical and ...
... Ions flow along their chemical gradient when they move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Ions flow along their electrical gradient when they move toward an area of opposite charge Electrochemical gradient – the electrical and ...
Chapter 14 Part 2
... • Present in membrane of axons of nociceptor neurons • Mechanically gated channels • Temperature sensitive neurons called thermoreceptor neurons have temperature gated channels – Sense cold or warm: burning is sensed by different neurons called nociceptors which signal damaging temperature extremes ...
... • Present in membrane of axons of nociceptor neurons • Mechanically gated channels • Temperature sensitive neurons called thermoreceptor neurons have temperature gated channels – Sense cold or warm: burning is sensed by different neurons called nociceptors which signal damaging temperature extremes ...
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... of the membranes exposed to the stimulus. 3. The stimulus affects the membrane potential of a neuron by opening a gated ion channel. 4. A membrane is hyperpolarized if the membrane potential becomes more negative than the resting potential. 5. A membrane is depolarized if the membrane becomes less n ...
... of the membranes exposed to the stimulus. 3. The stimulus affects the membrane potential of a neuron by opening a gated ion channel. 4. A membrane is hyperpolarized if the membrane potential becomes more negative than the resting potential. 5. A membrane is depolarized if the membrane becomes less n ...
Information Processing in Motor Learning
... – Action potential is always the same intensity regardless of the strength of synaptic transmission above the threshold level – Action potential intensity remains constant along the nerve fibre Sport Books Publisher ...
... – Action potential is always the same intensity regardless of the strength of synaptic transmission above the threshold level – Action potential intensity remains constant along the nerve fibre Sport Books Publisher ...
Midterm Review Answers
... dependent Na+ channels. What would you expect the pattern of TTX labeling to be in a … a) myelinated axon TTX labeling would be localized only at the Nodes of Ranvier as these areas have a high concentration of voltage gated Na+ channels. b) non-myelinated axon TTX labeling would be distributed even ...
... dependent Na+ channels. What would you expect the pattern of TTX labeling to be in a … a) myelinated axon TTX labeling would be localized only at the Nodes of Ranvier as these areas have a high concentration of voltage gated Na+ channels. b) non-myelinated axon TTX labeling would be distributed even ...
Instructions to Surgeons: Nerve and Muscle Biopsies
... should not be severely affected and have evidence of fibrosis, since it would be an “end-stage” muscle. In recent onset disorders, a severely affected muscle can be biopsied. In the upper extremities, the typical sites are deltoid or biceps. In the lower extremities, the typical site is the vastus l ...
... should not be severely affected and have evidence of fibrosis, since it would be an “end-stage” muscle. In recent onset disorders, a severely affected muscle can be biopsied. In the upper extremities, the typical sites are deltoid or biceps. In the lower extremities, the typical site is the vastus l ...
Structure of a Neuron
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
Bones of the Wrist Some Lovers Try Positions That
... Pectoralis major attaches to lateral lip of bicipital groove, the teres major attaches to medial lip of bicipital groove, and the latissimus dorsi attaches to the floor of bicipital groove. The ...
... Pectoralis major attaches to lateral lip of bicipital groove, the teres major attaches to medial lip of bicipital groove, and the latissimus dorsi attaches to the floor of bicipital groove. The ...
Neuronal Signaling
... - Decreases time to charge the nearby membrane, increasing conduction velocity - Myelin increases the passive conduction distance (remember that larger Rm increases the length constant, lambda) - Myelin decreases the time to charge the membrane by decreasing Cm ...
... - Decreases time to charge the nearby membrane, increasing conduction velocity - Myelin increases the passive conduction distance (remember that larger Rm increases the length constant, lambda) - Myelin decreases the time to charge the membrane by decreasing Cm ...
Development of the central nervous system
... A neuron is a structural and functional unit consisting of the cell body and all its processes. ...
... A neuron is a structural and functional unit consisting of the cell body and all its processes. ...
(with Perception 6
... • Light enters the eye through a transparent window at the front called the cornea. • The iris (the colored part of the eye) regulates the amount of light entering the eye because it controls the size of the pupil. • The pupil (black part of your eye) is the opening that permits light to pass into ...
... • Light enters the eye through a transparent window at the front called the cornea. • The iris (the colored part of the eye) regulates the amount of light entering the eye because it controls the size of the pupil. • The pupil (black part of your eye) is the opening that permits light to pass into ...
document
... I) NERVOUS SYSTEM = Master control and communication system of the body. This system works with the ENDOCRINE system to maintain and regulate body HOMEOSTASIS (balance). NERVOUS SYSTEM – Fast action, uses electrical impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – ...
... I) NERVOUS SYSTEM = Master control and communication system of the body. This system works with the ENDOCRINE system to maintain and regulate body HOMEOSTASIS (balance). NERVOUS SYSTEM – Fast action, uses electrical impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – ...
O rganization of the nervous system To go toward
... If the action potential (nerve impulse) starts, it is propagated over the entire axon ...
... If the action potential (nerve impulse) starts, it is propagated over the entire axon ...
Reflex Arc - Point Loma High School
... The sensory neurons pass through the spinal cord which allows reflex actions to occur relatively quickly by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of steering signals through the brain, although the brain will receive sensory input while the reflex action occurs. ...
... The sensory neurons pass through the spinal cord which allows reflex actions to occur relatively quickly by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of steering signals through the brain, although the brain will receive sensory input while the reflex action occurs. ...
FUNCTIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF NERVE FIBER LEARNING
... Nervous system along with endocrine system control all activities of the body .primarily it is divided into Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Nerves that extend from the brain and spinal cord The central nervous system is composed of large number of excitable nerve cells and th ...
... Nervous system along with endocrine system control all activities of the body .primarily it is divided into Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Nerves that extend from the brain and spinal cord The central nervous system is composed of large number of excitable nerve cells and th ...
Hearing and Equilibrium Human Ear Major questions Anatomy of
... Sound Sensory Receptors (Fig 16.20d) • Hair cells sit on basilar membrane • Apical surface stereocilia- longest embedded in overlying tectorial membrane • Perilymph vibrating -->basilar membrane--> stereocilia flex back and forth in or against tectorial membrane • Mechanical opening of ion channels ...
... Sound Sensory Receptors (Fig 16.20d) • Hair cells sit on basilar membrane • Apical surface stereocilia- longest embedded in overlying tectorial membrane • Perilymph vibrating -->basilar membrane--> stereocilia flex back and forth in or against tectorial membrane • Mechanical opening of ion channels ...
Sensation & Perception
... the retina called rods and cones (process information for darkness and color). 5. The rods and cones set off chemical reactions they form a synapse with bipolar cells which change light energy into neural impulses. 6. These neural impulses go to the optic nerve (bundle of neurons that take informati ...
... the retina called rods and cones (process information for darkness and color). 5. The rods and cones set off chemical reactions they form a synapse with bipolar cells which change light energy into neural impulses. 6. These neural impulses go to the optic nerve (bundle of neurons that take informati ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.