nervous systems
... Generating and Conducting Nerve Impulses (12) An action potential is a sudden and major change in membrane potential that lasts for about 1–2 milliseconds. Action potentials are conducted along axons at speeds of up to 100 meters per second. If the membrane potential of an axon is measured when an ...
... Generating and Conducting Nerve Impulses (12) An action potential is a sudden and major change in membrane potential that lasts for about 1–2 milliseconds. Action potentials are conducted along axons at speeds of up to 100 meters per second. If the membrane potential of an axon is measured when an ...
Lecture 13: The Nervous System
... B. Play a role in forming the blood brain barrier and can form scar tissue in the brain following an injury C. Found primarily in gray matter because they are associated with the cell bodies of neurons. D. They are the neuron Mamas...they remove NT from synapses, help form new synapses, help main ...
... B. Play a role in forming the blood brain barrier and can form scar tissue in the brain following an injury C. Found primarily in gray matter because they are associated with the cell bodies of neurons. D. They are the neuron Mamas...they remove NT from synapses, help form new synapses, help main ...
ISHIK UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY
... Local anesthetics are weak bases. The pKa for most local anesthetics is in the range of 8.0-9.0. A balance of charged and uncharged forms is present in the body. The ratio between the cationic and uncharged forms of these drugs is determined by the HendersonHasselbalch equation (Log (cationic form/u ...
... Local anesthetics are weak bases. The pKa for most local anesthetics is in the range of 8.0-9.0. A balance of charged and uncharged forms is present in the body. The ratio between the cationic and uncharged forms of these drugs is determined by the HendersonHasselbalch equation (Log (cationic form/u ...
Nervous System Nervous System
... Broad Concept: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
... Broad Concept: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
The Peripheral Nervous System and Reflex Activity
... Reciprocal inhibition also occurs—IIa fibers synapse with interneurons that inhibit motor neurons of antagonistic muscles ...
... Reciprocal inhibition also occurs—IIa fibers synapse with interneurons that inhibit motor neurons of antagonistic muscles ...
What is real? How do you define real?
... what are they !responding to"? Action potentials convey information through their timing. Although ac• sensory neuroscience: activity as a function of sensory stimulus (eg. tion potentials can vary somewhat in duration, amplitude, and shape, image, skin stimulation, sound, odor etc..). they visual a ...
... what are they !responding to"? Action potentials convey information through their timing. Although ac• sensory neuroscience: activity as a function of sensory stimulus (eg. tion potentials can vary somewhat in duration, amplitude, and shape, image, skin stimulation, sound, odor etc..). they visual a ...
Cranial nerve of smell, plus olfactory pathway
... associated with childhood – general mood (such as contentment) Many memories, b/c that’s when we first experience most smells ...
... associated with childhood – general mood (such as contentment) Many memories, b/c that’s when we first experience most smells ...
EXAMINATION OF NERVES OF LOWER LIMB
... At the end of this lecture the students should know: •The sensory and motor nerve supplies of the different regions of lower limb •Examination of nerves of lower limb •Significance of lesions of different nerves of lower limb and what abnormality would appear in case of a lesion ...
... At the end of this lecture the students should know: •The sensory and motor nerve supplies of the different regions of lower limb •Examination of nerves of lower limb •Significance of lesions of different nerves of lower limb and what abnormality would appear in case of a lesion ...
EXAMINATION OF NERVES OF LOWER LIMB
... At the end of this lecture the students should know: •The sensory and motor nerve supplies of the different regions of lower limb •Examination of nerves of lower limb •Significance of lesions of different nerves of lower limb and what abnormality would appear in case of a lesion ...
... At the end of this lecture the students should know: •The sensory and motor nerve supplies of the different regions of lower limb •Examination of nerves of lower limb •Significance of lesions of different nerves of lower limb and what abnormality would appear in case of a lesion ...
Senses
... group of hearing receptor cells (hair cells) on upper surface of basilar membrane different frequencies of vibration move different parts of basilar membrane particular sound frequencies cause hairs of receptor cells to bend Ca influx causes NT release onto sensory nerve AP generated-to medulla-to t ...
... group of hearing receptor cells (hair cells) on upper surface of basilar membrane different frequencies of vibration move different parts of basilar membrane particular sound frequencies cause hairs of receptor cells to bend Ca influx causes NT release onto sensory nerve AP generated-to medulla-to t ...
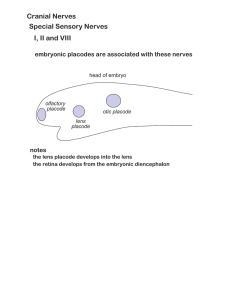
Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII
... Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII embryonic placodes are associated with these nerves ...
... Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII embryonic placodes are associated with these nerves ...
Graded Potentials
... o Changes in transmembrane potential That cannot spread far from site of stimulation o Any stimulus that opens a gated channel Produces a graded potential ...
... o Changes in transmembrane potential That cannot spread far from site of stimulation o Any stimulus that opens a gated channel Produces a graded potential ...
Synapses and Synaptic Transmission
... which is the IPSP. Causes: it is produced by localized increase in membrane permeability to Cl¯ of post-synaptic memb. (produced by inhibitory neurotransmitter) excitability and memb. ...
... which is the IPSP. Causes: it is produced by localized increase in membrane permeability to Cl¯ of post-synaptic memb. (produced by inhibitory neurotransmitter) excitability and memb. ...
CENTENNIAL HONORS COLLEGE Western Illinois University Undergraduate Research Day 2015
... Undergraduate Research Day 2015 Poster Presentation Characterizing an Abnormal Action Potential Pattern in Ion-Channel-Mutant Drosophila Mariah Maiman Faculty Mentor: Jeffrey Engel Biology Repetitive activities such as flight are organized by neural networks called central pattern generators and the ...
... Undergraduate Research Day 2015 Poster Presentation Characterizing an Abnormal Action Potential Pattern in Ion-Channel-Mutant Drosophila Mariah Maiman Faculty Mentor: Jeffrey Engel Biology Repetitive activities such as flight are organized by neural networks called central pattern generators and the ...
UPMC St. Margaret Nerve Block Rotation
... Lumbar plexus blocks provide anesthesia or analgesia to the entire distribution of the plexus, including the anterolateral and medial thigh, the knee, and the saphenous nerve below the knee. Continuous infusion is always initiated after an initial bolus of dilute local anesthetic through the cathe ...
... Lumbar plexus blocks provide anesthesia or analgesia to the entire distribution of the plexus, including the anterolateral and medial thigh, the knee, and the saphenous nerve below the knee. Continuous infusion is always initiated after an initial bolus of dilute local anesthetic through the cathe ...
Simulation of myelinated neuron with focus on conduction speed
... disappeared when Naf was shutdown (Fig. 5a). Linear leakage channel seemed to have the least influence on DAP and HAP since neither changed much when Lk was shut down (Fig. 5c). Persistent Na+ channel seemed to cause DAP as well because only DAP disappeared after shutdown (Fig. 5b). ...
... disappeared when Naf was shutdown (Fig. 5a). Linear leakage channel seemed to have the least influence on DAP and HAP since neither changed much when Lk was shut down (Fig. 5c). Persistent Na+ channel seemed to cause DAP as well because only DAP disappeared after shutdown (Fig. 5b). ...
peripheral neuropathy
... neuropathies because of its steroid-sparing effect. Concurrent use of these two medications allows corticosteroids to be tapered more quickly and more completely once the neuropathy is brought under control. The usual dosage of azathioprine is 2-3 mg/kg/day given in divided doses. This medication ha ...
... neuropathies because of its steroid-sparing effect. Concurrent use of these two medications allows corticosteroids to be tapered more quickly and more completely once the neuropathy is brought under control. The usual dosage of azathioprine is 2-3 mg/kg/day given in divided doses. This medication ha ...
Ch6 - Unit3Biology
... after a nerve impulse has passed along the membrane, the original distribution of ions across the membrane is restored ...
... after a nerve impulse has passed along the membrane, the original distribution of ions across the membrane is restored ...
Chapter 12 Central Nervous System – Brain
... inactivity – increase amplitude active – complex, low amplitude waves ...
... inactivity – increase amplitude active – complex, low amplitude waves ...
Nervous System Mega Matching Table
... astrocytes axon basal nuclei (basal ganglia) Broca's area cauda equina central sulcus cerebellum cerebral peduncles choroid plexus commissural tract conus medullaris corpus callosum decussation of pyramids dendrite dermatome dorsal root ganglia dorsal root of spinal nerve dura mater endoneurium ente ...
... astrocytes axon basal nuclei (basal ganglia) Broca's area cauda equina central sulcus cerebellum cerebral peduncles choroid plexus commissural tract conus medullaris corpus callosum decussation of pyramids dendrite dermatome dorsal root ganglia dorsal root of spinal nerve dura mater endoneurium ente ...
Name: Date: Period:
... types are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons send information to the brain. Motor neurons carry out instructions from the brain. Interneurons carry the messages ‘in between’ the sensory and motor neurons. In today’s activity, we will be modeling how neurons work using ...
... types are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons send information to the brain. Motor neurons carry out instructions from the brain. Interneurons carry the messages ‘in between’ the sensory and motor neurons. In today’s activity, we will be modeling how neurons work using ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.