WHAT IS THE MAMMALIAN DENTATE GYRUS GOOD FOR? Alessandro Treves
... performing expansion recoding (Marr, 1969). In the cerebellum, however, the granule cells are postsynaptic to the axons that are called (there) mossy fibers, and the huge cerebellar expansion factor from mossy fibers to granule cells is not observed in the hippocampus, where the striking element, in ...
... performing expansion recoding (Marr, 1969). In the cerebellum, however, the granule cells are postsynaptic to the axons that are called (there) mossy fibers, and the huge cerebellar expansion factor from mossy fibers to granule cells is not observed in the hippocampus, where the striking element, in ...
Behavioural Brain Research Learning processing in the basal ganglia
... after the second half of the last century. Studies involving patients who became amnesic after lesion to the medial temporal lobe (such as patient H.M.) have shown that these patients conserved some learning and memory abilities later named nondeclarative or procedural memories [190,196]. These clin ...
... after the second half of the last century. Studies involving patients who became amnesic after lesion to the medial temporal lobe (such as patient H.M.) have shown that these patients conserved some learning and memory abilities later named nondeclarative or procedural memories [190,196]. These clin ...
THE SYNAPSE
... symmetric synapses involve axons that contain clusters of vesicles that are predominantly flattened or elongate in their appearance. The pre-and postsynaptic membranes are more parallel than the surrounding nonsynaptic membrane, and the synapse does not contain a prominent postsynaptic density. Clic ...
... symmetric synapses involve axons that contain clusters of vesicles that are predominantly flattened or elongate in their appearance. The pre-and postsynaptic membranes are more parallel than the surrounding nonsynaptic membrane, and the synapse does not contain a prominent postsynaptic density. Clic ...
Functional characterization of the synaptic
... tumor or an infection in the adult brain and span throughout life. Although the underlying etiology of the various disorders might be different, all of them lead to similar brain dysfunctions (defects of the sensory and motor system) and to comparable cognitive deficits in learning and memory. Epile ...
... tumor or an infection in the adult brain and span throughout life. Although the underlying etiology of the various disorders might be different, all of them lead to similar brain dysfunctions (defects of the sensory and motor system) and to comparable cognitive deficits in learning and memory. Epile ...
Temporal Sequence Detection with Spiking Neurons: Towards
... active dendrites and dynamic synapses in an integrated model. For a long time, dendrites have been thought to be the structures where complex neuronal computation takes place, but only recently have we begun to understand how they operate. The dendrites do not simply collect and pass synaptic inputs ...
... active dendrites and dynamic synapses in an integrated model. For a long time, dendrites have been thought to be the structures where complex neuronal computation takes place, but only recently have we begun to understand how they operate. The dendrites do not simply collect and pass synaptic inputs ...
REVIEWS - Institute for Applied Psychometrics
... central to the playing of music30 (e). LTD, long-term depression; LTP, long-term potentiation. ...
... central to the playing of music30 (e). LTD, long-term depression; LTP, long-term potentiation. ...
A thalamic reticular networking model of consciousness
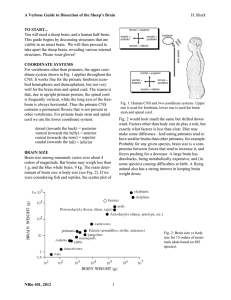
... [Background]: It is reasonable to consider the thalamus a primary candidate for the location of consciousness, given that the thalamus has been referred to as the gateway of nearly all sensory inputs to the corresponding cortical areas. Interestingly, in an early stage of brain development, communic ...
... [Background]: It is reasonable to consider the thalamus a primary candidate for the location of consciousness, given that the thalamus has been referred to as the gateway of nearly all sensory inputs to the corresponding cortical areas. Interestingly, in an early stage of brain development, communic ...
Complete morphologies of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in
... One of the most studied networks in the human brain is the basal forebrain network, which is made up of large neurons that communicate with one another using a chemical transmitter called acetylcholine. This network has a key role in cognition, and its neurons are among the first to degenerate in Al ...
... One of the most studied networks in the human brain is the basal forebrain network, which is made up of large neurons that communicate with one another using a chemical transmitter called acetylcholine. This network has a key role in cognition, and its neurons are among the first to degenerate in Al ...
A Verbose Guide to Dissection of the Sheep`s Brain H
... on other sensory modalities, the optic nerve is punier (see alligator). In the Ganges River dolphin, "this nerve is as thin as a thread" (Pilleri & Gihr, 1970), as vision is of little use in its turgid environment. The 5th cranial nerve, the trigeminal, actually consists of two nerves running togeth ...
... on other sensory modalities, the optic nerve is punier (see alligator). In the Ganges River dolphin, "this nerve is as thin as a thread" (Pilleri & Gihr, 1970), as vision is of little use in its turgid environment. The 5th cranial nerve, the trigeminal, actually consists of two nerves running togeth ...
Unsupervised feature learning from finite data by
... reveals that αc = β14 (Appendix C). Next, we show the entropy per neuron in the inset of Fig. 2(a). This quantity that describes how many feature vectors are consistent with the data becomes negative (i.e., entropy crisis [13,14]) at a zero-entropy αZE . However, the BP equation is still stable (con ...
... reveals that αc = β14 (Appendix C). Next, we show the entropy per neuron in the inset of Fig. 2(a). This quantity that describes how many feature vectors are consistent with the data becomes negative (i.e., entropy crisis [13,14]) at a zero-entropy αZE . However, the BP equation is still stable (con ...
Demonstrating the Implicit Processing of Visually Presented Words
... have legitimate word forms with semantic and phonological representations; related activity was detected in the left medial extrastriate visual cortex and a left prefrontal area. Pseudowords have legitimate word forms from which phonological but not semantic associations can be computed; related act ...
... have legitimate word forms with semantic and phonological representations; related activity was detected in the left medial extrastriate visual cortex and a left prefrontal area. Pseudowords have legitimate word forms from which phonological but not semantic associations can be computed; related act ...
Fatty acid amide hydrolase expression in rat choroid plexus
... With both FAAH antibodies tested, FAAH immunoreactivity was localised in the somata of identi®ed neurons in several regions of the brain including cerebellar Purkinje cells, hippocampal pyramidal cells, neocortical pyramidal cells and mitral cells of the olfactory bulbs, as reported previously [6,12 ...
... With both FAAH antibodies tested, FAAH immunoreactivity was localised in the somata of identi®ed neurons in several regions of the brain including cerebellar Purkinje cells, hippocampal pyramidal cells, neocortical pyramidal cells and mitral cells of the olfactory bulbs, as reported previously [6,12 ...
Basal Ganglia Outputs Map Instantaneous Position Coordinates
... The basal ganglia (BG) are implicated in many movement disorders, yet how they contribute to movement remains unclear. Using wireless in vivo recording, we measured BG output from the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr) in mice while monitoring their movements with video tracking. The firing rate ...
... The basal ganglia (BG) are implicated in many movement disorders, yet how they contribute to movement remains unclear. Using wireless in vivo recording, we measured BG output from the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr) in mice while monitoring their movements with video tracking. The firing rate ...
REVIEW Reticular formation and spinal cord injury
... classical distinction between neurotransmitters and neurohormones is blurred. It can be seen from the table that one area or one type of neuron may release more than one type of neurotransmitters whereas one type of neurotransmitter can be synthesized by more than one area or one type of neurons. Th ...
... classical distinction between neurotransmitters and neurohormones is blurred. It can be seen from the table that one area or one type of neuron may release more than one type of neurotransmitters whereas one type of neurotransmitter can be synthesized by more than one area or one type of neurons. Th ...
In transverse section, the spinal cord features: -
... Fig. 15. Meninges are connective tissue layers surrounding the brain, the spinal cord, and the roots of peripheral nerves. The pia mater (P) is a delicate connective tissue layer attached directly to the white matter of the spinal cord. The dura mater (D) is a thick connective tissue layer. It is t ...
... Fig. 15. Meninges are connective tissue layers surrounding the brain, the spinal cord, and the roots of peripheral nerves. The pia mater (P) is a delicate connective tissue layer attached directly to the white matter of the spinal cord. The dura mater (D) is a thick connective tissue layer. It is t ...
The projection of the lateral geniculate nucleus to area 17 of the rat
... are asymmetric in form. While dendrite 2 has a relatively uniform thickness of about 1 9.m the surprising feature of dendrite I is the very thin middle segment. In this segment, including the place where it receives the degenerating geniculocortical axon terminal, the diameter of the dendrite is onl ...
... are asymmetric in form. While dendrite 2 has a relatively uniform thickness of about 1 9.m the surprising feature of dendrite I is the very thin middle segment. In this segment, including the place where it receives the degenerating geniculocortical axon terminal, the diameter of the dendrite is onl ...
R Spinal Cord A-1 - UMass Medical School
... nucleus (also called the nucleus dorsalis or column of Clarke) forms a bulge in the intermediate gray matter that pushes up into the posterior columns. Be sure that you identify Clarke's nucleus in this section (it is one of the circled structures). While Clarke's nucleus extends from T1 to L2, it i ...
... nucleus (also called the nucleus dorsalis or column of Clarke) forms a bulge in the intermediate gray matter that pushes up into the posterior columns. Be sure that you identify Clarke's nucleus in this section (it is one of the circled structures). While Clarke's nucleus extends from T1 to L2, it i ...
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) PNS – all neural structures
... Hair follicle receptors (free nerve endings wrapped around hair follicles) are light touch receptors that detect bending hair (e.g. detection of a landing mosquito) ...
... Hair follicle receptors (free nerve endings wrapped around hair follicles) are light touch receptors that detect bending hair (e.g. detection of a landing mosquito) ...
Chapter 1
... – Activation of one cortical area by an inducing stimulus (say, letters) causes co-activation of another cortical area (say, the color area), ...
... – Activation of one cortical area by an inducing stimulus (say, letters) causes co-activation of another cortical area (say, the color area), ...
Corollary Discharge Inhibition and Preservation of Temporal
... (Slesinger and Bell, 1985), and no corollary discharge effect is observed inside ampullary afferents (C. C. Bell, unpublished observations). Histology.At least 2 hr were allowed to pass between the last intracellular injection of HRP or Lucifer yellow and perfusion of the fish. For perfusion, the fi ...
... (Slesinger and Bell, 1985), and no corollary discharge effect is observed inside ampullary afferents (C. C. Bell, unpublished observations). Histology.At least 2 hr were allowed to pass between the last intracellular injection of HRP or Lucifer yellow and perfusion of the fish. For perfusion, the fi ...
LESSON 2.3 WORKBOOK How fast do our neurons signal?
... Remember that the problem with a single action potential was that the current would decay. To prevent that decay glial cells wrap around the axon like beads on a necklace covering the axon tightly except for the areas in between the beads called nodes of Ranvier which remain naked axon (Figure 17). ...
... Remember that the problem with a single action potential was that the current would decay. To prevent that decay glial cells wrap around the axon like beads on a necklace covering the axon tightly except for the areas in between the beads called nodes of Ranvier which remain naked axon (Figure 17). ...
Basal Forebrain Cholinergic System Is Involved in Rapid Nerve
... under behavioral conditions when cortical representations need to be rapidly augmented by increasing cortical excitability and by recruiting more neurons, cortical neurons release NGF in an activity-dependent manner in addition to the basal release of NGF needed for the survival and maintenance of t ...
... under behavioral conditions when cortical representations need to be rapidly augmented by increasing cortical excitability and by recruiting more neurons, cortical neurons release NGF in an activity-dependent manner in addition to the basal release of NGF needed for the survival and maintenance of t ...
successful transplantation of motoneurons into the peripheral nerve
... Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan) was used to selectively label the nuclei. For each preparation, the number of b-tubulin III positive and islet-1 positive cells was counted in 100 fields of cells from at least 10 different coverslips. MN ratio was calculated by dividing the number of cells stained with bot ...
... Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan) was used to selectively label the nuclei. For each preparation, the number of b-tubulin III positive and islet-1 positive cells was counted in 100 fields of cells from at least 10 different coverslips. MN ratio was calculated by dividing the number of cells stained with bot ...
THE AREA POSTREMA: A POTENTIAL SITE FOR CIRCADIAN REGULATION BY
... ion substitution experiments revealed a PK2-induced Cl- current was responsible for membrane depolarization, while hyperpolarizations were the result of inhibition of an inwardly rectifying non-selective cation current. In contrast to these differential effects on membrane potential, nearly all neur ...
... ion substitution experiments revealed a PK2-induced Cl- current was responsible for membrane depolarization, while hyperpolarizations were the result of inhibition of an inwardly rectifying non-selective cation current. In contrast to these differential effects on membrane potential, nearly all neur ...
Slide 1
... eye abducts normally. Involvement of the medial longitudinal fasciculus interrupts the pathway to the left oculomotor (III) nucleus, and the left eye fails to adduct. On attempted gaze toward the lesion (B), the left lateral gaze center cannot be activated, and the eyes do not move. There is a compl ...
... eye abducts normally. Involvement of the medial longitudinal fasciculus interrupts the pathway to the left oculomotor (III) nucleus, and the left eye fails to adduct. On attempted gaze toward the lesion (B), the left lateral gaze center cannot be activated, and the eyes do not move. There is a compl ...