Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... ended, the axon splits up and ends with a bulbous portion called the axon terminal When the nerve impulse reaches the axon terminal it causes the axon terminal to release a neurotransmitter into the synapse The synapse is the gap between the axon terminals and the next cell A neurotransmitter ...
... ended, the axon splits up and ends with a bulbous portion called the axon terminal When the nerve impulse reaches the axon terminal it causes the axon terminal to release a neurotransmitter into the synapse The synapse is the gap between the axon terminals and the next cell A neurotransmitter ...
* Certain neurons in the brain have receptors (opioid receptors) for
... neurons. The excitatory (gas) inputs remain “unchecked”; results in excessive, involuntary skeletal muscle contraction. Spasms of the jaw muscles are early signs. Tetanus shot! ...
... neurons. The excitatory (gas) inputs remain “unchecked”; results in excessive, involuntary skeletal muscle contraction. Spasms of the jaw muscles are early signs. Tetanus shot! ...
04 Physiology of large hemispheres, cerebellum
... Effects of Aging on the Nervous System As a person ages, there’s a gradual decline in sensory function because the number of sensory neurons declines, the function of remaining neurons decreases, and CNS processing decreases. In the skin, free nerve endings and hair follicle receptors remain largel ...
... Effects of Aging on the Nervous System As a person ages, there’s a gradual decline in sensory function because the number of sensory neurons declines, the function of remaining neurons decreases, and CNS processing decreases. In the skin, free nerve endings and hair follicle receptors remain largel ...
lesson 6
... 1) synthesized and released by neurons 2) released at the nerve terminal in a 'chemically identifiable' form 3) the chemical should reproduce the activity of the presynaptic neuron 4) can be blocked by competitive antagonist based on concentration 5) active mechanisms to stop the function of the neu ...
... 1) synthesized and released by neurons 2) released at the nerve terminal in a 'chemically identifiable' form 3) the chemical should reproduce the activity of the presynaptic neuron 4) can be blocked by competitive antagonist based on concentration 5) active mechanisms to stop the function of the neu ...
chapter48
... The voltage-activated ion channels are concentrated at the nodes where the membrane is in contact with the interstitial fluid. This mode of conduction is called saltatory conduction (saltare = to leap in Latin). It is fifty times faster than continuous conduction: 150 meters/sec. ...
... The voltage-activated ion channels are concentrated at the nodes where the membrane is in contact with the interstitial fluid. This mode of conduction is called saltatory conduction (saltare = to leap in Latin). It is fifty times faster than continuous conduction: 150 meters/sec. ...
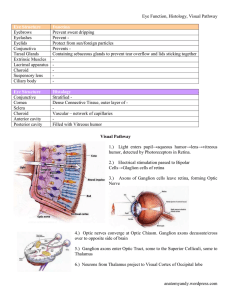
Eye Structure - WordPress.com
... Prevent Protect from sun/foreign particles Prevents Containing sebaceous glands to prevent tear overflow and lids sticking together ...
... Prevent Protect from sun/foreign particles Prevents Containing sebaceous glands to prevent tear overflow and lids sticking together ...
Slide 1
... serotonin by preventing its reuptake into the presynaptic cell, increasing the level of serotonin in the synaptic cleft available to bind to the postsynaptic receptor. Low seratonin causes depression or anxiety, Bipolar, OCD ...
... serotonin by preventing its reuptake into the presynaptic cell, increasing the level of serotonin in the synaptic cleft available to bind to the postsynaptic receptor. Low seratonin causes depression or anxiety, Bipolar, OCD ...
12-2cut
... 2) extra K+ channels open and lots of K+ flows out This repolarizes membrane 3) Refractory period: time during which original state is regenerated by Na-K pumps. During this time, neuron __________ fire again. ...
... 2) extra K+ channels open and lots of K+ flows out This repolarizes membrane 3) Refractory period: time during which original state is regenerated by Na-K pumps. During this time, neuron __________ fire again. ...
Nervous System Notes
... serotonin by preventing its reuptake into the presynaptic cell, increasing the level of serotonin in the synaptic cleft available to bind to the postsynaptic receptor. Low seratonin causes depression or anxiety, Bipolar, OCD ...
... serotonin by preventing its reuptake into the presynaptic cell, increasing the level of serotonin in the synaptic cleft available to bind to the postsynaptic receptor. Low seratonin causes depression or anxiety, Bipolar, OCD ...
24. Sensory organs
... – Free nerve endings are the simplest type: they are the dendrites of sensory neurons – Complex receptors (eyes) are housed in organs – Some receptors respond to only one kind of stimulus ...
... – Free nerve endings are the simplest type: they are the dendrites of sensory neurons – Complex receptors (eyes) are housed in organs – Some receptors respond to only one kind of stimulus ...
chapter 8 lecture ppt
... • “Electricity” that cause depolarization and repolarization • Change resting membrane potential by activating gated ion channels • Local Current: movement of Na+ which causes inside of cell to be more positive (depolarize) ...
... • “Electricity” that cause depolarization and repolarization • Change resting membrane potential by activating gated ion channels • Local Current: movement of Na+ which causes inside of cell to be more positive (depolarize) ...
Slide 1 - AccessPhysiotherapy
... dendrites and also on its cell body, the soma. The soma of this type of cell integrates the electrical information and also provides metabolic support for the cell as a whole. The place where the axon comes out of the soma is called the axon hillock, and this is where the information is encoded into ...
... dendrites and also on its cell body, the soma. The soma of this type of cell integrates the electrical information and also provides metabolic support for the cell as a whole. The place where the axon comes out of the soma is called the axon hillock, and this is where the information is encoded into ...
Study Questions - Nervous System
... 2. What type of information does the nervous system gather? From where is it gathered? (slide 1; Fig 11.1) 3. The output consists of activating _______________ or _____________. (sl.1; p243) 4. CNS refers to the ___________________ ___________________ _______________ which is composed of ___________ ...
... 2. What type of information does the nervous system gather? From where is it gathered? (slide 1; Fig 11.1) 3. The output consists of activating _______________ or _____________. (sl.1; p243) 4. CNS refers to the ___________________ ___________________ _______________ which is composed of ___________ ...
Slide ()
... The pattern of motor neuron activity can change the biochemical and functional properties of skeletal muscle cells. A. Muscle fibers have characteristic metabolic, molecular, and electrical properties that identify them as "slow" (tonic) or "fast" (phasic) types. The micrograph on the right shows a ...
... The pattern of motor neuron activity can change the biochemical and functional properties of skeletal muscle cells. A. Muscle fibers have characteristic metabolic, molecular, and electrical properties that identify them as "slow" (tonic) or "fast" (phasic) types. The micrograph on the right shows a ...
The Nervous System
... membrane pumps sodium (Na+) ions out of the cell and potassium (K+) ions into the cell by means of active transport. • As a result, the inside of the cell contains more K+ ions and fewer Na+ ions than the outside. ...
... membrane pumps sodium (Na+) ions out of the cell and potassium (K+) ions into the cell by means of active transport. • As a result, the inside of the cell contains more K+ ions and fewer Na+ ions than the outside. ...
Lectures 26-27 Study Guide
... I have organized some terms and topics that I think are important. This does not mean that other topics mentioned during lecture or in the book will not be tested. This guide is meant to clarify and emphasize certain points, NOT to list everything you need to know. I will focus on tying things toget ...
... I have organized some terms and topics that I think are important. This does not mean that other topics mentioned during lecture or in the book will not be tested. This guide is meant to clarify and emphasize certain points, NOT to list everything you need to know. I will focus on tying things toget ...
Neurophysiology,Dr Sravanti
... The excitation and inhibition caused by all the active synapses on the dendrites and cell body are summed and the net effect is reflected in the rate at which the axon hillock generates action potentials ...
... The excitation and inhibition caused by all the active synapses on the dendrites and cell body are summed and the net effect is reflected in the rate at which the axon hillock generates action potentials ...
Unit 1 – Nervous and Endocrine System
... A stimulus at the dendrites causes voltage-gated sodium gates to open and the neuron starts to be depolarized ...
... A stimulus at the dendrites causes voltage-gated sodium gates to open and the neuron starts to be depolarized ...
2 Guided Notes for PPT 7, Hearing and Sight
... Both senses reside in the inner ear within a maze of fluid filled passages and sensory cells. Sensory cells convert this motion into a pattern of _________________________ ...
... Both senses reside in the inner ear within a maze of fluid filled passages and sensory cells. Sensory cells convert this motion into a pattern of _________________________ ...
Characteristic for receptor cells
... directly influencing ion channels in membrane of receptor • Weak acid vinegar ionize in water to produce protons (H+) and anions (- ions), in mud puppy, H+ ions block specific type of K+ channel in receptor • For salty substances like table salt Na+ and other cations act as stimuli, Na+ ions of salt ...
... directly influencing ion channels in membrane of receptor • Weak acid vinegar ionize in water to produce protons (H+) and anions (- ions), in mud puppy, H+ ions block specific type of K+ channel in receptor • For salty substances like table salt Na+ and other cations act as stimuli, Na+ ions of salt ...
Nerve cells - Spark (e
... In biology are defined dendrites the minor fibers branching from the neuron, they carry nerve signals in centripetal direction. The dendrites are shorter and thinner than the axon. ...
... In biology are defined dendrites the minor fibers branching from the neuron, they carry nerve signals in centripetal direction. The dendrites are shorter and thinner than the axon. ...
Bio 103 Nervous System
... Sodium-Potassium exchange pump - exchange of 3 Na+ for every 2 K+ [ moves 3 Na+ out of the cell; moves 2 K+ into the cell; uses ATP as energy source to move these ions] - used to maintain the resting potential (______) ...
... Sodium-Potassium exchange pump - exchange of 3 Na+ for every 2 K+ [ moves 3 Na+ out of the cell; moves 2 K+ into the cell; uses ATP as energy source to move these ions] - used to maintain the resting potential (______) ...
Biology 30 NERVOUS SYSTEM - Salisbury Composite High School
... hyperpolarized – more positively charged on the outside than the resting state ...
... hyperpolarized – more positively charged on the outside than the resting state ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.