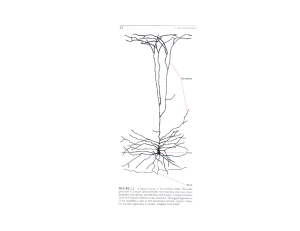
neurons and the nervous system
... message) from the soma to the opposite end of the neuron. Carries messages away from the cell body Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between Schwann cells. Function: Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an im ...
... message) from the soma to the opposite end of the neuron. Carries messages away from the cell body Myelin Sheath An insulating layer around an axon. Made up of Schwann cells. Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between Schwann cells. Function: Conduction of the impulse. (Situation where speed of an im ...
Lecture 14 - School of Computing
... to the output in the Kohonen net revealed that a small subset of neurons (<50) that are not category-specific yet respond with different intensities to different categories are crucial for correct classification. Conclusions: The IT employs a distributed representation to encode categories of differ ...
... to the output in the Kohonen net revealed that a small subset of neurons (<50) that are not category-specific yet respond with different intensities to different categories are crucial for correct classification. Conclusions: The IT employs a distributed representation to encode categories of differ ...
Ch 8 Neurons and Network properties part-1
... Now let’s try to think about a living excitable cell… ...
... Now let’s try to think about a living excitable cell… ...
Perception
... -neurons responded to different views of the stimulus, different modes of depiction, and even words signifying the stimulus -neurons respond to concepts -these neurons were in the hippocampus and the MTL (medial temporal lobe) areas associated with the storage of memories -However they are not gran ...
... -neurons responded to different views of the stimulus, different modes of depiction, and even words signifying the stimulus -neurons respond to concepts -these neurons were in the hippocampus and the MTL (medial temporal lobe) areas associated with the storage of memories -However they are not gran ...
Brain_stemCh45
... does not affect consciousness Acute transection rostral to inferior colliculus result in coma (unarousability) ...
... does not affect consciousness Acute transection rostral to inferior colliculus result in coma (unarousability) ...
Nervous System
... –Rods: Black and White –Cones: Color • Optic nerve takes electric signals from eye to brain ...
... –Rods: Black and White –Cones: Color • Optic nerve takes electric signals from eye to brain ...
Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are
... 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. Effects of dopamine? Serotonin? En ...
... 1. What is a neuron? What are the three basic types of neurons? What is the difference between a neuron with myelin compared to a neuron that is not myelinated? 2. What is stimulus threshold? All-or-none principle? (domino example in class) 3. What is a synapse? 4. Effects of dopamine? Serotonin? En ...
Nervous system slides
... ¾ Several cerebellum and brainstem centers control sleep and arousal, such as the reticular system that filters sensory input sent to the cortex. ¾The two hemispheres of the brain are specialized for different functions; the left hemisphere contains processes supporting speech, language, & analytic ...
... ¾ Several cerebellum and brainstem centers control sleep and arousal, such as the reticular system that filters sensory input sent to the cortex. ¾The two hemispheres of the brain are specialized for different functions; the left hemisphere contains processes supporting speech, language, & analytic ...
Neuron Summary - MsHughesPsychology
... 1. Dendrite – a specialised, short, thin and widely branching fibre that is specialised to detect and receive incoming neural information (neural impulses) 2. Soma – cell body, the section that determines whether the neuron will be activated and thus transmit (pass on) the neural stimulation to othe ...
... 1. Dendrite – a specialised, short, thin and widely branching fibre that is specialised to detect and receive incoming neural information (neural impulses) 2. Soma – cell body, the section that determines whether the neuron will be activated and thus transmit (pass on) the neural stimulation to othe ...
12-nervoussystemintro - Alexmac
... other tissues that detect changes in the internal or external environment. These receptors consist of specialized neuron endings or specialized cells in close contact with neurons that convert the energy of the stimulus (sound, color, odor, etc.) to electrical signals within the nervous system. Sens ...
... other tissues that detect changes in the internal or external environment. These receptors consist of specialized neuron endings or specialized cells in close contact with neurons that convert the energy of the stimulus (sound, color, odor, etc.) to electrical signals within the nervous system. Sens ...
Slide 1
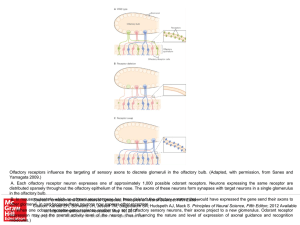
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Slide ()
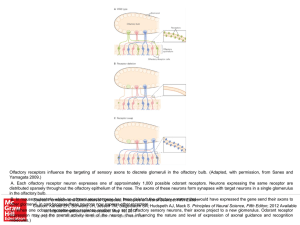
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
PSY110 Psychology
... Body - Pages 63-70 Complexity One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Sp ...
... Body - Pages 63-70 Complexity One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Sp ...
Biological roots of Behavioral Sciences
... Nervous system interaction with the endocrine and • ;immune system The nervous and endocrine and immune systems • have extensive neural and chemical means of communication and each is capable of affecting and .being affected by the others The endocrine system secretes hormones into the • ...
... Nervous system interaction with the endocrine and • ;immune system The nervous and endocrine and immune systems • have extensive neural and chemical means of communication and each is capable of affecting and .being affected by the others The endocrine system secretes hormones into the • ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... Purpose: network of cells/tissues that controls body’s responses to different circumstances o Input: environment changes sensory receptors receive stimulus and send a signal o Integration: signal is interpreted appropriate response signal is conducted o Motor output: signal is conducted from the ...
... Purpose: network of cells/tissues that controls body’s responses to different circumstances o Input: environment changes sensory receptors receive stimulus and send a signal o Integration: signal is interpreted appropriate response signal is conducted o Motor output: signal is conducted from the ...
PNS and CNS Nervous System Organization Peripheral Nervous
... • Dorsal Root = sensory – Dorsal root ganglion = afferent cell bodies ...
... • Dorsal Root = sensory – Dorsal root ganglion = afferent cell bodies ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and
... response to several successive releases of neurotransmitter, and spatial summation, which occurs when the postsynaptic cell is stimulated at the same time by multiple terminals. ...
... response to several successive releases of neurotransmitter, and spatial summation, which occurs when the postsynaptic cell is stimulated at the same time by multiple terminals. ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... processes auditory information • Lower regions are involved with visual processing • Also involved in recognizing, identifying, and naming objects • Damage to this lobe results in disorders called agnosias, in which the individual is aware of an object but cannot identify it ...
... processes auditory information • Lower regions are involved with visual processing • Also involved in recognizing, identifying, and naming objects • Damage to this lobe results in disorders called agnosias, in which the individual is aware of an object but cannot identify it ...
Functional imaging of hippocampal palace cells at celluar resolution
... Whether hippocampal neurons with similar place fields are spatially organized within the hippocampus? Three obstacles: cellular resolution imaging in the brain of a mobile mouse imaging more than a millimeter beneath the cortical surface imaging that is compatible with navigation behavior ...
... Whether hippocampal neurons with similar place fields are spatially organized within the hippocampus? Three obstacles: cellular resolution imaging in the brain of a mobile mouse imaging more than a millimeter beneath the cortical surface imaging that is compatible with navigation behavior ...
ARIEL LEVINE Postdoctoral Associate, The Salk Institute for
... orchestrate motor programs, as well as their cellular properties and connectivity are poorly understood. We have identified a population of premotor spinal neurons that may provide the cellular basis for encoding coordinated motor output programs. These molecularly-defined “motor synergy encoder” ( ...
... orchestrate motor programs, as well as their cellular properties and connectivity are poorly understood. We have identified a population of premotor spinal neurons that may provide the cellular basis for encoding coordinated motor output programs. These molecularly-defined “motor synergy encoder” ( ...
An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology - Home
... Explain behavior in terms of a single cause Could mean a paradigm, school, or conceptual approach Tendency to ignore information from other areas ...
... Explain behavior in terms of a single cause Could mean a paradigm, school, or conceptual approach Tendency to ignore information from other areas ...
File
... Neurons either fire maximally or not at all, this is referred to as the “all or none” response Increasing neuronal stimulation beyond a critical level will not result in an increased response Neurons response to increased stimulation by increasing the frequency of firing, not the intensity at wh ...
... Neurons either fire maximally or not at all, this is referred to as the “all or none” response Increasing neuronal stimulation beyond a critical level will not result in an increased response Neurons response to increased stimulation by increasing the frequency of firing, not the intensity at wh ...
Study Guide Chapter 10 in Fox
... What is the difference between phasic and tonic receptors? What kind are pain receptors? What is a neural transmitter found in pain pathways? What does the term ‘sensory adaptation’ mean? What does the “Law of Specific nerve Energies” mean? Give an example You say you are “cold” What is meant by tha ...
... What is the difference between phasic and tonic receptors? What kind are pain receptors? What is a neural transmitter found in pain pathways? What does the term ‘sensory adaptation’ mean? What does the “Law of Specific nerve Energies” mean? Give an example You say you are “cold” What is meant by tha ...
A neuron receives input from other neurons
... of neural networks, independent of how they are actually "implemented" in the brain. This means that we can use much simpler, abstract "neurons", which (hopefully) capture the essence of neural computation even if they leave out much of the details of how biological neurons work. ...
... of neural networks, independent of how they are actually "implemented" in the brain. This means that we can use much simpler, abstract "neurons", which (hopefully) capture the essence of neural computation even if they leave out much of the details of how biological neurons work. ...