Innervation of the Eye and Orbit
... There are a lot of terms, anatomy and pathways you’ll need to know. ...
... There are a lot of terms, anatomy and pathways you’ll need to know. ...
Inside the brain
... from the cell body towards other neurons. The membrane voltage change from an incoming signal here triggers the opening of channels that allow ions (charged atoms) to flow into the cell from outside. This causes more channels further along the axon to open, creating an electrical signal (action pote ...
... from the cell body towards other neurons. The membrane voltage change from an incoming signal here triggers the opening of channels that allow ions (charged atoms) to flow into the cell from outside. This causes more channels further along the axon to open, creating an electrical signal (action pote ...
Biology 3201 - Corner Brook Regional High
... evolution the human brain has doubled in size. • Compared to other primates, newborns have very large heads relative to their body size. • Some researchers believe that humans have reached their maximum brain size. • Why??? ...
... evolution the human brain has doubled in size. • Compared to other primates, newborns have very large heads relative to their body size. • Some researchers believe that humans have reached their maximum brain size. • Why??? ...
CHAPTER 7 Nervous system Notes
... Specific areas have specific functions Temporal lobe’s auditory areas interpret incoming nervous signals as specific sounds Visual area of the occipital lobe helps you understand and identify images If a specific part of the brain is damaged, for example ...
... Specific areas have specific functions Temporal lobe’s auditory areas interpret incoming nervous signals as specific sounds Visual area of the occipital lobe helps you understand and identify images If a specific part of the brain is damaged, for example ...
IV. PSYCHOBIOLOGY
... Other “3/4” of cerebral cortex. Integrates, interprets, acts on information. (i.e. important to communication). Areas and their associated behaviors have been identified based on what happens when those areas are damaged. ...
... Other “3/4” of cerebral cortex. Integrates, interprets, acts on information. (i.e. important to communication). Areas and their associated behaviors have been identified based on what happens when those areas are damaged. ...
the nervous system - Miss Gleason`s Science
... Zoloft is part of a class of drugs called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or SSRIs for short. SSRIs act on a specific chemical within the brain known as serotonin. This is one of several chemicals used to send messages from one nerve cell to another. ...
... Zoloft is part of a class of drugs called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or SSRIs for short. SSRIs act on a specific chemical within the brain known as serotonin. This is one of several chemicals used to send messages from one nerve cell to another. ...
Slide ()
... arginine vasopressin (AVP) or oxytocin (OXY). Most of their axons project directly to the posterior pituitary, from which AVP and OXY are secreted into the systemic circulation to regulate their target tissues. Neurons that regulate the anterior lobe cluster in the mediobasal hypothalamus, including ...
... arginine vasopressin (AVP) or oxytocin (OXY). Most of their axons project directly to the posterior pituitary, from which AVP and OXY are secreted into the systemic circulation to regulate their target tissues. Neurons that regulate the anterior lobe cluster in the mediobasal hypothalamus, including ...
Topic A.3 notes
... space between the lens and the retina • 11. fovea = responsible for sharp central vision • 12. optic nerve = transmits visual information from the retina to the brain • 13. blind spot = the specific region of the retina where the optic nerve and blood vessels pass through to connect to the back of t ...
... space between the lens and the retina • 11. fovea = responsible for sharp central vision • 12. optic nerve = transmits visual information from the retina to the brain • 13. blind spot = the specific region of the retina where the optic nerve and blood vessels pass through to connect to the back of t ...
Evolutionary Psychology: Understanding Human Nature
... - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. - Association area: areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as ...
... - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. - Association area: areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as ...
Perception of stimuli special senses
... space between the lens and the retina • 11. fovea = responsible for sharp central vision • 12. optic nerve = transmits visual information from the retina to the brain • 13. blind spot = the specific region of the retina where the optic nerve and blood vessels pass through to connect to the back of t ...
... space between the lens and the retina • 11. fovea = responsible for sharp central vision • 12. optic nerve = transmits visual information from the retina to the brain • 13. blind spot = the specific region of the retina where the optic nerve and blood vessels pass through to connect to the back of t ...
PDF
... authors take a first step towards understanding this, showing that ABC transporter inhibition disrupts migration of the small micromeres at later stages of embryogenesis. While there is still much to be understood about the regulation and role of these plasma membrane pumps, this study provides evid ...
... authors take a first step towards understanding this, showing that ABC transporter inhibition disrupts migration of the small micromeres at later stages of embryogenesis. While there is still much to be understood about the regulation and role of these plasma membrane pumps, this study provides evid ...
Lecture 11a Nervous System
... • Synapse: Area where a neuron communicates with another cell • Presynaptic cell: – neuron that sends message ...
... • Synapse: Area where a neuron communicates with another cell • Presynaptic cell: – neuron that sends message ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Topic iQuiz
... The pathway of a reflex arc involves the following structures: 1 – sense organ; 2 – spinal cord; 3 – motor neuron; 4 – muscle; 5 – sensory neurons. The correct sequence of events is … ...
... The pathway of a reflex arc involves the following structures: 1 – sense organ; 2 – spinal cord; 3 – motor neuron; 4 – muscle; 5 – sensory neurons. The correct sequence of events is … ...
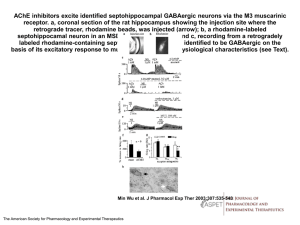
48 0007-4888/05/14010048 © 2005 Springer Science+Business
... some acute models of epilepsy and epileptiform status cell loss in epileptogenic zones correlates with the decrease in synaptic inhibition [1]. This correlation is not obligatory for chronic experimental epilepsy: cell loss is not paralleled by disorders in GABAergic inhibition [11] or can take plac ...
... some acute models of epilepsy and epileptiform status cell loss in epileptogenic zones correlates with the decrease in synaptic inhibition [1]. This correlation is not obligatory for chronic experimental epilepsy: cell loss is not paralleled by disorders in GABAergic inhibition [11] or can take plac ...
Ch. 2 Practice
... 8. The brain’s ability to shift functions from damaged to undamaged brain areas is called: a. neurogenesis b. functional plasticity c. phrenology d. structural plasticity ...
... 8. The brain’s ability to shift functions from damaged to undamaged brain areas is called: a. neurogenesis b. functional plasticity c. phrenology d. structural plasticity ...
Neurons & the Nervous System
... – Uses energy reserves to cope with stress or emergency – Adrenaline! ...
... – Uses energy reserves to cope with stress or emergency – Adrenaline! ...
The Auditory System
... cortex is thought to be involved in identifying sounds (“what”); the posterior auditory pathway is thought to be involved in locating sounds (“where”). ...
... cortex is thought to be involved in identifying sounds (“what”); the posterior auditory pathway is thought to be involved in locating sounds (“where”). ...
The Brain and Nervous System
... other parts of the brain that influence our motives. This includes release of pleasure hormones, rats that could stimulate their HT electrically would do so 7000 times an hour. ...
... other parts of the brain that influence our motives. This includes release of pleasure hormones, rats that could stimulate their HT electrically would do so 7000 times an hour. ...
Neurons are the cells that carry messages between parts of the body
... The endocrine system uses chemicals released into the blood (hormones) to communicate between parts of the body. An organ that releases hormones is called a gland. The gland releases the hormones into the blood stream so they can then reach the target cells. Target cells have receptors on their cell ...
... The endocrine system uses chemicals released into the blood (hormones) to communicate between parts of the body. An organ that releases hormones is called a gland. The gland releases the hormones into the blood stream so they can then reach the target cells. Target cells have receptors on their cell ...
Central Nervous System
... Provides a means to send messages (impulses) to all parts of the body from the brain Stores ________________ and allows for __________________ ...
... Provides a means to send messages (impulses) to all parts of the body from the brain Stores ________________ and allows for __________________ ...
CHAPTER10B
... www.mc.vanderbilt.edu/histology/slide.php?image_name=myelin&slide_file=images/histology/nervous_tissue/display/schwann3.jpg&image_id=1058 ...
... www.mc.vanderbilt.edu/histology/slide.php?image_name=myelin&slide_file=images/histology/nervous_tissue/display/schwann3.jpg&image_id=1058 ...
Fill in the blanks on LB page 67-68.
... c. Norepinephrine affects brain regions concerned with emotions, dreaming, and awaking. d. Dopamine and GABA are other neurotransmitters that are present in different parts of the brain. e. Two debilitating diseases, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's, are testimony to the effects that the loss of neurotr ...
... c. Norepinephrine affects brain regions concerned with emotions, dreaming, and awaking. d. Dopamine and GABA are other neurotransmitters that are present in different parts of the brain. e. Two debilitating diseases, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's, are testimony to the effects that the loss of neurotr ...