Peripheral Nervous System
... Ganglia are small group of nerve cells outside the CNS. They are nodular masses of neuronal cell bodies, glial cells and Satellite cells supporting by C.T, ganglia transmit nerve impulses. According the direction of the nerve impulse, there are two kinds of ganglia in the PNS: 1- Sensory ganglia: It ...
... Ganglia are small group of nerve cells outside the CNS. They are nodular masses of neuronal cell bodies, glial cells and Satellite cells supporting by C.T, ganglia transmit nerve impulses. According the direction of the nerve impulse, there are two kinds of ganglia in the PNS: 1- Sensory ganglia: It ...
Chapter 15 - Nervous System Brain & Cranial Nerves
... Sulci and gyri = valleys and ridges on surface of cerebral hemispheres. Five lobes: Frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal and insula. ...
... Sulci and gyri = valleys and ridges on surface of cerebral hemispheres. Five lobes: Frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal and insula. ...
P312Ch11_Auditory III (Coding Frequency And Intensity
... If a sound is composed of several frequencies, it will activate several receptors – one for each of the frequencies comprising the sound. Analogy: 100s of different cone types in the eye - a different type of cone for each wavelength of light. Since each auditory nerve synapses only with hair cells ...
... If a sound is composed of several frequencies, it will activate several receptors – one for each of the frequencies comprising the sound. Analogy: 100s of different cone types in the eye - a different type of cone for each wavelength of light. Since each auditory nerve synapses only with hair cells ...
Vision
... Sensitive to mechanical energy Sensitive to heat and cold Detect changes in concentration of solutes in body fluids and resultant changes in osmotic activity Sensitive to specific chemicals Include receptors for smell and taste and receptors that detect O2 and CO2 concentrations in blood and chemica ...
... Sensitive to mechanical energy Sensitive to heat and cold Detect changes in concentration of solutes in body fluids and resultant changes in osmotic activity Sensitive to specific chemicals Include receptors for smell and taste and receptors that detect O2 and CO2 concentrations in blood and chemica ...
Articular Receptors
... A muscle spindle is oriented parallel to extrafusal muscle fibers. It is covered with a capsule and contains two types of intrafusal muscle fibers: bag fibers (BF) and chain fibers (CF). Two types of sensory endings can be found in muscle spindles: primary (Ia) and secondary (II). Primary endings ar ...
... A muscle spindle is oriented parallel to extrafusal muscle fibers. It is covered with a capsule and contains two types of intrafusal muscle fibers: bag fibers (BF) and chain fibers (CF). Two types of sensory endings can be found in muscle spindles: primary (Ia) and secondary (II). Primary endings ar ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 19.1 Evidence of synapse elimination
... innervated neuromuscular junctions are on twitch muscle fibers that have voltage-sensitive sodium channels. The multiply innervated neuromuscular junctions are found on tonic muscle fibers that do not have regenerative potentials. Labeling of different axons with different colors was accomplished by ...
... innervated neuromuscular junctions are on twitch muscle fibers that have voltage-sensitive sodium channels. The multiply innervated neuromuscular junctions are found on tonic muscle fibers that do not have regenerative potentials. Labeling of different axons with different colors was accomplished by ...
Foot Drop and the Common Peroneal Nerve
... the opening into the muscle compartment is opened. You can walk immediately after the surgery. Sensory and motor function can take up to one year to recover. ...
... the opening into the muscle compartment is opened. You can walk immediately after the surgery. Sensory and motor function can take up to one year to recover. ...
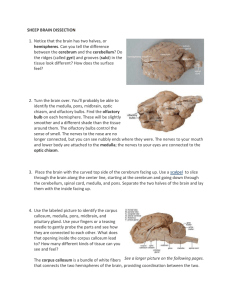
Sheep Brain Dissection Instructions
... The temporal lobe is involved in hearing and smell. You can find this by looking on the outside of one of the hemispheres. You will see a horizontal groove called the lateral fissure. The temporal lobe is the section of the cerebrum below this line. The frontal lobe also plays a part in smell, plus ...
... The temporal lobe is involved in hearing and smell. You can find this by looking on the outside of one of the hemispheres. You will see a horizontal groove called the lateral fissure. The temporal lobe is the section of the cerebrum below this line. The frontal lobe also plays a part in smell, plus ...
Fact Sheet 2 - Consulting Foot Pain
... How will I know that I have a neuroma? The foot suffers from tingling or shooting into the toes. Pain is usually concentrated between the second and third digits or third and fourth digits, possibly accompanied by a clicking sensation. When the pain has been present for only a short period of time, ...
... How will I know that I have a neuroma? The foot suffers from tingling or shooting into the toes. Pain is usually concentrated between the second and third digits or third and fourth digits, possibly accompanied by a clicking sensation. When the pain has been present for only a short period of time, ...
1. A unicellular protest may use a contractile vacuole to expel
... 28. After the depolarization of an action potential, the fall in the membrane potential occurs due to the a. Closing of sodium inactivation gates. b. Closing of potassium and sodium channels. c. Refractory period in which the membrane is hyperpolarized. d. Opening of voltage-gated potassium channels ...
... 28. After the depolarization of an action potential, the fall in the membrane potential occurs due to the a. Closing of sodium inactivation gates. b. Closing of potassium and sodium channels. c. Refractory period in which the membrane is hyperpolarized. d. Opening of voltage-gated potassium channels ...
STUDY GUIDE 8
... neuron. A depolarized membrane is repolarized Neurotransmitter 11) ___________________________________________ when ____8___ ions diffuse out of the neuron and 12) ___________________________________________ Synaptic cleft replace the ____9___ ions that entered the neuron. Neurotransmitter 13) _____ ...
... neuron. A depolarized membrane is repolarized Neurotransmitter 11) ___________________________________________ when ____8___ ions diffuse out of the neuron and 12) ___________________________________________ Synaptic cleft replace the ____9___ ions that entered the neuron. Neurotransmitter 13) _____ ...
Chapter 48
... The equilibrium potential of K+ (EK) is negative, while the equilibrium potential of Na+ (ENa) is positive In a resting neuron, the currents of K+ and Na+ are equal and opposite, and the resting potential across the membrane remains steady © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... The equilibrium potential of K+ (EK) is negative, while the equilibrium potential of Na+ (ENa) is positive In a resting neuron, the currents of K+ and Na+ are equal and opposite, and the resting potential across the membrane remains steady © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
48 BIOLOGY 1. Overview of Neurons 11/3/2014
... The equilibrium potential (Eion) is the membrane voltage for a particular ion at equilibrium and can be calculated using the Nernst equation Eion = 62 mV (log[ion]outside/[ion]inside) The equilibrium potential of K+ (EK) is negative, while the equilibrium potential of Na+ (ENa) is positive In ...
... The equilibrium potential (Eion) is the membrane voltage for a particular ion at equilibrium and can be calculated using the Nernst equation Eion = 62 mV (log[ion]outside/[ion]inside) The equilibrium potential of K+ (EK) is negative, while the equilibrium potential of Na+ (ENa) is positive In ...
in the name of god faraji.z.md
... Is the injured structure still as tender to touch? Is there any deformity present today that was not as obvious yesterday? ...
... Is the injured structure still as tender to touch? Is there any deformity present today that was not as obvious yesterday? ...
The Nervous System
... by another neuron or by the environment Resting neuron have a charge, or electrical potential, across their cell membranes. The inside of a neuron has a voltage of –70 millivolts (mV) compared to the outside. This difference is known as the resting potential ...
... by another neuron or by the environment Resting neuron have a charge, or electrical potential, across their cell membranes. The inside of a neuron has a voltage of –70 millivolts (mV) compared to the outside. This difference is known as the resting potential ...
a)write short notes about the anatomy of optic nerve
... a)write short notes about the anatomy of optic nerve Optic Nerve (Cranial Nerve II) Origin of the Optic Nerve ...
... a)write short notes about the anatomy of optic nerve Optic Nerve (Cranial Nerve II) Origin of the Optic Nerve ...
Zoology Assignment - Wikimedia Commons
... respond to mechanically induced changes caused by stretching, compression, bending, or tension. These receptors give an animal information about the movement of its body parts and their positions relative to each other. Proprioceptors have been most thoroughly studied in arthropods, where they are a ...
... respond to mechanically induced changes caused by stretching, compression, bending, or tension. These receptors give an animal information about the movement of its body parts and their positions relative to each other. Proprioceptors have been most thoroughly studied in arthropods, where they are a ...
The Brain
... hemispheres separated by a longitudinal fissure o Cerebellum – second largest part of the brain, inferior to the cerebrum o Brainstem – all of the brain except the cerebrum and cerebellum Major components include the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and diencephalon Grey and White Matter o Gre ...
... hemispheres separated by a longitudinal fissure o Cerebellum – second largest part of the brain, inferior to the cerebrum o Brainstem – all of the brain except the cerebrum and cerebellum Major components include the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and diencephalon Grey and White Matter o Gre ...
File
... •That contains nucleus Dendrites Mutiple branching hair like extensions that arise from the cell body of a neuron . It receives messages from other neurone and conducts impulses toward the cell body Axon Single long extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers ( called axon termina ...
... •That contains nucleus Dendrites Mutiple branching hair like extensions that arise from the cell body of a neuron . It receives messages from other neurone and conducts impulses toward the cell body Axon Single long extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers ( called axon termina ...
Neural Conduction - U
... • the resting potential exists because positively and negatively charged ions are distributed unequally on the two sides of the neural membrane: the concentration of Na+ and Cl- are higher outside the neuron, and the concentration of K+ and various negatively charged proteins are higher inside the n ...
... • the resting potential exists because positively and negatively charged ions are distributed unequally on the two sides of the neural membrane: the concentration of Na+ and Cl- are higher outside the neuron, and the concentration of K+ and various negatively charged proteins are higher inside the n ...
nervous system
... 28.16 CONNECTION: Injuries and brain operations provide insight into brain function Brain injuries and surgeries reveal brain functions. – After a 13-pound steel rod pierced his skull, Phineas Gage appeared to have an intact intellect but his associates noted negative changes to his personality. ...
... 28.16 CONNECTION: Injuries and brain operations provide insight into brain function Brain injuries and surgeries reveal brain functions. – After a 13-pound steel rod pierced his skull, Phineas Gage appeared to have an intact intellect but his associates noted negative changes to his personality. ...
The Nervous System
... •If your body is too hot, the hypothalamus tells it to sweat. •If you're too cold, the hypothalamus gets you shivering. •Both shivering and sweating are attempts to get your body's temperature back where it needs to be. ...
... •If your body is too hot, the hypothalamus tells it to sweat. •If you're too cold, the hypothalamus gets you shivering. •Both shivering and sweating are attempts to get your body's temperature back where it needs to be. ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.