Exam 5 - Spring13 - Take home
... include the roles of the K+ and Na+ concentration gradients, electrical forces, passive ion channels and the relative permeabilities of K+ and Na+. Now, say that an alien race was discovered from a distant galaxy. Their cells have a higher concentration of Na+ inside than outside their cells and a h ...
... include the roles of the K+ and Na+ concentration gradients, electrical forces, passive ion channels and the relative permeabilities of K+ and Na+. Now, say that an alien race was discovered from a distant galaxy. Their cells have a higher concentration of Na+ inside than outside their cells and a h ...
Deep Fibular Nerve Entrapment
... Fabella in Gastrocnemius Close to its proximal attachment, lateral head of the gastrocnemius contains a ...
... Fabella in Gastrocnemius Close to its proximal attachment, lateral head of the gastrocnemius contains a ...
Chapter 40
... 3. Specialized function into peripheral afferent and efferent nerves, connecting to the CNS 4. An increased number of association neurons and other synaptic connections 5. Cephalization, with a concentration of nervous (including sensory) tissue at the head end D. Flatworms have cerebral ganglia tha ...
... 3. Specialized function into peripheral afferent and efferent nerves, connecting to the CNS 4. An increased number of association neurons and other synaptic connections 5. Cephalization, with a concentration of nervous (including sensory) tissue at the head end D. Flatworms have cerebral ganglia tha ...
lecture - McLoon Lab - University of Minnesota
... Glial cells wrap around the axons, synthesize the molecules associated with myelin-type membrane, and exclude cytoplasm from all but the mesaxon and ...
... Glial cells wrap around the axons, synthesize the molecules associated with myelin-type membrane, and exclude cytoplasm from all but the mesaxon and ...
Sensory System –L4
... the larger the nerve fiber diameter the faster the rate of transmission of the signal velocity of transmission can be as fast as 120 m/sec or as slow as 0.5 m/sec nerve fiber classification type A - myelinated fibers of varying sizes, generally fast transmission speed subdivided into a, b, ...
... the larger the nerve fiber diameter the faster the rate of transmission of the signal velocity of transmission can be as fast as 120 m/sec or as slow as 0.5 m/sec nerve fiber classification type A - myelinated fibers of varying sizes, generally fast transmission speed subdivided into a, b, ...
7-1_SegmOrgSpinCord_BogdanyP
... The spinal cord is a part of the central nervous system. It collects data from the peripherical nervous system – sensory information - , and innervate skeletal and smooth muscles – motoric function - that mediate voluntary and involuntary reflexes. As an example, the knee jerk reflex can happen with ...
... The spinal cord is a part of the central nervous system. It collects data from the peripherical nervous system – sensory information - , and innervate skeletal and smooth muscles – motoric function - that mediate voluntary and involuntary reflexes. As an example, the knee jerk reflex can happen with ...
Unit – M Neuron, Impulse Generation, and Reflex Arc Structures and
... is carried out by chemicals called Neurotransmitters. These substances are stored in vesicles at the end of the axon. Noradrenalin (speeds up activity) and acetylcholine (slows down activity) are examples of neurotransmitters. ...
... is carried out by chemicals called Neurotransmitters. These substances are stored in vesicles at the end of the axon. Noradrenalin (speeds up activity) and acetylcholine (slows down activity) are examples of neurotransmitters. ...
ch 48 nervous system
... Time (msec) (c) Action potential triggered by a depolarization that reaches the ...
... Time (msec) (c) Action potential triggered by a depolarization that reaches the ...
Reaching for the brain: stimulating neural activity as the big leap in
... approach, a prerequisite for successful axonal regeneration is to make sure that a sufficient population of neurons survives the initial insult, where after they can regrow their axons. Besides being a fruitful approach for axonal regeneration, the treatment paradigm presented by Lim and co-workers ...
... approach, a prerequisite for successful axonal regeneration is to make sure that a sufficient population of neurons survives the initial insult, where after they can regrow their axons. Besides being a fruitful approach for axonal regeneration, the treatment paradigm presented by Lim and co-workers ...
Cranial Nerve I
... • There are five components of a reflex arc • Receptor – site of stimulus • Sensory neuron – transmits the afferent impulse to the CNS • Integration center – either monosynaptic or polysynaptic region within the CNS • Motor neuron – conducts efferent impulses from the integration center to an effect ...
... • There are five components of a reflex arc • Receptor – site of stimulus • Sensory neuron – transmits the afferent impulse to the CNS • Integration center – either monosynaptic or polysynaptic region within the CNS • Motor neuron – conducts efferent impulses from the integration center to an effect ...
Unit 7 PowerPoint (PDF file)
... an action potential (impulse) is conducted Each action potential (impulse) is conducted at maximum strength unless there are toxic materials within the cell or the membrane has been disrupted ...
... an action potential (impulse) is conducted Each action potential (impulse) is conducted at maximum strength unless there are toxic materials within the cell or the membrane has been disrupted ...
Unit 6 Powerpoint
... an action potential (impulse) is conducted Each action potential (impulse) is conducted at maximum strength unless there are toxic materials within the cell or the membrane has been disrupted ...
... an action potential (impulse) is conducted Each action potential (impulse) is conducted at maximum strength unless there are toxic materials within the cell or the membrane has been disrupted ...
Nerve
... cytoplasm can be identified because it is also the location of the Schwann cell nuclei, whereas you will not find any nuclei in the neuronal process itself. Notice that the myelin sheaths are not all the same thickness. Some fibers are heavily myelinated while others are more lightly myelinated, eve ...
... cytoplasm can be identified because it is also the location of the Schwann cell nuclei, whereas you will not find any nuclei in the neuronal process itself. Notice that the myelin sheaths are not all the same thickness. Some fibers are heavily myelinated while others are more lightly myelinated, eve ...
Sensory Pathways (Ascending Tracts)
... Descriminative touch Vibratory sense Conscious muscle joint sense ...
... Descriminative touch Vibratory sense Conscious muscle joint sense ...
Ice Ice Baby: Effects of Temperature on Typing Speed
... output caused by a continuous amount of force 2. • Nerve conduction velocity is influenced by nerve temperature in peripheral nerve fibers 3. • Temperature may affect the activation of the muscle in use can result in muscle potentiation which is characterized by increase in twitch force and decrease ...
... output caused by a continuous amount of force 2. • Nerve conduction velocity is influenced by nerve temperature in peripheral nerve fibers 3. • Temperature may affect the activation of the muscle in use can result in muscle potentiation which is characterized by increase in twitch force and decrease ...
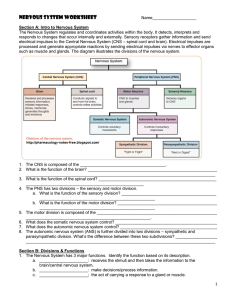
Nervous System Worksheet - Jackson County Faculty Sites!
... when we are learning and removes unneeded synapses. Our brain is constantly adapting to reflect our lives. http://www.healthybrainforlife.com/ 12. Label the neuron. ...
... when we are learning and removes unneeded synapses. Our brain is constantly adapting to reflect our lives. http://www.healthybrainforlife.com/ 12. Label the neuron. ...
Nerve Regeneration in the Cornea
... Sensory Innervation to the Cornea from the Trigeminal Ganglion is important for the Perception of Stimuli, Maintenance of Hydration and Avoidance of Injury. ...
... Sensory Innervation to the Cornea from the Trigeminal Ganglion is important for the Perception of Stimuli, Maintenance of Hydration and Avoidance of Injury. ...
Learning Skill
... Simultaneously, conscious image of movement (based on sensory input) is compared to conscious memory of what we should look like while we do it and we make conscious adjustments to mimic the conscious memory of the skill. Integration of conscious and subconscious adjustments based on conscious and s ...
... Simultaneously, conscious image of movement (based on sensory input) is compared to conscious memory of what we should look like while we do it and we make conscious adjustments to mimic the conscious memory of the skill. Integration of conscious and subconscious adjustments based on conscious and s ...
Chapter 6 The peripheral nervous system Unit
... system with the receptors, muscles and glands make up the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system consists of nerve fibres that carry information to and from the central nervous system and groups of nerve cell bodies, ganglia, which lie outside the brain and spinal cord. The nerve c ...
... system with the receptors, muscles and glands make up the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system consists of nerve fibres that carry information to and from the central nervous system and groups of nerve cell bodies, ganglia, which lie outside the brain and spinal cord. The nerve c ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.