A Symmetric Approach Elucidates Multisensory Information Integration
... elucidates what the BUT brings on the table, when applied to multimodal neurons. 1. Classical vs. Current View Traditional research on the basic science of sensation asks what types of information the brain receives from the external world. To elucidate the classical view, as an example we will go t ...
... elucidates what the BUT brings on the table, when applied to multimodal neurons. 1. Classical vs. Current View Traditional research on the basic science of sensation asks what types of information the brain receives from the external world. To elucidate the classical view, as an example we will go t ...
Direct cortical control of muscle activation in voluntary arm movements
... managed to decode the mixed MI signal in real time. The other extreme is to question whether “movement parameters are recognizably coded in the activity of single neurons” in the first place22. It is argued that they are not and do not need to be, as all that matters is the population average of the ...
... managed to decode the mixed MI signal in real time. The other extreme is to question whether “movement parameters are recognizably coded in the activity of single neurons” in the first place22. It is argued that they are not and do not need to be, as all that matters is the population average of the ...
Reflex arcs PowerPoint
... Stimulation of the Reflex Response The speed of the reflex response can be increase by several factors: Exposure to adrenaline (Sympathetic Nervous System) Exposure to stimulant drugs (Caffeine, Beta Amphetamines/Speed) ...
... Stimulation of the Reflex Response The speed of the reflex response can be increase by several factors: Exposure to adrenaline (Sympathetic Nervous System) Exposure to stimulant drugs (Caffeine, Beta Amphetamines/Speed) ...
ORGANIZATION OF NEUROPIL
... two groups, glomerular and stratified. Glomerular neuropil is characterized by tight, profuse ramifications of pre- and postsynaptic elements at the site of junction (Fig. 6). These ramifications form the discrete, knot-like clusters of fibers that give this kind of neuropil its name. The glomeruli ...
... two groups, glomerular and stratified. Glomerular neuropil is characterized by tight, profuse ramifications of pre- and postsynaptic elements at the site of junction (Fig. 6). These ramifications form the discrete, knot-like clusters of fibers that give this kind of neuropil its name. The glomeruli ...
Acquired Equivalence and Distinctiveness of Cues
... Revaluation of A and C and Test Trials With B and D Prior to the appetitive revaluation procedure, we established that rats’ behavior in the presence of B and D did not differ (see following Results section). We did this by recording the rates of magazine entries during the 10-s periods that immedia ...
... Revaluation of A and C and Test Trials With B and D Prior to the appetitive revaluation procedure, we established that rats’ behavior in the presence of B and D did not differ (see following Results section). We did this by recording the rates of magazine entries during the 10-s periods that immedia ...
A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in
... We shall make the following physical assumptions for our calculus. 1. The activity of the neuron is an "all-or-none" process. 2. A certain fixed number of synapses must be excited within the period of latent addition in order to excite a neuron at any time, and this number is independent of previous ...
... We shall make the following physical assumptions for our calculus. 1. The activity of the neuron is an "all-or-none" process. 2. A certain fixed number of synapses must be excited within the period of latent addition in order to excite a neuron at any time, and this number is independent of previous ...
Information Processing in Motor Learning
... Transport the information necessary for all activities we carry out The language of the nervous system Relay of impulse within neuron: ...
... Transport the information necessary for all activities we carry out The language of the nervous system Relay of impulse within neuron: ...
Information Processing in Motor Learning
... Transport the information necessary for all activities we carry out The language of the nervous system Relay of impulse within neuron: ...
... Transport the information necessary for all activities we carry out The language of the nervous system Relay of impulse within neuron: ...
to a of the units.
... The first lesson of this unit introduces different parts of the nervous system by constructing a model of the nervous system with a full body tracing. Students will learn how the brain sends and receives messages via the nervous system. Any part of the body that can move or feel is connected to the ...
... The first lesson of this unit introduces different parts of the nervous system by constructing a model of the nervous system with a full body tracing. Students will learn how the brain sends and receives messages via the nervous system. Any part of the body that can move or feel is connected to the ...
Chapter 48
... Neurons communicate with other cells at synapses At electrical synapses, the electrical current flows from one neuron to another through gap junctions At chemical synapses, a chemical neurotransmitter carries information between neurons ...
... Neurons communicate with other cells at synapses At electrical synapses, the electrical current flows from one neuron to another through gap junctions At chemical synapses, a chemical neurotransmitter carries information between neurons ...
48 BIOLOGY 1. Overview of Neurons 11/3/2014
... Neurons communicate with other cells at synapses At electrical synapses, the electrical current flows from one neuron to another through gap junctions At chemical synapses, a chemical neurotransmitter carries information between neurons ...
... Neurons communicate with other cells at synapses At electrical synapses, the electrical current flows from one neuron to another through gap junctions At chemical synapses, a chemical neurotransmitter carries information between neurons ...
Information Processing at the Calyx of Held Under Natural Conditions
... results in the context of a mathematical vesicle-release model. One of the hallmarks of auditory neurons in vivo is spontaneous activity that occurs even in the absence of any sensory stimuli. Sound evoked bursts of discharges are thus embedded within this background of random firing. The calyx of H ...
... results in the context of a mathematical vesicle-release model. One of the hallmarks of auditory neurons in vivo is spontaneous activity that occurs even in the absence of any sensory stimuli. Sound evoked bursts of discharges are thus embedded within this background of random firing. The calyx of H ...
Sensory Part 1
... Neurons of the retina and vision Cones Allow for detailed color vision Densest in the center of the retina Fovea centralis—area of the retina with only cones No photoreceptor cells are at the optic disc, or blind spot ...
... Neurons of the retina and vision Cones Allow for detailed color vision Densest in the center of the retina Fovea centralis—area of the retina with only cones No photoreceptor cells are at the optic disc, or blind spot ...
Cxcl12/Cxcr4 signaling controls the migration and
... neuroblasts and neurons (Smidt et al., 2000); and Nurr1, which is a nuclear receptor expressed by postmitotic mDA neuroblasts and neurons (Castillo et al., 1998; Saucedo-Cardenas et al., 1998; Zetterström et al., 1997; Castillo et al., 1998; Saucedo-Cardenas et al., 1998; Zetterström et al., 1997). ...
... neuroblasts and neurons (Smidt et al., 2000); and Nurr1, which is a nuclear receptor expressed by postmitotic mDA neuroblasts and neurons (Castillo et al., 1998; Saucedo-Cardenas et al., 1998; Zetterström et al., 1997; Castillo et al., 1998; Saucedo-Cardenas et al., 1998; Zetterström et al., 1997). ...
Dopamine: generalization and bonuses
... sometimes consists of a short-term increase above baseline followed by a short-term decrease below baseline. Second, dopamine release is associated with a set of motor effects, such as species- and stimulus-specific approach behaviors, that seem either irrelevant or detrimental to the delivery of re ...
... sometimes consists of a short-term increase above baseline followed by a short-term decrease below baseline. Second, dopamine release is associated with a set of motor effects, such as species- and stimulus-specific approach behaviors, that seem either irrelevant or detrimental to the delivery of re ...
Nerve Cell Communication - URMC
... Place the pink impulse card on the neuron and move it along the axon to the terminal branches. When the impulse reaches the terminal branches, the receiving neuron becomes a sending neuron that releases its neurotransmitters to send messages to other neurons. 13. Which part of a neuron receives ...
... Place the pink impulse card on the neuron and move it along the axon to the terminal branches. When the impulse reaches the terminal branches, the receiving neuron becomes a sending neuron that releases its neurotransmitters to send messages to other neurons. 13. Which part of a neuron receives ...
Stimulus Dependence of Local Field Potential Spectra: Experiment
... network. Because our model does not take into account the spatial organization of cortical neurons, we used the simpler approach of Mazzoni et al. (2008) to describe the generation of the LFP. This approach is based on the fact that the major contribution to the LFP generation is given by pyramidal ...
... network. Because our model does not take into account the spatial organization of cortical neurons, we used the simpler approach of Mazzoni et al. (2008) to describe the generation of the LFP. This approach is based on the fact that the major contribution to the LFP generation is given by pyramidal ...
Mirror neurons and their clinical relevance
... Traditionally, it has been assumed that the understanding of actions performed by others depends on inferential reasoning.1–3 Theoretically, when we witness the actions of others, the information could initially be subjected to sensory processing and then be sent to higher order ‘association’ areas ...
... Traditionally, it has been assumed that the understanding of actions performed by others depends on inferential reasoning.1–3 Theoretically, when we witness the actions of others, the information could initially be subjected to sensory processing and then be sent to higher order ‘association’ areas ...
Spike-timing dependent plasticity and the cognitive map
... for background neurons. An examination of the resultant neural dynamics confirms that this form of input produces a Gaussian distribution of ISI (data not shown). In each of these simulations, all synaptic connections in the network are initialized with a weight of wij = 0.3 unless specified otherwi ...
... for background neurons. An examination of the resultant neural dynamics confirms that this form of input produces a Gaussian distribution of ISI (data not shown). In each of these simulations, all synaptic connections in the network are initialized with a weight of wij = 0.3 unless specified otherwi ...
Nerve Cell Communication - URMC
... Place the pink impulse card on the neuron and move it along the axon to the terminal branches. When the impulse reaches the terminal branches, the receiving neuron becomes a sending neuron that releases its neurotransmitters to send messages to other neurons. 13. Which part of a neuron receives ...
... Place the pink impulse card on the neuron and move it along the axon to the terminal branches. When the impulse reaches the terminal branches, the receiving neuron becomes a sending neuron that releases its neurotransmitters to send messages to other neurons. 13. Which part of a neuron receives ...
RIKEN Center for Developmental Biology (CDB)
... olfactory bulb viewed from front. Nrp1-positive axons normally targeted to the posterior were mistargeted to anterior. Nrp-positive and -negative axons were jumbled and formed small glomerular-like structures (blue, nucleus; green, ONS; red, Nrp1; scale bar 100 μm) ...
... olfactory bulb viewed from front. Nrp1-positive axons normally targeted to the posterior were mistargeted to anterior. Nrp-positive and -negative axons were jumbled and formed small glomerular-like structures (blue, nucleus; green, ONS; red, Nrp1; scale bar 100 μm) ...
Olfaction
... However, each olfactory nerve fiber and central olfactory neuron responds to multiple odorants. The spatial distribution of activity in the salamander olfactory bulb is the same for three very different odors (although absolute levels of activity are different). ...
... However, each olfactory nerve fiber and central olfactory neuron responds to multiple odorants. The spatial distribution of activity in the salamander olfactory bulb is the same for three very different odors (although absolute levels of activity are different). ...
pdf file
... Recently it has been found that in humans a specific type of neurons exists, called mirror neurons, which both are active to prepare for certain actions or bodily changes and when such actions or body states are observed in other persons. The discovery of mirror neurons originates from single cell r ...
... Recently it has been found that in humans a specific type of neurons exists, called mirror neurons, which both are active to prepare for certain actions or bodily changes and when such actions or body states are observed in other persons. The discovery of mirror neurons originates from single cell r ...
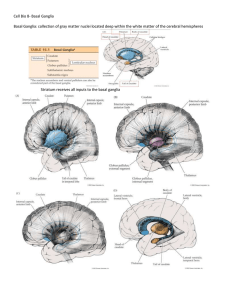
Cell Bio 8- Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia: collection of gray matter
... Increased resistance to passive movement of a limb In spasticity, which results from upper motor neuron lesions, rigidity is velocity dependent. Resistive tone initially increases as the muscles of the limb are stretched, but it may then decrease, giving rise to claspknife rigidity in corticospinal ...
... Increased resistance to passive movement of a limb In spasticity, which results from upper motor neuron lesions, rigidity is velocity dependent. Resistive tone initially increases as the muscles of the limb are stretched, but it may then decrease, giving rise to claspknife rigidity in corticospinal ...
M555 Medical Neuroscience
... Compare the size amd the relative amounts of gray and white matter at the four levels of the spinal cord so that you can identify the spinal level when shown a cross-section of the cord. ...
... Compare the size amd the relative amounts of gray and white matter at the four levels of the spinal cord so that you can identify the spinal level when shown a cross-section of the cord. ...