Quantitative analysis of APP axonal transport in neurons: role of
... been independently identified as a kinesin light chain (KLC)–binding protein (Verhey et al., 2001; Inomata et al., 2003; Matsuda et al., 2003). Recently JIP1 was found to also associate with kinesin heavy chain (KHC; Fu and Holzbaur, 2013). APP is transported anterogradely by the conventional kinesi ...
... been independently identified as a kinesin light chain (KLC)–binding protein (Verhey et al., 2001; Inomata et al., 2003; Matsuda et al., 2003). Recently JIP1 was found to also associate with kinesin heavy chain (KHC; Fu and Holzbaur, 2013). APP is transported anterogradely by the conventional kinesi ...
Anandamide as an intracellular messenger regulating ion channel
... to directly inhibit Shaker-related voltage sensitive K+ -channels at low micromolar concentrations [41]. Although the effect was shared by THC and other polyunsaturated Nacylethanolamines, it was insensitive towards blockade by SR141716A. This suggests that the modulation of the K+ -channel was inde ...
... to directly inhibit Shaker-related voltage sensitive K+ -channels at low micromolar concentrations [41]. Although the effect was shared by THC and other polyunsaturated Nacylethanolamines, it was insensitive towards blockade by SR141716A. This suggests that the modulation of the K+ -channel was inde ...
Image-based Screening Identifies Novel Roles for I B Kinase and
... that begin with swelling and blebbing and culminate in fragmentation that is complete by 24 h in vitro. To quantify axon degeneration dynamically at multiple time points, we employed automated microscopy and image analysis. The extent of axon fragmentation can be quantified from brightfield or phase ...
... that begin with swelling and blebbing and culminate in fragmentation that is complete by 24 h in vitro. To quantify axon degeneration dynamically at multiple time points, we employed automated microscopy and image analysis. The extent of axon fragmentation can be quantified from brightfield or phase ...
Week 3 – Day 1
... The mass of a rusty bicycle is found to be slightly greater than the mass of the same bicycle before it rusted. The change in mass indicates that the rusting process — A) is a physical change B) involves an energy-to-matter conversion C) decreases the density of the metal D) involves metal bonding w ...
... The mass of a rusty bicycle is found to be slightly greater than the mass of the same bicycle before it rusted. The change in mass indicates that the rusting process — A) is a physical change B) involves an energy-to-matter conversion C) decreases the density of the metal D) involves metal bonding w ...
Neurobiological mechanisms of puberty in higher primates
... (NPY) (Plant and Shahab, 2002). This hypothesis is based on the following ®ndings. First, central administration of NPY arrests GnRH pulsatility in agonadal postpubertal male and female monkeys (Pau et al., 1995; Kaynard et al., 1990; Shahab et al., 2003). Second, ontogenetic changes in NPY gene exp ...
... (NPY) (Plant and Shahab, 2002). This hypothesis is based on the following ®ndings. First, central administration of NPY arrests GnRH pulsatility in agonadal postpubertal male and female monkeys (Pau et al., 1995; Kaynard et al., 1990; Shahab et al., 2003). Second, ontogenetic changes in NPY gene exp ...
The Use of Cross-Correlation Mapping in Identifying Backwards Projecting Connections between Visual Cortical Areas
... embedding–for a single variable but are not actually close to one another–that is, they have different values for the other variables. The time-lagged embedding seeks to distance these points: points not near each other on the parent manifold are unlikely to evolve through time similarly. If contigu ...
... embedding–for a single variable but are not actually close to one another–that is, they have different values for the other variables. The time-lagged embedding seeks to distance these points: points not near each other on the parent manifold are unlikely to evolve through time similarly. If contigu ...
Mechanisms of Sleep Control - UCLA Integrative Center for
... Raphe—Locus ceruleus—Basal forebrain—Acetylcholine—Norepi-nephrine. ...
... Raphe—Locus ceruleus—Basal forebrain—Acetylcholine—Norepi-nephrine. ...
Isoform-specific expression and function of neuregulin
... sequences; (II) type II isoforms (originally identified as GGF) contain a signal peptide, a kringle-like sequence plus Ig and EGF-like (β-variant) domains; (III) type III isoforms (originally identified as SMDF) share only the EGF-like domain (βvariant) with other isoforms; notable in the N-terminal ...
... sequences; (II) type II isoforms (originally identified as GGF) contain a signal peptide, a kringle-like sequence plus Ig and EGF-like (β-variant) domains; (III) type III isoforms (originally identified as SMDF) share only the EGF-like domain (βvariant) with other isoforms; notable in the N-terminal ...
Neural systems for guilt from actions affecting self versus others
... superior temporal sulcus (STS) (Takahashi et al., 2004). In parallel to these studies of emotion, social cognition research has uncovered the neural systems associated with empathy or adopting the thoughts, feelings, and emotions of others (Amodio and Frith, 2006; Mason and Macrae, 2008). Empathy re ...
... superior temporal sulcus (STS) (Takahashi et al., 2004). In parallel to these studies of emotion, social cognition research has uncovered the neural systems associated with empathy or adopting the thoughts, feelings, and emotions of others (Amodio and Frith, 2006; Mason and Macrae, 2008). Empathy re ...
First-in-first-out item replacement in a model of
... 1987; Stewart and Fox, 1990; Skaggs et al., 1996; Wallenstein and Hasselmo, 1997; Brazhnik and Fox, 1999). The bi-exponential synaptic responses that cause this modulation have reversal potential Etheta = −90 mV, a conductance amplitude of Gtheta = 10 nS and time constants τrise,theta = 0.1 ms and τ ...
... 1987; Stewart and Fox, 1990; Skaggs et al., 1996; Wallenstein and Hasselmo, 1997; Brazhnik and Fox, 1999). The bi-exponential synaptic responses that cause this modulation have reversal potential Etheta = −90 mV, a conductance amplitude of Gtheta = 10 nS and time constants τrise,theta = 0.1 ms and τ ...
The Formation of Specific Synaptic Connections Between Muscle
... actual formation of specific synaptic connections, is the set of monosynaptic excitatory connections between muscle spindle afferent fibers and motoneurons projecting to limb muscles. These are the connections that underlie the simple myotatic stretch reflex. Intracellular recordings can be made fro ...
... actual formation of specific synaptic connections, is the set of monosynaptic excitatory connections between muscle spindle afferent fibers and motoneurons projecting to limb muscles. These are the connections that underlie the simple myotatic stretch reflex. Intracellular recordings can be made fro ...
Structure-Function Relationships in Rat Brainstem Subnucleus
... et al., 1988). Therefore, cortical map changes induced by neonatal deafferentation may be due, at least in part, to subcortical events. To explain cortical plasticity, one must therefore be able to explain subcortical plasticity. The results of Waite and de Permentier (199 1) provide an indication t ...
... et al., 1988). Therefore, cortical map changes induced by neonatal deafferentation may be due, at least in part, to subcortical events. To explain cortical plasticity, one must therefore be able to explain subcortical plasticity. The results of Waite and de Permentier (199 1) provide an indication t ...
Dateien anzeigen - Universität Düsseldorf
... Maternal screen .............................................................................................. 45 ...
... Maternal screen .............................................................................................. 45 ...
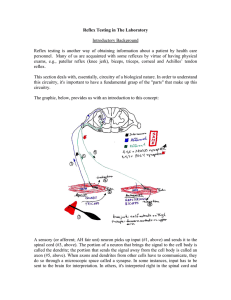
Reflex Testing in The Laboratory
... called the dendrite; the portion that sends the signal away from the cell body is called an axon (#5, above). When axons and dendrites from other cells have to communicate, they do so through a microscopic space called a synapse. In some instances, input has to be sent to the brain for interpretatio ...
... called the dendrite; the portion that sends the signal away from the cell body is called an axon (#5, above). When axons and dendrites from other cells have to communicate, they do so through a microscopic space called a synapse. In some instances, input has to be sent to the brain for interpretatio ...
Anatomy & Physiology I
... دیدریت های برهنه عدم موجودیت ساختمان مخصوص میکروسکوپیک درد ،حرارت ،خزیدن ،خارش ،بعضی از تماس نهایات عصبی داخل کپسولی دندریت های در یک کپسول نسج منضم قرار دارند کپسول اختصاصیت و حساسیت اخذه ها را تقویه میکند فشار ،لرزه ( ، )lamelletedتماس ( )meisner حجرات جداگان ...
... دیدریت های برهنه عدم موجودیت ساختمان مخصوص میکروسکوپیک درد ،حرارت ،خزیدن ،خارش ،بعضی از تماس نهایات عصبی داخل کپسولی دندریت های در یک کپسول نسج منضم قرار دارند کپسول اختصاصیت و حساسیت اخذه ها را تقویه میکند فشار ،لرزه ( ، )lamelletedتماس ( )meisner حجرات جداگان ...
Topic - We can offer most test bank and solution manual you need.
... 2. Which of the following are tiny sacs in a synaptic knob that release chemicals into the synapse? a) synaptic vesicles c) terminal buttons b) synaptic nodes d) synaptic gaps 3. Which of the following are responsible for acting as a facilitator of communication between neurons? a) motor neurons c) ...
... 2. Which of the following are tiny sacs in a synaptic knob that release chemicals into the synapse? a) synaptic vesicles c) terminal buttons b) synaptic nodes d) synaptic gaps 3. Which of the following are responsible for acting as a facilitator of communication between neurons? a) motor neurons c) ...
Amphetamine-induced release of dopamine from the substantia
... 20 minutes as described above, after which it was centrifuged and resuspended in 3.0 ml of medium (without dopamine) twice. Following the second rinse the tissue was centrifuged and resuspended in 3.0 ml of medium once again and then incubated as described above for 20 minutes. At the conclusion of ...
... 20 minutes as described above, after which it was centrifuged and resuspended in 3.0 ml of medium (without dopamine) twice. Following the second rinse the tissue was centrifuged and resuspended in 3.0 ml of medium once again and then incubated as described above for 20 minutes. At the conclusion of ...
Rules Ventral Prefrontal Cortical Axons Use to Reach Their Targets
... differences in the trajectories of fibers from different vPFC areas. Overall, the medial/lateral vPFC position dictates the route that fibers take to enter major WM tracts, as well as the position within specific tracts: axons from medial vPFC regions travel ventral to those from more lateral areas. ...
... differences in the trajectories of fibers from different vPFC areas. Overall, the medial/lateral vPFC position dictates the route that fibers take to enter major WM tracts, as well as the position within specific tracts: axons from medial vPFC regions travel ventral to those from more lateral areas. ...
... (Cln3–/–) present with a JNCL-like phenotype, including the intralysosomal accumulation of autofluorescent storage material and the loss of subpopulations of GABAergic interneurons [11,12]. Both Cln3–/– mice and individuals with JNCL have circulating autoantibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase (GA ...
Author`s personal copy - Laboratoire de Neurosciences Cognitives
... segment of the globus pallidus (GPi). The anatomo-physiological organization of the BG and their output suggested that interfering with such hyper-activity could restore motor function and improve parkinsonism. Several animal models in rodents and primates, as well as clinical studies and neurosurgi ...
... segment of the globus pallidus (GPi). The anatomo-physiological organization of the BG and their output suggested that interfering with such hyper-activity could restore motor function and improve parkinsonism. Several animal models in rodents and primates, as well as clinical studies and neurosurgi ...
Central projections of the glossopharyngeal and
... buds located in the oropharyngeal region and thus constitute the oropharyngeal taste system, which is important for selective food ingestion (Atema, '71). Further, electrophysiological recordings from facial (Caprio, '75, '78, '82; Davenport and Caprio, '82), glossopharyngeal, and vagal (Kanwal and ...
... buds located in the oropharyngeal region and thus constitute the oropharyngeal taste system, which is important for selective food ingestion (Atema, '71). Further, electrophysiological recordings from facial (Caprio, '75, '78, '82; Davenport and Caprio, '82), glossopharyngeal, and vagal (Kanwal and ...
Supplementary Information (doc 1146K)
... included in each round of cross-validation, and then among these features, features were sorted by absolute value of the average SVM weight. ...
... included in each round of cross-validation, and then among these features, features were sorted by absolute value of the average SVM weight. ...
Graziano's CV
... Graziano MSA and Aflalo TN (2007) Rethinking cortical organization: Moving away from discrete areas arranged in hierarchies. The Neuroscientist, 13: 138-147. Aflalo TN and Graziano MSA (2007) Relationship between unconstrained arm movement and single neuron firing in the macaque motor cortex. Journ ...
... Graziano MSA and Aflalo TN (2007) Rethinking cortical organization: Moving away from discrete areas arranged in hierarchies. The Neuroscientist, 13: 138-147. Aflalo TN and Graziano MSA (2007) Relationship between unconstrained arm movement and single neuron firing in the macaque motor cortex. Journ ...
Common Mechanisms Underlying Growth Cone Guidance and Axon
... molecular cues present during CNS development. However, typically only a small region of the axon can be imaged at any given time and for periods of only a few hours. Moreover, the resolution of individual axons in these preparations is not sufficient to demonstrate precisely how growth cone behavio ...
... molecular cues present during CNS development. However, typically only a small region of the axon can be imaged at any given time and for periods of only a few hours. Moreover, the resolution of individual axons in these preparations is not sufficient to demonstrate precisely how growth cone behavio ...