013368718X_CH31_483-498.indd
... Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system collects information about the body’s internal and external environment, processes that information, and responds to it. The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves and supporting cells. It collects information about the body’s internal and ext ...
... Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system collects information about the body’s internal and external environment, processes that information, and responds to it. The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves and supporting cells. It collects information about the body’s internal and ext ...
Functional Classification of the Peripheral Nervous System
... • Chronic, potentially debilitating disease that affects the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. • Myelin sheath is destroyed- It hardens to a tissue called the scleroses • Transmitted nerve impulses are short-circuited • Affected person loses control of his/her mu ...
... • Chronic, potentially debilitating disease that affects the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. • Myelin sheath is destroyed- It hardens to a tissue called the scleroses • Transmitted nerve impulses are short-circuited • Affected person loses control of his/her mu ...
Central Nervous System Part 2
... cerebellum and spinal cord to keep the cortex alert and conscious. Also acts as a filter for sensory input to the cortex … filters out 99% of sensory input as unimportant. RAS: arousal system Complex polysynaptic path in brainstem and thalamus RF Receives messages from neurons on spine and other par ...
... cerebellum and spinal cord to keep the cortex alert and conscious. Also acts as a filter for sensory input to the cortex … filters out 99% of sensory input as unimportant. RAS: arousal system Complex polysynaptic path in brainstem and thalamus RF Receives messages from neurons on spine and other par ...
Unit 3 Biology of Behavior The Neuron Dendrites: Tree
... Temporal Lobes: Contain the primary auditory cortex (audition) and areas for the senses of smell (olfaction) and taste (gustatory sense). The LEFT temporal lobe contains Wernicke's Area which control language comprehension and expression. Occipital Lobes: Contains the Primary Visual Cortex. Associat ...
... Temporal Lobes: Contain the primary auditory cortex (audition) and areas for the senses of smell (olfaction) and taste (gustatory sense). The LEFT temporal lobe contains Wernicke's Area which control language comprehension and expression. Occipital Lobes: Contains the Primary Visual Cortex. Associat ...
Powerpoint - Center Grove Community School
... Inputs may number in thousands If enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
... Inputs may number in thousands If enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
Chapter 02: Neurons and Glia
... Dendritic membrane (postsynaptic membrane) contains many specialized receptors for neurotransmitters Dendritic spines Some neurons have these structures for receiving some types of inputs Discovered by Cajal Believed to isolate various chemical reactions Dynamic structures affected by the type and a ...
... Dendritic membrane (postsynaptic membrane) contains many specialized receptors for neurotransmitters Dendritic spines Some neurons have these structures for receiving some types of inputs Discovered by Cajal Believed to isolate various chemical reactions Dynamic structures affected by the type and a ...
So, do worms sleep?
... about the regulation of the absence of movement. Yet behavioral quiescent states are universal to the animal world, with the most famous and mysterious of these being sleep. The roundworm C. elegans is in many respects the simplest — and admittedly the most simplistic — model system that exhibits a ...
... about the regulation of the absence of movement. Yet behavioral quiescent states are universal to the animal world, with the most famous and mysterious of these being sleep. The roundworm C. elegans is in many respects the simplest — and admittedly the most simplistic — model system that exhibits a ...
chapter 3 – sensation and perception
... B. Taste 1. Flavor – 2. Taste buds – 3. Contained in 4. Each taste bud contains 5. 1/10 second can 6. 4 primary 7. Sensory adaptation 8. Cross adaptation C. The Vestibular Senses 1. Equilibrium and awareness of 2. Arise inner ear and sense 3. 2 Kinds a. Body rotation b. Gravitation and movement 1) U ...
... B. Taste 1. Flavor – 2. Taste buds – 3. Contained in 4. Each taste bud contains 5. 1/10 second can 6. 4 primary 7. Sensory adaptation 8. Cross adaptation C. The Vestibular Senses 1. Equilibrium and awareness of 2. Arise inner ear and sense 3. 2 Kinds a. Body rotation b. Gravitation and movement 1) U ...
Nervous Tissue
... The nervous system is part of the body’s 11 systems and though small, it’s extremely complex. The nervous system consists of 2 types of cells, neurons and neuroglia that work together to form an extremely intricate network. It is made up of the body’s most important structures the brain, spinal cord ...
... The nervous system is part of the body’s 11 systems and though small, it’s extremely complex. The nervous system consists of 2 types of cells, neurons and neuroglia that work together to form an extremely intricate network. It is made up of the body’s most important structures the brain, spinal cord ...
activities unit 5 - Junta de Andalucía
... ACTIVITIES UNIT 5. THE NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS.1. Put the following organs and systems in the correct order to describe the basic process of relation: a) Sensory organs b) Effectors organs c) External stimuli d) Nervous system. 2. What is a stimulus? 3. Imagine you burn your hand: a) What is t ...
... ACTIVITIES UNIT 5. THE NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS.1. Put the following organs and systems in the correct order to describe the basic process of relation: a) Sensory organs b) Effectors organs c) External stimuli d) Nervous system. 2. What is a stimulus? 3. Imagine you burn your hand: a) What is t ...
Chapter 10: Sensory Physiology
... are transducers → convert stimuli into graded potential (receptor potential) are of various complexity ...
... are transducers → convert stimuli into graded potential (receptor potential) are of various complexity ...
2004 - 21st Century Science Initiative, Palisades, New York
... and Temporal Processing of Auditory Cortex Neurons ...
... and Temporal Processing of Auditory Cortex Neurons ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... a. Each neuron will have only one axon, however it may be branched. b. At the end of the axon will be axon terminal (AKA - synaptic knobs or synaptic boutons). c. Some axons will be covered by white, fatty insulation called a myelin sheath. Myelin sheaths increase the speed of impulse transmission. ...
... a. Each neuron will have only one axon, however it may be branched. b. At the end of the axon will be axon terminal (AKA - synaptic knobs or synaptic boutons). c. Some axons will be covered by white, fatty insulation called a myelin sheath. Myelin sheaths increase the speed of impulse transmission. ...
Instructions for authors of poster abstracts for the
... Mechanical and Optical Properties of Müller Cells Müller cells, the principal glial cells of the vertebrate retina, are the only cells spanning its entire thickness, suggesting an important contribution to the stability of the tissue. They are thought to be involved in the genesis of different retin ...
... Mechanical and Optical Properties of Müller Cells Müller cells, the principal glial cells of the vertebrate retina, are the only cells spanning its entire thickness, suggesting an important contribution to the stability of the tissue. They are thought to be involved in the genesis of different retin ...
The Nervous System
... • White matter – myelinated axons • Gray matter – cell bodies • Anterior – median fissure • Posterior – median sulcus • Central canal ...
... • White matter – myelinated axons • Gray matter – cell bodies • Anterior – median fissure • Posterior – median sulcus • Central canal ...
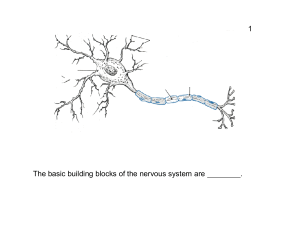
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
Somatic Sensory Systems
... systems or general sensory systems. The somatic sensory systems include the senses of touch, temperature, pain, and proprioception. The receptors that are responsible for these senses are scattered throughout the body both internally and externally. The receptors of the general senses can be divided ...
... systems or general sensory systems. The somatic sensory systems include the senses of touch, temperature, pain, and proprioception. The receptors that are responsible for these senses are scattered throughout the body both internally and externally. The receptors of the general senses can be divided ...
Biology and Behaviour
... The nervous system is built out of neurons or nerve cells, and glial cells, which are sort of the glue Glial cells do other support functions ...
... The nervous system is built out of neurons or nerve cells, and glial cells, which are sort of the glue Glial cells do other support functions ...
Specialized Cells!!!!
... Leaves are complex. They have a covering called the cuticle. It is a waxy covering that prevents water loss. It is located on both sides of the leaf. The epidermis is layer under the cuticle. Epidermis is another name for skin. Photosynthesis takes place primarily in the mesophyll. It is directly un ...
... Leaves are complex. They have a covering called the cuticle. It is a waxy covering that prevents water loss. It is located on both sides of the leaf. The epidermis is layer under the cuticle. Epidermis is another name for skin. Photosynthesis takes place primarily in the mesophyll. It is directly un ...