CHAPTER NINE: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... neurotransmitters ii. Composed of two parts 1. ________ terminal of the presynaptic neuron 2. ___________ region on the postsynaptic neuron g. Synaptic cleft i. Fluid-filled space separating the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons ii. Prevents nerve impulses from ___________ passing from one neuron ...
... neurotransmitters ii. Composed of two parts 1. ________ terminal of the presynaptic neuron 2. ___________ region on the postsynaptic neuron g. Synaptic cleft i. Fluid-filled space separating the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons ii. Prevents nerve impulses from ___________ passing from one neuron ...
Document
... The nervous system is one of the 2 control systems in our body. The nervous system is designed for fast action. It coordinates fast or rapid activities, such as muscle movement. Signaling is by electrical impulses, these are rapid, specific and produce an almost immediate response. ...
... The nervous system is one of the 2 control systems in our body. The nervous system is designed for fast action. It coordinates fast or rapid activities, such as muscle movement. Signaling is by electrical impulses, these are rapid, specific and produce an almost immediate response. ...
1 Background to psychobiology - Assets
... not single structures but in fact consist of around a dozen interconnected nuclei (Aggleton, 1993). Bilateral removal of the amygdala in monkeys leads to profound impairments in social and emotional behaviours, while bilateral amygdala damage in humans leads to similar deficits in emotional processin ...
... not single structures but in fact consist of around a dozen interconnected nuclei (Aggleton, 1993). Bilateral removal of the amygdala in monkeys leads to profound impairments in social and emotional behaviours, while bilateral amygdala damage in humans leads to similar deficits in emotional processin ...
Review #2 - Course Notes
... b. light waves. c. 200 miles per hour. d. electricity through a wire. 37. Increasing the intensity of a stimulus above the threshold will not similarly increase the intensity of a neural response to that stimulus. This highlights the nature of the: a. synaptic gap. b. myelin sheath. c. all-or-none r ...
... b. light waves. c. 200 miles per hour. d. electricity through a wire. 37. Increasing the intensity of a stimulus above the threshold will not similarly increase the intensity of a neural response to that stimulus. This highlights the nature of the: a. synaptic gap. b. myelin sheath. c. all-or-none r ...
p. A5 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... if transected nerve is not anastomosed, axons will grow into surrounding tissue recovery will be slow and rarely functional; axons only rarely reach their appropriate end organ, more often they are misdirected (ABERRANT INNERVATION). if connective tissue scar is extensive, švanocitai, negalėdami jo ...
... if transected nerve is not anastomosed, axons will grow into surrounding tissue recovery will be slow and rarely functional; axons only rarely reach their appropriate end organ, more often they are misdirected (ABERRANT INNERVATION). if connective tissue scar is extensive, švanocitai, negalėdami jo ...
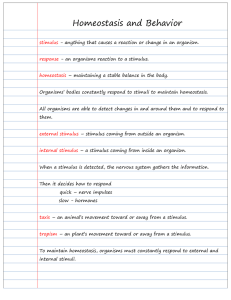
Homeostasis and Behavior
... homeostasis – maintaining a stable balance in the body. Organisms’ bodies constantly respond to stimuli to maintain homeostasis. All organisms are able to detect changes in and around them and to respond to them. external stimulus – stimulus coming from outside an organism. internal stimulus – a sti ...
... homeostasis – maintaining a stable balance in the body. Organisms’ bodies constantly respond to stimuli to maintain homeostasis. All organisms are able to detect changes in and around them and to respond to them. external stimulus – stimulus coming from outside an organism. internal stimulus – a sti ...
Practice Test #2
... neural response to that stimulus. This highlights the nature of the: a. synaptic gap. b. myelin sheath. c. all-or-none response. d. parasympathetic nervous system. e. neurotransmitters. 38. The sensory cortex is located in the ________ lobe. a. occipital b. temporal c. frontal d. parietal 39. Neurot ...
... neural response to that stimulus. This highlights the nature of the: a. synaptic gap. b. myelin sheath. c. all-or-none response. d. parasympathetic nervous system. e. neurotransmitters. 38. The sensory cortex is located in the ________ lobe. a. occipital b. temporal c. frontal d. parietal 39. Neurot ...
Paper: Temporal Convergence of Dynamic Cell Assemblies in the
... presentation. The population average response of MSNs was composed of three distinct response groups that were temporally differentiated and fired in serial episodes along the trial. In the GPe, the average sustained response was composed of two response groups that were primarily differentiated by ...
... presentation. The population average response of MSNs was composed of three distinct response groups that were temporally differentiated and fired in serial episodes along the trial. In the GPe, the average sustained response was composed of two response groups that were primarily differentiated by ...
7-6_TheGenOfSpecResp_MajorosMyrtill
... is a spinal reflex intended to protect the body from damaging stimuli. It is polysynaptic, causing stimulation of sensory-, and motor neurons. We have all experienced this reflex after accidentally touching a hot stove or a sharp object, as we withdraw our hand even before we consciously experience ...
... is a spinal reflex intended to protect the body from damaging stimuli. It is polysynaptic, causing stimulation of sensory-, and motor neurons. We have all experienced this reflex after accidentally touching a hot stove or a sharp object, as we withdraw our hand even before we consciously experience ...
Chapter 2 Notes Packet (Part 1)
... o What makes them different? ________________: short fibers that branch out from the cell body and pick up incoming messages ________________: Single long fiber extending from the cell body; carries outgoing messages to other neurons, muscles or glands All neurons only have one axon but at the ...
... o What makes them different? ________________: short fibers that branch out from the cell body and pick up incoming messages ________________: Single long fiber extending from the cell body; carries outgoing messages to other neurons, muscles or glands All neurons only have one axon but at the ...
Lecture Suggestions and Guidelines
... Each dermatome produces an action potential that is always delivered to a precise spinal cord segment. For example, chest pains on the left side as a result of a heart attack may be explained by pain information being transmitted from the heart to the left side of the spinal cord. LEARNING OBJECTIVE ...
... Each dermatome produces an action potential that is always delivered to a precise spinal cord segment. For example, chest pains on the left side as a result of a heart attack may be explained by pain information being transmitted from the heart to the left side of the spinal cord. LEARNING OBJECTIVE ...
No Slide Title
... central part of cell body, only at edges - enlargement of cell body with rounding - nucleus displaced to periphery - can also see in pellagra and Wernicke’s encephalopathy ...
... central part of cell body, only at edges - enlargement of cell body with rounding - nucleus displaced to periphery - can also see in pellagra and Wernicke’s encephalopathy ...
Chapter 3 Class Notes / Biological Foundations
... GENERAL PSYCHOLOGY / Chapter 3 Biological Foundations of Behavior Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System ...
... GENERAL PSYCHOLOGY / Chapter 3 Biological Foundations of Behavior Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System ...
Exploring the Human Nervous System
... Saltatory conduction is faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
... Saltatory conduction is faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
The Role of Natriuretic Peptides in Hearing
... 1. Formation of the neural plate • Underlying dorsal mesoderm signals ectodermal cells to elongate and form the neural plate (columnar cells) 2. Bending of the neural plate • MHP cells become anchored to the notochord and change shape forcing formation of the neural groove • DLHP cells become anchor ...
... 1. Formation of the neural plate • Underlying dorsal mesoderm signals ectodermal cells to elongate and form the neural plate (columnar cells) 2. Bending of the neural plate • MHP cells become anchored to the notochord and change shape forcing formation of the neural groove • DLHP cells become anchor ...
Nervous System Neuron: nerve cell, functional unit of nervous
... ● Folds may have to do with intelligence, the folding leads to an increased surface area and thus more neurons. ● There is no correlation between the size of the brain and the level of intelligence it has to do with how well neurons can “talk” to each other. ● “little brain” many neurons. Voluntary ...
... ● Folds may have to do with intelligence, the folding leads to an increased surface area and thus more neurons. ● There is no correlation between the size of the brain and the level of intelligence it has to do with how well neurons can “talk” to each other. ● “little brain” many neurons. Voluntary ...
Learning in a neural network model in real time using real world
... using chunked sampling (23 ms), keeping stimulation of the input neurons constant during that time. This limits the phase information available, and hence does not allow usual approaches to localization of sound sources. This problem may be addressed by shortening the length of data samples, or usin ...
... using chunked sampling (23 ms), keeping stimulation of the input neurons constant during that time. This limits the phase information available, and hence does not allow usual approaches to localization of sound sources. This problem may be addressed by shortening the length of data samples, or usin ...
投影片 1
... corresponded to one of the four emotional states. The number of neurons in the hidden layer was empirically assigned based on the half of summation of neurons in the input and output layers. ...
... corresponded to one of the four emotional states. The number of neurons in the hidden layer was empirically assigned based on the half of summation of neurons in the input and output layers. ...
05First2yearsBiosocial
... • What is the least developed sense at birth? • What are some of the basic immunizations a child should receive? • How do the risks from disease relate to the risks from immunization? • What is the difference between colostrum and milk? ...
... • What is the least developed sense at birth? • What are some of the basic immunizations a child should receive? • How do the risks from disease relate to the risks from immunization? • What is the difference between colostrum and milk? ...
2014 nervous system ppt
... 3. Voltage gated Na+ channels close, and K+ channels open, causing more negative change inside of neuron ...
... 3. Voltage gated Na+ channels close, and K+ channels open, causing more negative change inside of neuron ...
Module 4 Neural and Hormonal Systems
... understanding the rest of the course. Action potentials travel down the axon until reaching a tiny junction, the synapse. Then, the action potential stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules. They cross the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron. This allows ions ...
... understanding the rest of the course. Action potentials travel down the axon until reaching a tiny junction, the synapse. Then, the action potential stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules. They cross the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron. This allows ions ...
One of key missions of the BRAIN Initiative is “Demonstrating
... The hypothalamus is well established to play a critical function in feeding behavior. Previous studies have demonstrated that the neurons expressing Agouti-gene related protein (AgRP neurons) promote feeding through GABAergic projections to a variety of other brain regions. Prevalent research effort ...
... The hypothalamus is well established to play a critical function in feeding behavior. Previous studies have demonstrated that the neurons expressing Agouti-gene related protein (AgRP neurons) promote feeding through GABAergic projections to a variety of other brain regions. Prevalent research effort ...
On the Brain of a Scientist: Albert Einstein
... to be concerned with "higher" neural functions. These regions do not directly receive primary sensory information, but rather, as their name implies, ,.associate,, or. analyze inputs from other brain regions. The associaiion-cortices are the last domains of the cortex to myerinate, indicating their ...
... to be concerned with "higher" neural functions. These regions do not directly receive primary sensory information, but rather, as their name implies, ,.associate,, or. analyze inputs from other brain regions. The associaiion-cortices are the last domains of the cortex to myerinate, indicating their ...
extra pyramidal system
... • The term extrapyramidal motor system is denote all those portions of the brain and brain stem that contribute to motor control but are not part of the direct corticospinalpyramidal system. • These include pathways through the basal ganglia, the reticular formation of the brain stem, the vestibula ...
... • The term extrapyramidal motor system is denote all those portions of the brain and brain stem that contribute to motor control but are not part of the direct corticospinalpyramidal system. • These include pathways through the basal ganglia, the reticular formation of the brain stem, the vestibula ...
Psych 9A. Lec. 07 PP Slides: Brain and Nervous System, Part 3
... Damage to Broca’s and/or Wernicke’s areas can cause aphasia. For right-handed people, these sensitive areas are located on the brain’s left hemisphere. Broca’s area: helps to convert phonemic information into motor commands and lies close to motor areas controlling the vocal articulature Wernicke’s ...
... Damage to Broca’s and/or Wernicke’s areas can cause aphasia. For right-handed people, these sensitive areas are located on the brain’s left hemisphere. Broca’s area: helps to convert phonemic information into motor commands and lies close to motor areas controlling the vocal articulature Wernicke’s ...